 |
 |
| Plant Pathol J > Volume 37(5); 2021 > Article |
|
Abstract
Stem rot is a serious disease in Jerusalem artichoke (JA). To reduce the impact of this disease on yield and quality farmers often use fungicides, but this control method can be expensive and leave chemical residues. The objective of this study was to evaluate the efficacy of two biological control agents, Trichoderma harzianum T9 and Bacillus firmus BSR032 for control of Sclerotium rolfsii under field conditions. Four accessions of JA (HEL246, HEL65, JA47, and JA12) were treated or notreated with T. harzianum T9 and B. firmus BSR032 in a 4 ├Ś 2 ├Ś 2 factorial experiment in two fields (environments), one unfertilized and one fertilized. Plants were inoculated with S. rolfsii and disease was evaluated at 3-day intervals for 46 days. T. harzianum T9 and B. firmus BSR032 reduced disease incidence by 48% and 49%, respectively, whereas T. harzianum T9 + B. firmus BSR032 reduced disease incidence by 37%. The efficacy of T. harzianum T9 and B. firmus BSR032 for control of S. rolfsii was dependent on environments and genotypes. The expression of host plant resistance also depended on the environment. However, HEL246 showed consistently low disease incidence and severity index in both environments (fertilized and unfertilized). Individually, T. harzianum T9, B. firmus BSR032, or host plant resistance control stem rot caused by S. rolfsii in JA. However, no combination of these treatments provided more effective control than each alone.
Jerusalem artichoke (Helianthus tuberosus L.) (JA) produces edible tubers that contain inulin (Puttha et al., 2012). The levels of inulin in tubers range from 7% to 30% of fresh weight and about 50% of dry weight (Kays and Nottingham, 2007). JA is used as a functional food (Roberfroid, 2007), feed additive (Farnworth, 1994), or as bioethanal (Li et al., 2013).
Stem rot caused by Sclerotium rolfsii Sacc. [syn. Althelia rolfsii (Curzi) C.C. Tu & Kimbr.] is a major disease problem for JA production in the tropics (Sennoi et al., 2010). The pathogen infects tubers, causing 60% of yield loss in temperate regions (McCarter and Kays, 1984). In the tropical area of Thailand, disease incidences of up to 32% have been reported (Junsopa et al., 2016). The pathogen survives in soil for years and has a wide host range (McCarter and Kays, 1984).
In Thailand, JA is used mainly for the production of functional food products; therefore, it is important to control the disease by methods that reduce potential pesticide residues. Host resistance (Junsopa et al., 2017) and biological control are desirable choices for this purpose. Antagonistic organisms can control the target disease by several mechanisms including parasitism, competition, antibiosis, induced resistance, and plant growth promotion (Baker, 1968; Handelsman and Stabb, 1996). Organisms antagonistic to S. rolfsii and potential bio-control agents include Trichoderma spp. (Ali and Javaid, 2015; Singh and Singh, 2004), arbuscular mycorrhizae (Doley et al., 2014), Bacillus subtilis (El-Fiki et al., 2014), Streptomyces spp. (Errakhi et al., 2007), certain actinomycetes (Pattanapipitpaisal and Kamlandharn, 2012) and Pseudomonas spp. (Chanutsa et al., 2014; El-Fiki et al., 2014).
Arbuscular mycorrhizae and Trichoderma spp. have been used to control wilt, stalk, and tuber rots caused by Sclerotinia sclerotiorum and Rhizoctonia solani in JA (Ezzat et al., 2015). Arbuscular mycorrhizae and Trichoderma spp. have also reduced the percentage of tuber rot caused by S. rolfsii and increased survival of JA (Al-Askar et al., 2014). Other bio-control organisms that have reduced the incidence of stem rot in JA include Saccharomyces cerevisiae (55.5% reduction), T. viride (77.9% reduction), B. subtilis (88.8% reduction), and P. fluorescens (66.7% reduction) (Eid, 2013). Under greenhouse conditions in Thailand, T. harzianum T9 and the arbuscular mycorrhizal species Glomus clarum KKURA0305 controlled S. rolfsii in JA (Sennoi et al., 2013b); similar results were reported in a subsequent study with T. harzianum T9, B. firmus BSR032, and G. clarum (Charirak et al., 2016).
