 |
 |
| Plant Pathol J > Volume 37(1); 2021 > Article |
|
Abstract
Various management systems are being broadly employed to minimize crop yield loss resulting from abiotic and biotic stresses. Here we introduce a Bacillus zanthoxyli HS1 strain as a potent candidate for managing manifold stresses on vegetable plants. Considering 16S rDNA sequence and biochemical characteristics, the strain is closely related to B. zanthoxyli. The B. zanthoxyli HS1's soil-drench confers disease resistance on tomato and paprika plants against infection with Ralstonia solanacearum and Phytophthora capsici, respectively. Root and shoot growths are also increased in B. zanthoxyli HS1-treated cabbage, cucumber, and tomato plants, compared with those in mock-treated plants, after application of high salinity solution. Moreover, the pretreatment of B. zanthoxyli HS1 on cabbage plants inhibits the degradation of chloroplast pigments caused by high salinity stresses, whereas the inhibitory effect is not observed in cucumber plants. These findings suggest that B. zanthoxyli HS1 stain inhibits disease development and confers tolerance to salinity stress on vegetable plants.
As sessile living-organisms, plants are always exposed to diverse biotic and abiotic stresses. Microorganisms, such as fungus, bacterium, nematode, insect, and virus, infect and destruct plants, and abiotic stresses caused by drought, cold, high temperature, flooding, and high salinity also adversely affect plants’ growth and reproduction (Dangl and Jones, 2001; Mahajan and Tuteja, 2005; Miller et al., 2017). Researchers and farmers have been developing many managing systems to protect plants from these biotic and abiotic stresses, e.g., biological control, chemical control, cultural control, and plant breeding (Fita et al., 2015; Haas and Défago, 2005; Thurston, 1992; Walters et al., 2005). From a perspective of environmental safety, exploitation and application of biomaterials, including plantgrowth-promoting bacteria (PGPB) and biostimulants, are expanded worldwide (Majeed et al., 2018; Ullah et al., 2015; Van Oosten et al., 2017). In addition, the induction of multiple resistance by treatment of PGPB and biostimulants is a useful crop managing strategy for sustainable agricultural development (Bai et al., 2018; Choudhary et al., 2015; Rouphael and Colla, 2018).
