 |
 |
| Plant Pathol J > Volume 38(6); 2022 > Article |
|
Abstract
Pectobacterium odoriferum is the primary causative agent in Kimchi cabbage soft-rot diseases. The pathogenic bacteria Pectobacterium genera are responsible for significant yield losses in crops. However, P. odoriferum shares a vast range of hosts with P. carotovorum, P. versatile, and P. brasiliense, and has similar biochemical, phenotypic, and genetic characteristics to these species. Therefore, it is essential to develop a P. odoriferum-specific diagnostic method for soft-rot disease because of the complicated diagnostic process and management as described above. Therefore, in this study, to select P. odoriferum-specific genes, species-specific genes were selected using the data of the P. odoriferum JK2.1 whole genome and similar bacterial species registered with NCBI. Thereafter, the specificity of the selected gene was tested through blast analysis. We identified novel species-specific genes to detect and quantify targeted P. odoriferum and designed specific primer sets targeting HAD family hydrolases. It was confirmed that the selected primer set formed a specific amplicon of 360 bp only in the DNA of P. odoriferum using 29 Pectobacterium species and related species. Furthermore, the population density of P. odoriferum can be estimated without genomic DNA extraction through SYBR Green-based real-time quantitative PCR using a primer set in plants. As a result, the newly developed diagnostic method enables rapid and accurate diagnosis and continuous monitoring of soft-rot disease in Kimchi cabbage without additional procedures from the plant tissue.
Pectobacterium (previously classified as the genus Erwinia) belonging to the family Pectobacteriaceae are robust phytopathogens that cause soft-rot disease in economically important vegetables, fruits, and ornamental plants (Ma et al., 2007). Currently, this group has been classified into 20 species (P. carotovorum, P. odoriferum, P. versatile, P. brasiliense, P. atrosepticum, P. aroidearum, P. betavasculorum, P. fontis, P. cacticida, P. wasabiae, P. zantedeschiae, P. parmentieri, P. peruviense, P. polaris, P. punjabense, P. polonicum, P. aquaticum, P. actinidiae, P. parvum, and P. quasiaquaticum) based on advanced genomic analysis techniques (Jee et al., 2020; Moussa et al., 2021; Pasanen et al., 2020; Portier et al., 2019, 2020; Zhang et al., 2016).The genus is a gram negative, primarily rod-shaped bacteria and most of them are plant pathogens. Pectobacterium usually invades through wounds on the host plant caused by various factors like insects, other diseases, and physical factors (Oskiera et al., 2017). They can produce pectin and cellulolytic enzymes that break down cell walls, causing maceration (Charkowski, 2018). This series of processes can be repeated for a long time not only in the field but also in the storage and distribution process (Bhat et al., 2010; Glasner et al., 2008).
Kimchi cabbage (Brassica rapa var. pekinensis) is one of the economically significant stored vegetables produced and supplied year-round in Korea (Lee et al., 2016). However, it is vulnerable to various diseases and pests when exposed to high temperatures. In particular, soft rot, which occurs frequently occurs in Kimchi cabbage growing at high altitudes in summer, causes huge losses (Kim and Yeoung, 2004). Although P. carotovorum had been known to cause most Kimchi cabbage soft rot, P. odoriferum, P. brasiliense, and P. versatile were recently isolated from soft rot in Kimchi cabbage (Lee et al., 2014; Park et al., 1999; Roh et al., 2009; Seo et al., 2004). P. odoriferum was primarily isolated from chicory in France and Japan, and was initially recognized a narrow host range (Gallois et al., 1992). However, it has been isolated from various vegetables (celery, cabbage, Chinese cabbage, artichoke, carrot, parsley, onion, potato, sugar beet, and sweet potato), and has been identified as the causal agent of bacterial soft rot in many other countries (Gao et al., 2016; Oskiera et al., 2017; Waleron et al., 2014). For that reason, there is a need for rapid and accurate identification of pathogens for an appropriate disease control strategy for important stored vegetables, including Kimchi cabbage.