Although these studies indicate that biological control of stem rot is possible, antagonistic organisms are often specific to the target pathogens in each environment. Therefore, indigenous antagonistic organisms may be more effective for the control of the target disease than non-native antagonists. The objective of this study was to evaluate the efficacy of selected indigenous strains of T. harzianum T9 and B. firmus BSR032 for control of S. rolfsii under field conditions.
A 4 ├Ś 2 ├Ś 2 factorial experiment was conducted in July-October 2015 at Khon Kaen University, Thailand. Factors included four JA genotypes (factor A), HEL246, HEL65, JA12, and JA47. HEL246, and HEL65 are resistant genotypes, and JA12, and JA47 are susceptible genotypes (Junsopa et al., 2017). Factor B was T. harzianum T9 and an uninoculated control, and factor C was B. firmus BSR032 and an uninoculated control. The 16 treatment combinations were arranged in a randomized complete block design with four replications. This field test was planted in two environments, one being an unfertilized field and the second being a fertilized field. Both fields were located on the same research station.
The research areas were prepared using conventional tillage including plowing twice and then leveling. Small plots with raised beds (2 ├Ś 5 m) were then created. Seed tubers were cut into small pieces that included 2 to 3 active buds and then incubated in a moist charred rice husk medium. After 3 days of incubation, the seedlings were transferred into plug trays containing a 1:1 (v:v) mixture of soil and charred rice husk and were grown for an additional 7 days. Uniform seedlings with 4 to 6 leaves were transplanted on the raised beds of a four-row plot, Plant spacing of 50 ├Ś 50 cm was used for sowing, for a total of 36 plants per plot. Plots were hand weeded and a 15-15-15 fertilizer formula, was applied at the rate of 156.125 kg/ha to the fertilized field at 15 days after transplanting (DAT) and 25 DAT. A mini sprinkler was set up and used for irrigation. In general, irrigation was applied 2 times a week to support plants in non-drought stress condition.
Department of Entomology and Plant Pathology, Khon Kaen University, provided T. harzianum T9 and B. firmus BSR032 for this experiment. Potato dextrose agar (PDA) was used for the culture of T. harzianum T9 and the culture was placed in an incubator at 25 ┬▒ 2┬░C for 3 days. Sorghum seed was soaked overnight to soften, then steamed for an hour, placed in polypropylene bags (400 g per bag) and autoclaved at 121┬░C for 30 min. A cork borer was used to cut plugs 0.5 cm in diameter from the PDA cultures. Four plugs were placed in each bag of cooled autoclaved sorghum seed and bags were incubated at room temperature (30 ┬▒ 2┬░C) for 5 days (Charirak et al., 2016; Sennoi et al., 2013b). The sorghum seed inoculum was used to produce a spore suspension in sterilized distilled water. Then the spore suspension was counted in a hemocytometer and adjusted to a concentration of 1 ├Ś 109 spores/ml.
Nutrient agar was used to culture B. firmus BSR032 and incubated at 25 ┬▒ 2┬░C for 48 h. The cultures then were transferred into the nutrient broth and incubated for 24 h. The concentration of B. firmus BSR032 was counted using a spectrophotometer at 600 nm and adjusted to 0.1 OD to obtain the concentration of 1.62 ├Ś 109 cfu/ml (Maneesuwan and Sirithorn, 2013).
PDA was used to culture S. rolfsii. Cultures were incubated at 25 ┬▒ 2┬░C for 3 days. Plugs then were cut from the PDA with a 0.5 cm diameter cork borer and four plugs were added to cooled autoclaved bags of sorghum seed prepared as described above. Cultures were incubated at room temperature (30 ┬▒ 2┬░C) for 7 days (Junsopa et al., 2016).
At 38 DAT, 16 plants in two middle rows of each plot were inoculated with the designated bio-control treatment. Prior to inoculation at 15:00, mini-sprinkler irrigation was applied for 30 min to increase humidity. T. harzianum T9 suspension was applied at the crown of each plant at approximately10 ml per plant. Inoculation of B. firmus BSR032 at the rate of 10 ml per plant was carried out at the same time and with the same method.