Saline condition, the most unfavorable environment for plant growth, causes rapid osmotic stress and ion toxicity to plants grown in (semi)arid areas, coastal areas, and reclaimed lands (Flowers, 2004; Hariadi et al. 2011). Additionally, most vegetable crops are cultivated on a closed or semi-closed system, such as a greenhouse, in which proper irrigation by rainfall is difficult. Indiscreet fertilization and continuous cultivation also result in eutrophication and salt accumulation in arable lands (Flowers, 2004; Munns and Gilliham, 2015; Yoo et al., 2019). Thus, it is known that about 7% of arable land and 20% of irrigated farm fields are under salinity stress (Flowers and Yeo, 1995; Ruan et al., 2010). In these cases, plants are put at risk of salinity stress persistently, and then, the plants become highly susceptible to other biotic and abiotic stresses (Bai et al., 2018).
Conventional crop breeding is the most well-established strategy to increase tolerance against abiotic stresses. For example, guar (Cyamopsis tetragonoloba), Ethiopian mustard (Brassica carinata), and arugula (Eruca sativa) were bred to have a deep root system easy to absorb water from the soil more effectively (Kumar, 2005; Liang et al., 1992). A tolerant cultivar of peanut adjusted to salinity condition with Na+-exclusion and K+-accumulation was also developed (Chakraborty et al., 2016; Mungala et al., 2008). Genetic engineering technology also allows plants to increase the tolerance response by regulating the signal transduction pathway and osmoprotectant metabolites (Deinlein et al., 2014; Li et al., 2011; Muñoz-Mayor et al., 2012; Rathinasabapathi, 2000). However, the former takes a long time, and many governments have not accepted the latter. Therefore, effective strategies are necessary to decrease salt content in soil and confer tolerance on plants against salinity stress (Ilangumaran and Smith, 2017; Munns and Gilliham, 2015).
PGPB is highlighting as one of the emerging sources to improve crop production growing in saline soil (Egamberdieva, 2011; Etesami and Glick, 2020; Qu et al., 2016). So far, various PGPB strains, such as Azospirillum, Burkholderia, Rhizobium, Pseudomonas, Acetobacter, and Bacillus, were successfully applied to enhance tolerance response against salinity stress (Kumar and Verma, 2018; Ullah et al., 2017). Most PGPB strains produce 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate (ACC) deaminase and indole-3-acetic acid (IAA), which degrades ACC as an ethylene precursor, and promotes plant growth, respectively (Egamberdieva, 2009; Glick, 2005; Sarkar et al., 2018).
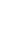