Seven days (or 45 DAT) after T. harzianum T9 and B. firmus BSR032 application, plants were inoculated with S. rolfsii. Prior to inoculation at 15:00, mini-sprinkler irrigation was applied for 30 min to increase humidity. Three seeds of the S. rolfsii infested sorghum were buried in the soil around the crown of the plant, at 1 cm below the soil surface.
Soil samples (30 cm depth) were collected twice, once before planting and a second time at 20 days after fertilizer application. The soil samples were taken from the experimental field (0-30 cm in depth), then bulked and mixed well before analysis. For analysis, the soil sample was divided into two subsamples. The values were averaged and presented in Table 1. The soil samples were analyzed for pH, cation exchange capacity, electrical conductivity, organic matter, total nitrogen, available phosphorus, exchangeable potassium, exchangeable calcium, and were subjected to soil texture analysis. Meteorological data were recorded for air relative humidity, temperature, and rainfall throughout the experimental period.
Disease assessment was done at 3-day intervals from 1 day after inoculation (DAI) until 46 DAI for disease incidence. Disease severity was assessed using a disease score of 0-5 (0 = healthy plant, 1 = lesion without wilting, 2 = 1-2 leaves wilting, 3 = more than two leaves wilting, 4 = damped off and 5 = plant dead) was used (Sennoi et al., 2013a). Disease scores were converted to a disease severity index (SI) as follows (Anfok, 2000);
Disease incidence and SI data were analyzed by Statistix 8 software (Analytical Software, 2003). An analysis of variance and combined analysis for the two environments, unfertilized and fertilized fields, were used to determine the significance of the main effects and interactions, and a least significant difference test was used to test the differences among treatments.
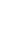
Total rainfall was 447 and 434 mm for environment 1 (fertilized field) and environment 2 (unfertilized field), respectively (Fig. 1). Temperatures and relative humidity in the two environments were similar. In both environments, the minimum temperatures ranged from 20.5┬░C to 26.0┬░C, and maximum temperatures ranged from 25.0┬░C to 39.5┬░C. Similarly, relative humidity ranged between 76% to 98%, in both environments.
Soil properties in both environments were similar (Table 1). After fertilizer was added, most soil nutrients were slightly higher in the fertilized field than in the unfertilized field.
Environments, JA genotypes, and the biological control organisms significantly affected disease incidence (Table 2). The environments differed in disease incidence, with higher levels of disease incidence (33.7% vs. 27.3%) and severity (28.3% vs. 23.5%) observed in environment 1 (fertilized field) compared to environment 2 (unfertilized field) (data not shown).
T. harzianum T9 reduced disease incidence in two environments, but disease severity was not reduced in environment 2 (Figs. 2 and 3). B. firmus BSR032 reduced disease incidence in environment 1 and SI in environment 2 (Figs. 2 and 3). The combination of the two biological control treatments (T. harzianum T9 and B. firmus BSR032) were less effective than either alone (Table 3).
Among the JA genotypes, HEL246 had less disease incidence than the other three genotypes (Table 4), whereas HEL246 and JA47 had less disease SI than the rest of the genotypes. Disease incidence was reduced by T. harzianum in the genotypes HEL65 and JA47 (Fig. 4A). Without the application of T. harzianum T9, HEL246 had less disease incidence than the other genotypes whereas with T. harzianum T9 added, HEL246 and JA47 had less disease incidence than the other genotypes (Fig. 4A). For disease SI, HEL246 and JA47 had less disease SI than other genotypes under with or without T. harzianum T9 added (Fig. 4B). HEL246 had less disease incidence than the other genotypes with and without B. firmus BSR032 (Fig. 5A), likewise HEL246 and JA47 had less disease SI than the other genotypes with and without B. firmus BSR032 added (Fig. 5B).
In general, disease incidence and disease SI in environment 1 (fertilized field) were higher than in environment 2 (unfertilized field) (Fig. 6). HEL246 and JA47 had less disease incidence than HEL65 and JA12 under environment 1, whereas HEL246 and HEL65 had less disease incidence than JA47 and JA12 under environment 2 (Fig. 6A). HEL246 and JA47 had less disease SI than HEL65 and JA12 under environment 1 and environment 2 (Fig. 6B).
Trichoderma spp. have been used for bio-control of several diseases for decades (Harman, 2006) and T. harzianum has been used more extensively than other species. Mechanisms of bio-control by Trichoderma spp. include mycoparasitism, antibiosis, competition, and induced resistance (Nautiyal and Dion, 2008). The Trichoderma spp. destroyed plant pathogen and induced plant resistance to other fungi (Mukherjee et al., 2013). Bacillus spp. had shown to be effective in controlling plant diseases caused by fungi and nematodes (Sarangi and Ramakrishnan, 2016). Mechanisms of bio-control by Bacillus spp. include competition, antibiosis, plant growth promotion, and induced resistance (Cawoy et al., 2011).
Similar to past greenhouse studies by Sennoi et al. (2013b) and Charirak et al. (2016), this field study found that T. harzianum T9 and B. firmus BSR032 could be used for biological control of S. rolfsii in JA under field conditions. The mechanism for bio-control of S. rolfsii by both T. harzianum T9 and B. firmus BSR032 is thought to be degradation of ╬▓-1,3-glucan and chitin in the cell wall (Charirak et al., 2016; Elad et al., 1982; El-Katatny et al., 2000).
In this study, Trichoderma and Bacillus appeared to interact negatively. The treatment with either T. harzianum T9 or B. firmus BSR032 greatly reduced disease incidence, but control was less effective when both organisms were used together (Table 3). This may indicate that interactions depend on the specific strains of Trichoderma and Bacillus. Similarly, under greenhouse conditions, co-inoculation of T. harzianum T9 and G. clarum KKURA0305 resulted in higher disease incidence in JA, JA37, than single inoculation of G. clarum KKURA0305 and the co-inoculation had disease incidence similar to the application of T. harzianum T9 alone (Sennoi et al., 2013b). Reduced control with co-inoculation compared to single inoculation may have been due to competition between the organisms for the same ecological niche for growth. Ruano-Rosa et al. (2014) reported that some bacteria strains reduced growth of some strains of Trichoderma in combined application for control of avocado white root rot. However, the compatibility of T. harzianum T9 and B. firmus BSR032 was not tested in this study.
Interaction of T. harzianum T9 and B. firmus BSR032 with environments and genotypes and interaction of genotypes by environment were observed for disease incidence and SI in JA (Table 2). These findings indicated that the efficacy of T. harzianum T9 and B. firmus BRS032 for control of S. rolfsii was dependent on environments and genotypes. Expression of host plant resistance of JA also was dependent on environments. HEL246 showed consistently low disease incidence. HEL246 and JA47 also showed the lowest disease SI in both environments (fertilized and unfertilized fields) (Fig. 6). However, HEL 65 showed low disease incidence only under environment 2 (unfertilized field). Handelsman and Stabb (1996) speculate that varietal differences may be due to differential growth patterns of rhizosphere microorganisms. In this study, the results revealed that the performance of T. harzianum T9 and B. firmus BSR032 were specific to environments (Figs. 2 and 3) and plant genotypes (Figs. 4 and 5). Harman (2006) also reported on the specificity of Trichoderma strains to plant genotypes. As noted in Figs. 2, 3, and 6, the environment also affected the bio-control of S. rolfsii. Likewise, JA genotypes varied in their response to disease and bio-control organisms across environments.