Recently, we isolated dozens of potential PGPB strains from rhizosphere soils of cucumber growing in the agricultural farm located in Gunsan, Korea, via testing biological activities of ACC-deaminase, phosphatase solubilization, and IAA production (data not shown). It was expectable that these bacterial strains would confer stress tolerance and disease resistance on vegetable crop plants. To test whether these soil-borne bacteria induce disease resistance against pathogen infection, we drenched these stains (OD600 = 0.25, 1 ml/g of the potting mixture) on tomato- and paprika-growing soil 7 days prior to pathogen inoculation and monitored disease development (data not shown). An HS1 strain reduced disease incidence caused by infection with Ralstonia solanacearum (OD600 = 0.2, 1 ml/g of the potting mixture) and Phytophthora capsici (2,000 zoospores/g of the potting mixture) on tomato and paprika plants, respectively (Fig. 1A). To taxonomically classify the HS1 strain, we obtained bacterial genome from the strain using the Gspin total DNA extraction kit (iNtRON, Seongnam, Korea), and 16S rDNA was amplified by using universal primers 785F and 907R (Lane, 1991). Based on the comparison of 16S rRNA sequences of identified various Bacillus strains and the amplified sequences (1,495 bp, completeness 99.9%) of HS1 strain, B. zanthoxyli seems to be the closest species of the HS1 strain (Fig. 1B). To confirm the classification, we carried out the biochemical test by using API 50 CHB (bioMérieux, Marcy-L’Etoile, France) (Li et al., 2017) (Table 1). Compared with biochemical traits of and B. aryabhattai B8W22T, the HS1 strain does not use any carbohydrates tested in this platform for its growth. Even if a type strain of B. zanthoxyli 1433T could utilize D-maltose and D-glucose, these analyses show that the HS1 might belong to B. zanthoxyli group.
Next, we evaluated the seedling growth of cabbage (Brassica oleracea cv. Ryeonggwang), cucumber (Cucumis sativus cv. Joeunbaeglogdadagi), and tomato (Solanum lycopersicum cv. Superdotaelang) plants to test if the B. zanthoxyli HS1 could confer tolerance against high salinity stress. We sowed germinated seeds on unsterilized soil (BioPlug, Nongwoo Bio, Suwon, Korea) (0 days) and grew them under 12 hours-day and 12 hours-night conditions at 26 ± 2 ° in a walk-in growth chamber. Either 10 mM MgSO4 or freshly prepared B. zanthoxyli HS1 strain (OD600=0.25/g of soil) was applied to 7-day-old seedlings of plants (7 days after sowing [das]). Seven days later, 1 ml of the balanced salinity solution (≈ ‒1,000 kPa) (125 mM KNO3, 82 mM Ca(NO3)2, 41 mM MgSO4, and 22 mM KH2PO4) (Polonenko et al., 1981) per gram of soil was added three times at every 2 days (14, 16, and 18 das). On 28 das, we measured weights of total seedling, root, and shoot of tested vegetable plants. Seedling growth of plants (cabbage, cucumber, and tomato) treated with B. zanthoxyli HS1 strain was not different from that of mocktreatment in the absence of any external stresses (data not shown). The weights of total seedling, root, and shoot of B. zanthoxyli HS1-treated cabbage plants increased 137%, 153%, and 138%, respectively, compared to mock-treated plants after salinity solution treatment (left panel, Fig. 2A). The sizes of leaf tissues and aerial parts are similar between each treatment (middle panel, Fig. 2A). The root part of B. zanthoxyli HS1-treated cabbage plants is bushier than that of mock-treated plants, even though the primary root length is shorter than mock-treated plants (right panel, Fig. 2A). Second, we tested the effect of B. zanthoxyli HS1 on cucumber seedling growth. The fresh weight of total seedlings and shoot parts rose 143% and 151%, respectively, in Bacillus-treated cucumber plants compared with those in the mock-treated plants (left panel, Fig. 2B). Although the root system was likely to be well-developed in Bacillus-treated plants (right panel, Fig. 2B), we did not see a statistical difference between each treatment (left panel, Fig. 2B). Unlike cabbage plants, aerial parts’ growth in Bacillus-treated plants is more prominent than in mock-treated plants (middle panel, Fig. 2B). We also showed that retardation of seedling growth by salinity solution treatment was also reduced in B. zanthoxyli HS1-treated tomato plants (Fig. 2C). Note that the weight of total seedling, root, and shoot increased 147%, 162%, and 148% in Bacillus-treated tomato plants. These results suggest that pretreatment of B. zanthoxyli HS1 strain could render plants tolerant in response to salinity stress, and consequently, the seedlings of vegetable plants tested in this study get less damage by salinity stress.
The level of photosynthetic pigment, chlorophyll, is a vital indicator to monitor plant growth and senescence, and the decrease of the pigment tightly correlates with the extent of environmental stresses (Kalaji et al., 2016; Mittal et al., 2012; Turan and Tripathy, 2015). Carotenoid also plays a role in photosynthesis by reducing reactive oxygen species‒ derived damage (Havaux, 2014). Salinity stress can reduce chlorophyll contents by enhancing chlorophyllase activity and being the pigment-protein complexes unstable (Jamil et al., 2007; Singh and Dubey, 1995). To closer look at the vegetable plants’ tolerance response, we determined chlorophyll and carotenoid contents in cabbage and cucumber plants after applying 50 mM