This experiment was conducted in unfertilized and fertilized fields. In general, the fertilized field environment showed higher disease incidence and SI than an unfertilized field environment. The fertilized field had higher N, P, K, and Ca than the unfertilized field (Table 1). Plant nutrition is an important factor in plant-disease interactions (Spann and Schumann, 2009). Dordas (2008) reviewed the role of plant nutrients in plant disease and revealed that application of N could increase or decrease the incidence of plant disease. However, Ca application generally enhances plant disease resistance (Dordas, 2008) and Ca reduced disease caused by S. rolfsii due to its effects on plant cell walls and cell wall degrading enzymes (Punja et al., 1986). Disease development was not consistent with the application of nitrogen because the effect depended on the form of nitrogen used, type of pathogen, stage of a developmental host, and interaction of N, pathogen, and bio-control microorganism (Dordas, 2008). Punja et al. (1986) reported that the application of ammonium bicarbonate and urea to carrot reduced sclerotial germination by S. rolfsii and the percentage of dead plants, infected by this pathogen. In the same study, application of nitrogen in the form of ammonium bicarbonate, ammonium nitrate, and ammonium sulfate reduced the percentage of dead carrot plants, with nitrogen application in form of ammonium bicarbonate being the most effective in reducing the percentage of dead plants. In contrast to Punja et al. (1986) in this study, the fertilized field had higher N than the unfertilized field and showed more stem rot disease incidence and SI. It is common for stem rot to be more serious with lush or rapid plant growth as we might find in high fertility environments. Ca reduced S. rolfsii due to its effects on cell walls and cell wall degrading enzymes (Punja et al., 1986).
The results of this study indicate that T. harzianum T9 or B. firmus BSR032 or host plant resistance could be a good choice for biological control of stem rot caused by S. rolfsii in JA. They reduced the incidence and SI of disease in JA. Consideration of plant genotype, environment, and combination of the bio-control organisms is necessary because T. harzianum T9 and B. firmus BSR032 are specific with plant genotypes (Figs. 4 and 5) and environments (Fig. 6). Without application of T. harzianum T9, HEL246 had less disease incidence than other varieties. The application of T. harzianum T9 can reduce disease incidence in resistant (HEL65) and susceptible (JA47) genotypes but cannot reduce disease incidence in the most resistant genotype (HEL246) and susceptible genotypes (Fig. 4). Similar results were found for disease SI (Fig. 5). Similar results were also found for the interaction of B. firmus BSR032 and JA genotypes (Fig. 5). Further enhancement of control may be possible with continued efforts to select improved resistant genotypes, bio-control strains, and finding good compatible combination strains of T. harzianum and B. firmus.
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by the Royal Golden Jubilee Ph.D. Program (jointly funded by Khon Kaen University and the Thailand Research Fund) (grant no. PHD/0110/2554); the Thailand Research Fund, through the Senior Scholar Project of Professor Dr. Sanun Jogloy (RTA 6180002). It was also supported in part by Peanut, Jerusalem artichoke, and Cassava Improvement Research Group, Khon Kaen University, Khon Kaen 40002, Thailand.
Fig.┬Ā1
Rainfall, relative humidity, maximum and minimum temperature of the experiment during July-October 2015. Environment 1 (fertilized field) during July 26-October 25, 2015, and environment 2 (unfertilized field), during July 31-October 30, 2015. The fertilizer formula 15-15-15 at 156 kg/ha.
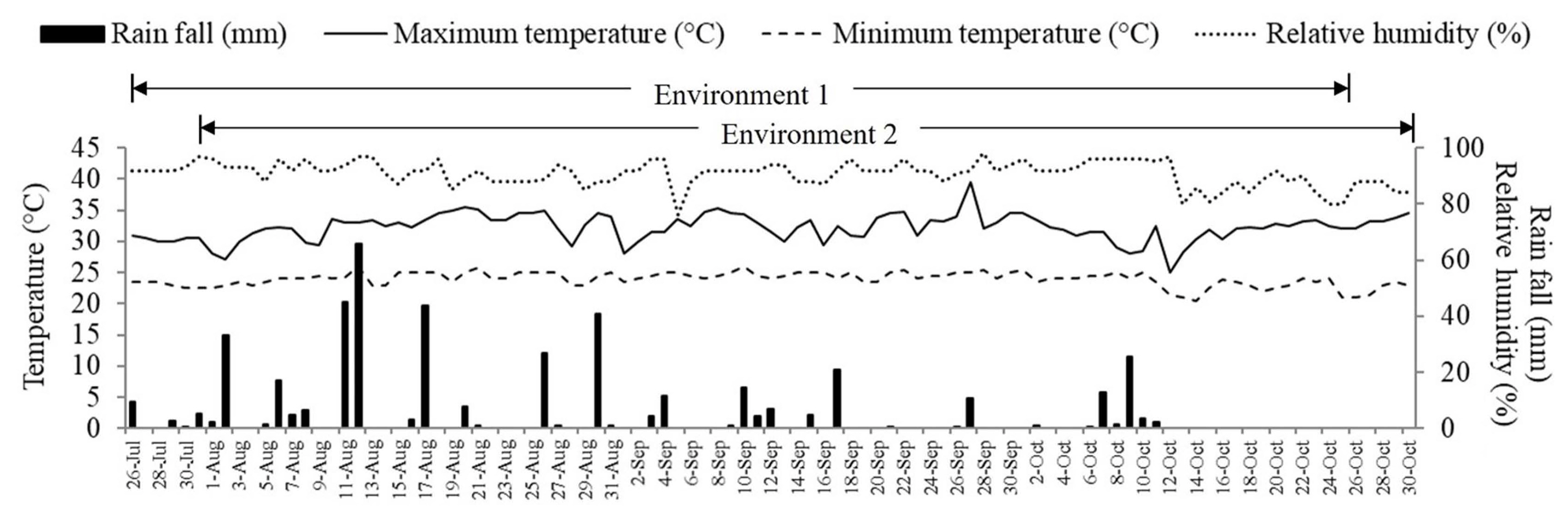
Fig.┬Ā2
Incidence (A) and severity index (B) of stem rot caused by Sclerotium rolfsii in the presence (+T) and absence (ŌłÆT) of Trichoderma harzianum T9 under two environments with fertilized field (E1) or unfertilized field (E2), means (from n = 32 observations) with the same letter(s) are not significantly different at 5% level by least significant difference test.
Fig.┬Ā3
Incidence (A) and severity index (B) of stem rot caused by Sclerotium rolfsii in the presence (+B) and absence (ŌłÆB) of Bacillus firmus BSR032 under environments with fertilized field (E1) or unfertilized field (E2), means (from n = 32 observations) with the same letter(s) are not significantly different at 5% level by least significant difference test.