NaCl or the balanced salinity solution. In cabbage plants after stress treatment, Bacillus-treated plants exhibited a higher chlorophyll level than mock-treated plants (Fig. 3A). Carotenoid level in Bacillus-treated plants also remained relatively higher than in mock-treated plants after 50 mM NaCl treatment, but not in the case of balanced salinity solution treatment (Fig. 3B). However, the pretreatment of the B. zanthoxyli HS1 strain did not protect these pigments’ degradation of cucumber plants from salinity stress (Fig. 3C and D). These results show that B. zanthoxyli HS1 can prevent pigments’ degradation of cabbage plants by salinity stress and has different effects on the pigment stability of cabbage and cucumber plants.
Conclusively, the B. zanthoxyli HS1 strain falling into B. zanthoxyli species can suppress disease development by soil-borne bacterium and oomycete and render seedlings less sensitive against high salinity stress. However, the biological activity of the B. zanthoxyli HS1 strain might depend on plant species and genotype. To avoid the inconsistent inducing activity, purification of a particular metabolite and development of new application method(s) using dead cells instead of living cells will be necessary.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by an agenda research program funded by the Rural Development Administration (PJ01475803) and a basic research program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (2020R1A6A1A03047729) (Ho Won Jung).
Fig. 1
Induced resistance by Bacillus sp. HS1 and taxonomic classification. (A) Disease incidence of tomato bacterial wilt disease by Ralstonia solanacearum, and paprika Phytophthora blight disease by Phytophthora capsici. The number of diseased plants among the number of whole plants (three replicates with six plants) was calculated as disease incidence. Data present the mean ± standard deviation. Asterisks above the bars indicate that the mean is significantly different among the treatment (**P < 0.05, least significant difference test). The experiments were repeated twice with the same results. (B) Phylogenetic trees present the position of Bacillus sp. strain HS1 16S rRNA sequences. Multiple alignments were generated using Clustal W, and the phylogenetic trees were constructed by the neighbor-joining method (maximum composite likelihood model; left) and maximum likelihood method (Kimura 2-parameter model; right) based on 1,000 bootstrap replications using MEGA version 6.0. Numbers at the branched points indicate bootstrapping values, expressed as a percentage of 1,000 repeats.
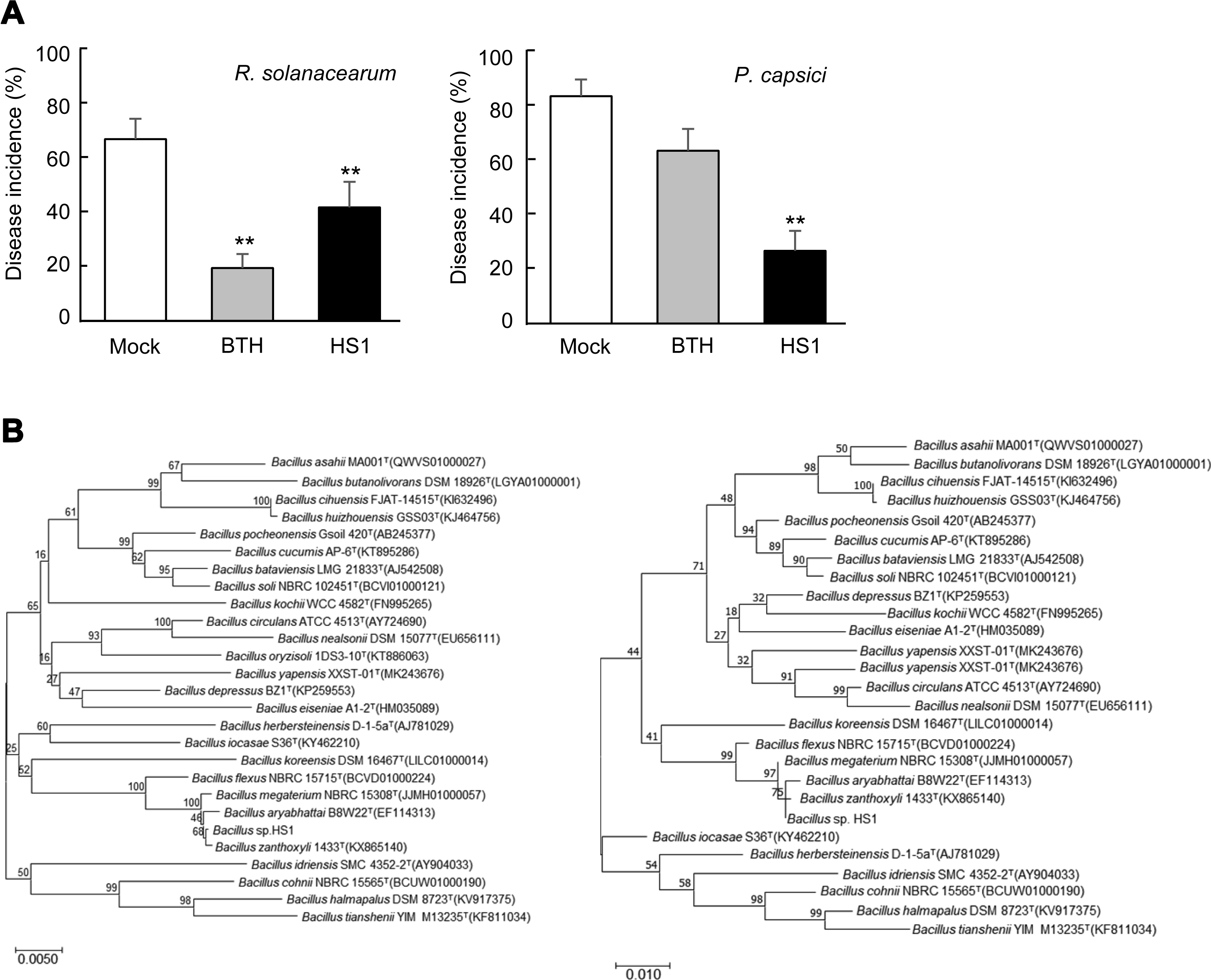
Fig. 2
Seedling growth of vegetable crops grown under salinity stress conditions. (A-C) Fresh weight of total seedling, root, and shoot of cabbage (A), cucumber (B), and tomato (C) plants. Ten mM MgSO4 (white bars) and Bacillus zanthoxyli HS1 strain (OD600 = 0.25/g of soil) (gray bars) were applied on plant-growing soil 7 days before treatment of the balanced salinity solution. Error bars indicate the standard errors from 6 biological replications (n = 4 in each experiment). Asterisks above the bars present statistically significant differences between mock- and treated-samples (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, two-sided student’s t-test). Insets show the fresh weight of the root. Photos were taken on the same day that fresh weights were examined.
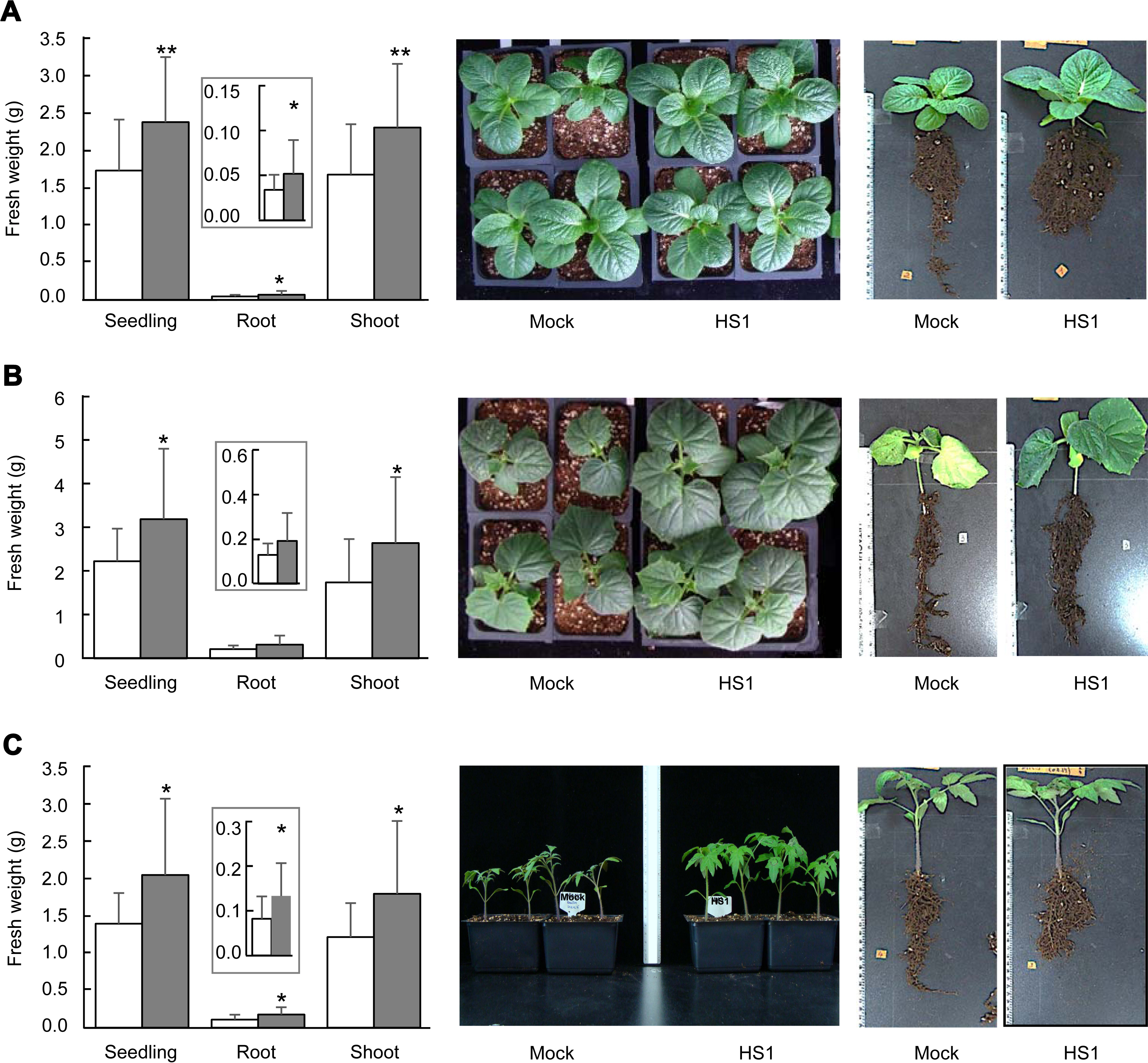
Fig. 3
Chlorophyll and carotenoid contents on cabbage and cucumber plants grown under salinity stress conditions. (A, B) Chlorophyll (A) and carotenoid (B) contents in leaves of mock- and Bacillus zanthoxyli HS1-treated cabbage plants after 50 mM NaCl and the balanced salinity solution. (C, D) Chlorophyll (C) and carotenoids (D) contents in cucumber leaves. Leaf discs were taken to measure the pigment contents. Data present the mean ± standard errors from 3 independent experiments (n = 4, each trial). Asterisks above the bars present statistically significant differences between mock- and treated-samples (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, two-sided student’s t-test).
Table 1
Biochemical characteristics for identification of Bacillus sp. HS1
| Tests performeda | Bacillus sp. HS1 | B. zanthoxyli 1433T b | B. aryabhattai B8W22T b |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH growth range | 6.0-10.0 | 6.0-10.0 | 6.0-9.0 |
| NaCl tolerance (%) | 0-7 | 0-7 | 0-11 |
| Acid production from | |||
| Erythritol | + | ‒ | + |
| Ribose | + | + | + |
| Galactose | ‒ | - | ‒ |
| D-Sorbitol | + | + | ‒ |
| D-Lyxose | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ |
| D-Fucose | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ |
| L-Fucose | ‒ | ‒ | ‒ |
| D-Arabitol | + | ‒ | ‒ |
| Utilization of | |||
| D-Maltose | ‒ | + | + |
| D-Melibiose | ‒ | ‒ | + |
| D-Glucose | ‒ | + | + |
| D-Mannose | ‒ | ‒ | + |
| D-Fructose | ‒ | ‒ | + |
| D-Sorbitol | ‒ | ‒ | + |
| D-Mannitol | ‒ | ‒ | + |
REFERENCES
Bai, Y., Kissoudis, C., Yan, Z., Visser, R. G. F. and van der Linden, G. 2018. Plant behaviour under combined stress: tomato responses to combined salinity and pathogen stress. Plant J. 93:781-793.