Fig.┬Ā4
Incidence (A) and severity index (B) of stem rot caused by Sclerotium rolfsii on four cultivars in Jerusalem artichoke in the presence (+T) or absence (ŌłÆT) of Trichoderma harzianum T9, means (from n = 16 observations) with the same letter(s) are not significantly different at 5% level by least significant difference test.

Fig.┬Ā5
Incidence (A) and severity index (B) of stem rot caused by Sclerotium rolfsii on four cultivars in Jerusalem artichoke in the presence (+B) or absence (ŌłÆB) of Bacillus firmus BSR032, means (from n = 16 observations) with the same letter(s) are not significantly different at 5% level by least significant difference test.

Fig.┬Ā6
Incidence (A) and severity index (B) of stem rot caused by Sclerotium rolfsii on four varieties of Jerusalem artichoke under two environments (E1) fertilized field with the application of fertilizer formula 15-15-15 at 156 kg/ha or (E2) unfertilized field. Means (from n = 16 observations) with the same letter(s) are not significantly different at 5% level by least significant difference test.

Table┬Ā1
Soil pH, total nitrogen (N), available phosphorus (P), exchangeable potassium (K), exchangeable calcium (Ca), organic matter (OM), electrical conductivity (EC), cation exchange capacity (CEC) and texture before and after fertilizer application in two environments
| Environmentsa | pH | Total N (%) | Available P (mg/kg) | Exchangeable K (mg/kg) | Exchangeable Ca (mg/kg) | OM (%) | EC (/dsm) | CEC (c mol/kg) | Soil texture |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before planting | |||||||||
| Environment 1 | 6.89 | 0.0225 | 25.99 | 35.99 | 335 | 0.455 | 0.036 | 1.674 | Loamy-sand |
| Environment 2 | 6.55 | 0.0208 | 35.89 | 42.32 | 305 | 0.428 | 0.079 | 1.757 | Loamy-sand |
| After fertilizer application | |||||||||
| Environment 1 | 7.02 | 0.0261 | 34.16 | 45.23 | 415 | 0.521 | 0.048 | 2.082 | Loamy-sand |
| Environment 2 | 7.15 | 0.0197 | 22.28 | 27.24 | 310 | 0.405 | 0.026 | 1.598 | Loamy-sand |
Table┬Ā2
Mean squares for disease incidence and severity index of stem rot in Jerusalem artichoke caused by Sclerotium rolfsii
| Source of variation | df | Disease incidence (%)a | Severity index (%)b |
|---|---|---|---|
| Environment (E) | 1 | 1,320.34** | 740.16** |
| Reps/environment | 6 | 26.75** | 163.43** |
| Varieties (V) | 3 | 1,330.13** | 2,428.07** |
| Trichoderma (T) | 1 | 2,187.08** | 301.97** |
| Bacillus (B) | 1 | 2,517.84** | 908.45** |
| E ├Ś V | 3 | 623.52** | 88.22** |
| E ├Ś T | 1 | 364.16** | 1,268.82** |
| E ├Ś B | 1 | 311.56** | 32.20** |
| V ├Ś T | 3 | 357.76** | 471.96** |
| V ├Ś B | 3 | 186.01** | 254.03** |
| T ├Ś B | 1 | 5,892.91** | 1,942.20** |
| E ├Ś V ├Ś T | 3 | 506.88** | 227.75** |
| E ├Ś V ├Ś B | 3 | 612.04** | 366.95** |
| E ├Ś T ├Ś B | 1 | 48.14** | 1,348.10** |
| V ├Ś T ├Ś B | 3 | 127.50** | 103.99** |
| E ├Ś V ├Ś T ├Ś B | 3 | 11.49** | 318.42** |
| Pooled error | 90 | 77.28** | 88.31** |
| CV (%) | 28.81** | 36.32** |
Table┬Ā3
Effect of Trichoderma harzianum T9 and Bacillus firmus BSR032 on incidence and severity index of stem rot in Jerusalem artichoke caused by Sclerotium rolfsii
References
Al-Askar, AAA, Ghoneem, KM, Ezzat, AES and Saber, WIA 2014. Improving growth and productivity as well as controlling Sclerotium rolfsii in Jerusalem Artichoke using biotic and abiotic agents. J Pure Appl Microbiol. 8:279-291.
Ali, A and Javaid, A 2015. Screening of Trichoderma species for their biological control potential against Sclerotium rolfsii, the cause of collar rot disease of chickpea. Mycopath. 13:93-96.
Analytical Software. 2003. Statistix 8: analytical software userŌĆÖs manual. Analytical Software, Tallahassee, FL, USA. 396.
Anfok, GH 2000. Benzo-(1,2,3)-thiadiazole-7-carbothioic acid S-methyl ester induces systemic resistance in tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum. Mill cv. Vollendung) to cucumber mosaic virus. Crop Prot. 19:401-405.

Baker, R 1968. Mechanisms of biological control of soil-borne pathogens. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 6:263-294.

Cawoy, H, Bettiol, W, Fickers, P and Ongena, M 2011.
Bacillus-based biological control of plant diseases. In: Pesticides in the modern world: pesticides use and management, eds. by M Stoytcheva, 273-302. IntechOpen, Rijeka, Croatia.

Chanutsa, N, Phonkerd, N and Bunyatratchata, W 2014. Potential of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to control Sclerotium rolfsii causing stem rot and collar rot disease of tomato. J Adv Agric Technol. 1:132-135.

Charirak, P, Saksirirat, W, Jogloy, S and Saepaisan, S 2016. Application of microorganisms for induced resistance in Jerusalem artichoke (Helianthus tuberosus L.) against stem rot caused by Sclerotium rolfsii Sacc. J Pure Appl Microbiol. 10:853-863.
Doley, K, Dudhane, M, Borde, M and Jite, PK 2014. Effects of Glomus fasciculatum and Trichoderma asperelloides in roots of groundnut (cv. Western-51) against pathogen Sclerotium rolfsii
. Int J Phytopathol. 3:89-100.


Dordas, C 2008. Role of nutrients in controlling plant diseases in sustainable agriculture: a review. Agron Sustain Dev. 28:33-46.

Eid, K 2013. Field applications of some bioagents and safety chemicals to control stem rot disease of Jerusalem artichoke (Helianthus tuberosus L.). J Appl Sci Res. 9:5825-5834.
Elad, Y, Chet, I and Henis, Y 1982. Degradation of plant pathogenic fungi by Trichoderma harzianum
. Can J Microbiol. 28:719-725.

El-Fiki, IAI, Shaheen, SIM, Youness, HEH and Kamel, SM 2014. Evaluation of some bioagents for controlling damping off and root rot diseases of bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Egypt J Biol Pest Control. 24:275-282.
El-Katatny, MH, Somitsch, W, Robra, KH, El-Katatny, MS and G├╝bitz, GM 2000. Production of chitinase and ╬▓-1,3-glucanase by Trichoderma harzianum for control of the phytopathogenic fungus Sclerotium rolfsii
. Food Technol Biotechnol. 38:173-180.
Errakhi, R, Bouteau, F, Lebrihi, A and Barakate, M 2007. Evidences of biological control capacities of Streptomyces spp. against Sclerotium rolfsii responsible for damping-off disease in sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.). World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 23:1503-1509.


Ezzat, AS, Ghoneem, KM, Saber, WIA and Al-Askar, AA 2015. Control of wilt, stalk and tuber rots diseases using Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, Trichoderma species and hydroquinone enhances yield quality and storability of Jerusalem artichoke (Helianthus tuberosus L.). Egypt J Biol Pest Control. 25:11-22.
Farnworth, ER 1994. Feeding Jerusalem artichoke (Helianthus tuberosus) to pigs. J Sci Food Agric. 64:217-221.