Chakraborty, K., Bhaduri, D., Meena, H. N. and Kalariya, K. 2016. External potassium (K+) application improves salinity tolerance by promoting Na+-exclusion, K+-accumulation and osmotic adjustment in contrasting peanut cultivars. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 103:143-153.


Choudhary, D. K., Kasotia, A., Jain, S., Vaishnav, A., Kumari, S., Sharma, K. P. and Varma, A. 2015. Bacterial-mediated tolerance and resistance to plants under abiotic and biotic stresses. J. Plant Growth Regul. 35:276-300.

Dangl, J. L. and Jones, J. D. 2001. Plant pathogens and integrated defence responses to infection. Nature. 411:826-833.


Deinlein, U., Stephan, A. B., Horie, T., Luo, W., Xu, G. and Schroeder, J. I. 2014. Plant salt-tolerance mechanisms. Trends Plant Sci. 19:371-379.



Egamberdieva, D. 2009. Alleviation of salt stress by plant growth regulators and IAA producing bacteria in wheat. Acta Physiol. Plant. 31:861-864.

Egamberdieva, D. 2011. Pseudomonas chlororaphis: a salttolerant bacterial inoculant for plant growth stimulation under saline soil conditions. Acta Physiol. Plant. 34:751-756.

Etesami, H. and Glick, B. R. 2020. Halotolerant plant growth- promoting bacteria: prospects for alleviating salinity stress in plants. Environ. Exp. Bot. 178:104124

Fita, A., Rodríguez-Burruezo, A., Boscaiu, M., Prohens, J. and Vicente, O. 2015. Breeding and domesticating crops adapted to drought and salinity: a new paradigm for increasing food production. Front. Plant Sci. 6:978



Flowers, T. J. and Yeo, A. R. 1995. Breeding for salinity resistance in crop plants: where next? Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 22:875-884.

Glick, B. R. 2005. Modulation of plant ethylene levels by the bacterial enzyme ACC deaminase. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 251:1-7.


Haas, D. and Défago, G. 2005. Biological control of soil-borne pathogens by fluorescent pseudomonads. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 3:307-319.


Hariadi, Y., Marandon, K., Tian, Y., Jacobsen, S. E. and Shabala, S. 2011. Ionic and osmotic relations in quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) plants grown at various salinity levels. J. Exp. Bot. 62:185-193.


Ilangumaran, G. and Smith, D. L. 2017. Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria in amelioration of salinity stress: a systems biology perspective. Front. Plant Sci. 8:1768



Jamil, M., Rehman, S. U., Lee, K. J., Kim, J. M., Kim, H.-S. and Rha, E. S. 2007. Salinity reduced growth PS2 photochemistry and chlorophyll content in radish. Sci. Agric. 64:111-118.

Kalaji, H. M., Jajoo, A., Oukarroum, A., Brestic, M., Zivcak, M., Samborska, I. A., Cetner, M. D., Łukasik, I., Goltsev, V. and Ladle, R. J. 2016. Chlorophyll a fluorescence as a tool to monitor physiological status of plants under abiotic stress conditions. Acta Physiol. Plant. 38:102


Kumar, A. and Verma, J. P. 2018. Does plant-Microbe interaction confer stress tolerance in plants: a review? Microbiol. Res. 207:41-52.


Kumar, D. eds. by M. Ashraf and P. J. C. Harris, 2005. Breeding for drought resistance. In: Abiotic stresses: plant resistance through breeding and molecular approaches, Food Products Press, New York, NY, USA. 145-147.
Lane, D. J. eds. by E. Stackebrandt and M. Goodfellow, 1991. 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. In: Nucleic acid techniques in bacterial systematics, Wiley, Chichester, UK. 115-175.
Li, H.-W., Zang, B.-S., Deng, X.-W. and Wang, X.-P. 2011. Overexpression of the trehalose-6-phosphate synthase gene OsTPS1 enhances abiotic stress tolerance in rice. Planta. 234:1007-1018.


Li, M., Hong, C. Y., Yan, W. X., Chao, Z. S., Gang, Y. C., Ling, D. J., Kui, Z. X., Qin, X. J., Liang, Z. M. and He, M. M. 2017. Bacillus zanthoxyli sp. nov., a novel nematicidal bacterium isolated from Chinese red pepper (Zanthoxylum bungeanum Maxim) leaves in China. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 110:1179-1187.


Liang, Z. S., Ding, Z. R. and Wang, S. T. R. 1992. Study on type of water stress adaptation in both Brassica napus and B. juncea L. species. Acta Bot. 12:38-45.
Mahajan, S. and Tuteja, N. 2005. Cold, salinity and drought stresses: an overview. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 444:139-158.


Majeed, A., Muhammad, Z. and Ahmad, H. 2018. Plant growth promoting bacteria: role in soil improvement, abiotic and biotic stress management of crops. Plant Cell Rep. 37:1599-1609.