Junsopa, C, Jogloy, S, Saksirirat, W, Songsri, P, Kesmala, T and Shew, BB 2017. Genotypic diversity of Jerusalem artichoke for resistance to stem rot caused by Sclerotium rolfsii under field conditions. Euphytica. 213:164.


Junsopa, C, Jogloy, S, Saksirirat, W, Songsri, P, Kesmala, T, Shew, BB and Patanothai, A 2016. Inoculation with Sclerotium rolfsii, cause of stem rot in Jerusalem artichoke, under field conditions. Eur J Plant Pathol. 146:47-58.


Kays, SJ and Nottingham, SF 2007. Biology and chemistry of Jerusalem artichoke: Helianthus tuberosus L. Taylor & Francis, Florida, FL, USA. 496.
Li, L, Li, L, Wang, Y, Du, Y and Qin, S 2013. Biorefinery products from the inulin-containing crop Jerusalem artichoke. Biotechnol Lett. 35:471-477.



Maneesuwan, P and Sirithorn, P 2013 Effect of Bacillus licheniformis BFP011 to inhibit Colletotrichum capsici, cause of Pepper anthracnose. Khon Kaen Agric J. 41:Suppl 1. 327-332 (in Thai).
McCarter, SM and Kays, SJ 1984. Disease limiting production of Jerusalem artichokes in Georgia. Plant Dis. 68:299-302.

Mukherjee, PK, Horwitz, BA, Herrera-Estrella, A, Schmoll, M and Kenerley, CM 2013.
Trichoderma research in the genome era. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 51:105-129.


Nautiyal, CS and Dion, P 2008. Molecular mechanisms of plant and microbe coexistence. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Germany. 486.
Pattanapipitpaisal, P and Kamlandharn, R 2012. Screening of chitinolytic actinomycetes for biological control of Sclerotium rolfsii stem rot disease of chilliSongklanakarin
. J Sci Technol. 34:387-393.
Punja, ZK, Carter, JD, Campbell, GM and Rossell, EL 1986. Effects of calcium and nitrogen fertilizers, fungicides, and tillage practices on incidence of Sclerotium rolfsii on processing carrots. Plant Dis. 70:819-824.

Puttha, R, Jogloy, S, Wangsomnuk, PP, Srijaranai, S, Kesmala, T and Patanothai, A 2012. Genotypic variability and genotype by environment interactions for inulin content of Jerusalem artichoke germplasm. Euphytica. 183:119-131.


Ruano-Rosa, D, Cazorla, FM, Bonilla, N, Mart├Łn-P├®rez, R, De Vicente, A and L├│pez-Herrera, CJ 2014. Biological control of avocado white root rot with combined applications of Trichoderma spp. and rhizobacteria. Eur J Plant Pathol. 138:751-762.


Sarangi, T and Ramakrishnan, S 2016. Influence of biomolecules of Bacillus spp. against phytopathogens: a review. Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci. 5:131-134.
Sennoi, R, Jogloy, S, Saksirirat, W, Kesmala, T and Patanothai, A 2013a. Genotypic variation of resistance to southern stem rot of Jerusalem artichoke caused by Sclerotium rolfsii
. Euphytica. 190:415-424.


Sennoi, R, Jogloy, S, Saksirirat, W and Patanothai, A 2010. Pathogenicity test of Sclerotium rolfsii, a causal agent of Jerusalem artichoke (Helianthus tuberosus L.) stem rot. Asian J Plant Sci. 9:281-284.

Sennoi, R, Singkham, N, Jogloy, S, Boonlue, S, Saksirirat, W, Kesmala, T and Patanothai, A 2013b. Biological control of southern stem rot caused by Sclerotium rolfsii using Trichoderma harzianum and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on Jerusalem artichoke (Helianthus tuberosus L.). Crop Prot. 54:148-153.

Singh, A and Singh, HB 2004. Control of collar rot in mint (Mentha spp.) caused by Sclerotium rolfsii using biological means. Curr Sci. 87:362-366.
Spann, TM and Schumann, AW 2009. The role of plant nutrients in disease development with emphasis on citrus and huanglongbing. Proc Fla State Hortic Soc. 122:169-171.
- TOOLS
-
METRICS

-
- 0 Crossref
- 0 Scopus
- 3,732 View
- 89 Download
- ORCID iDs
-
Sanun Jogloy

https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7455-4514 - Related articles



 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Full text via PMC
Full text via PMC Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print