Miller, R. N. G., Alves, G. S. and Van Sluys, M.-A. 2017. Plant immunity: unravelling the complexity of plant responses to biotic stresses. Ann. Bot. 119:681-687.



Mittal, S., Kumari, N. and Sharma, V. 2012. Differential response of salt stress on Brassica juncea: photosynthetic performance, pigment, proline, D1 and antioxidant enzymes. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 54:17-26.


Mungala, A. J., Radhakrishnan, T. and Dobaria, J. R. 2008. In vitro screening of 123 Indian peanut cultivars for sodium chloride induced salinity tolerance. World J. Agric. Sci. 4:574-582.
Munns, R. and Gilliham, M. 2015. Salinity tolerance of crops - what is the cost? New Phytol. 208:668-673.


Muñoz-Mayor, A., Pineda, B., Garcia-Abellán, J. O., Antón, T., Garcia-Sogo, B., Sanchez-Bel, P., Flores, F. B., Atarés, A., Angosto, T., Pintor-Toro, J. A., Moreno, V. and Bolarin, M. C. 2012. Overexpression of dehydrin tas14 gene improves the osmotic stress imposed by drought and salinity in tomato. J. Plant Physiol. 169:459-468.


Polonenko, D. R., Mayfield, C. I. and Dumbroff, E. B. 1981. Microbial responses to salt-induced osmotic stress. Plant Soil. 59:269-285.

Qu, L., Huang, Y., Zhu, C., Zeng, H., Shen, C., Liu, C., Zhao, Y. and Pi, E. 2016. Rhizobia-inoculation enhances the soybean's tolerance to salt stress. Plant Soil. 400:209-222.

Rathinasabapathi, B. 2000. Metabolic engineering for stress tolerance: installing osmoprotectant synthesis pathways. Ann. Bot. 86:709-716.

Rouphael, Y. and Colla, G. 2018. Synergistic biostimulatory action: designing the next generation of plant biostimulants for sustainable agriculture. Front. Plant Sci. 9:1655



Ruan, C.-J., da Silva, J. A. T., Mopper, S., Qin, P. and Lutts, S. 2010. Halophyte improvement for a salinized world. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 29:329-359.

Sarkar, A., Ghosh, P. K., Pramanik, K., Mitra, S., Soren, T., Pandey, S., Mondal, M. H. and Maiti, T. K. 2018. A halotolerant Enterobacter sp. displaying ACC deaminase activity promotes rice seedling growth under salt stress. Res. Microbiol. 169:20-32.


Singh, A. K. and Dubey, R. S. 1995. Changes in chlorophyll a and b contents and activities of photosystems 1 and 2 in rice seedlings induced by NaCl. Photosynthetica. 31:489-499.
Thurston, H. D. 1992. Sustainable practices for plant disease management in traditional farming systems. Westview Press, Boulder, CO, USA. 280.
Turan, S. and Tripathy, B. C. 2015. Salt-stress induced modulation of chlorophyll biosynthesis during de-etiolation of rice seedlings. Physiol. Plant. 153:477-491.


Ullah, A., Heng, S., Munis, M. F. H., Fahad, S. and Yang, X. 2015. Phytoremediation of heavy metals assisted by plant growth promoting (PGP) bacteria: a review. Environ. Exp. Bot. 117:28-40.

Ullah, S., Hussain, M. B., Khan, M. Y. and Asghar, H. N. eds. by D. P. Singh, H. B. Singh and R. Prabha, 2017. Ameliorating salt stress in crops through plant growthpromoting bacteria. In: Plant-microbe interactions in agroecological perspectives, Springer, Singapore. 549-575.

Van Oosten, M. J., Pepe, O., De Pascale, S., Silletti, S. and Maggio, A. 2017. The role of biostimulants and bioeffectors as alleviators of abiotic stress in crop plants. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 4:5

- TOOLS




 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Full text via PMC
Full text via PMC Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print