Identification of P. odoriferum has traditionally been based on morphology and host range, but most hosts overlap, and the phenotypic characteristics are unclear depending on growth conditions (Czajkowski et al., 2015). These traditional methods are poorly reproducible, time-consuming, and labor-intensive. Over the past three decades, ribosomal RNA operons, specifically the 16S rRNA genes, have been widely used for the diversity analysis and identification of prokaryotes. However, sequencing of the 16S rRNA gene has not differentiated the species of the genus Pectobacterium (Naum et al., 2008; Staley, 2006). Although some molecular methods have been developed for rapid detection and identification, using molecular methods such as amplified fragment length polymorphism and multi-coordinate sequencing (Nabhan et al., 2012). Iterative and time-consuming procedural difficulties usually accompany this species identification method. Subsequently, a phylogenetic analysis method was developed based on the single gene pmrA required for resistance to plant-derived antimicrobial peptides (Kettani-Halabi et al., 2013). The tests must be rapid, sensitive, and specific, as cost- and time-sensitive decisions are made when implementing a disease control strategy. In addition, two specific primers for P. odoriferum are six genes of the Pco-subspecific srl operon (i.e., srlAEBDMR) involved in sorbitol metabolism. Two specific primers for general polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and quantitative PCR (qPCR) based have been developed (Li et al., 2020).
We designed species-specific primers for general PCR and qPCR in this study based on the HAD family hydrolase gene. In addition, specificity and sensitivity were tested for the detection of pathogens in infected cabbage leaves according to the MIQE guidelines (Bustin, 2008). Currently, real-time qPCR is known as a rapid and accurate approach for pathogen diagnosis in plants. Therefore, we proposed an efficient method for specific and quantitative detection of the pathogen, P. odoriferum, in plant samples through direct qPCR based on SYBR Green. Thus, it shows that it can be used for sensitive and specific detection of target pathogens, simplifying diagnosis, pathogen monitoring and implementing of appropriate disease control strategies.
Twenty-nine culture were selected for the experiment. Among them, 24 type strains were provided from the Korean Agricultural Culture Collection (KACC) and five strains of P. odoriferum isolated from the Republic of Korea obtained from KACC and the Highland Agriculture Research Institute to validate the specificity of the species-specific primers developed in this study (Table 1).
The bacterial isolates were cultured at 28-30┬░C for 24-48 h on trypsin soy agar media (15 g/l digested casein, 5 g/l digested soy, 5 g/l NaCl, and 1.5% agar, Difco, Detroit, MI, USA) under aerophilic condition. The stock culture were preserved in glycerol stocks at ŌłÆ80┬░C. Total genomic DNA was extracted using the NucleoSpin Microbial DNA Kit (TaKaRa Bio USA, Inc., San Jose, CA, USA). The corresponding strains listed in Table 1 and isolated DNA was spectrophotometrically quantified. The concentration and quality of the extracted genomic DNA were determined using a NanoDrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (NanoDrop Technologies, Wilmington, DE, USA). All the extracted genomic DNA samples were stored at ŌłÆ20┬░C until used for further experiments.
The whole genome sequences from P. odoriferum JK2.1 (GenBank accession no. CP034938.1) and the other closely related species data were downloaded from the NCBI ftp site (ftp://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genomes/bacteria/). To mine species-specific genes for quantitative detection of the targeted microbe, candidate gene selection pipeline via computational clustering was carried out as described by Chen and Lang (Chen et al., 2010; Lang et al., 2010). From this candidate gene selection pipeline, the resulting candidate genes presented no substantial concordance with other P. carotovorum group strains that were selected as quantitative PCR targets. The specific primer set used for P. odoriferum was generated using the DNASTAR Lasergene Primerselect module (version 7.2.1, DNASTAR Inc., Madison, WI, USA) (Table 2). Primer synthesis was performed by XENOTECH Co. (Daejeon, Korea). The oligonucleotide primer set amplified a specific DNA fragment from only the targeted species. The nucleotide sequences of the primer set were evaluated for their specificity via NCBI BLAST modules such as BLASTn and BLASTx (https://blat.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi).
PCRs were conducted in T100 Thermal Cycler (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA, USA) with the following steps: initial denaturation at 95┬░C for 5 min; 35 cycles of denaturation (at 95┬░C for 1 min), annealing (at 65┬░C for 30 s), and extension (at 72┬░C for 1 min), and a final extension period of at 72┬░C for 10 min. All PCR reactions were performed in a total volume of 25 ╬╝l (1├Ś buffer, 0.2 mM each dNTP, 4.0 mM MgCl2) covering 1.25 U of GoTaq Flexi DNA polymerase (Promega, Madison, WI, USA), 25 ng of template DNA and a 0.1 ╬╝M final concentration of each primer (Table 2). PCR product was resolved by 1.5% (w/v) agarose gels and stained with LoadingStar (DYNEBIO, Seoul, Korea). The gel was visualized and the images were documented via a GelDoc Go Imaging System (Bio-Rad Laboratories).
All quantitative PCR assays were carried out in a final reaction volume of 20 ╬╝l containing 5 ng of purified DNA extracted from each sample, primers mentioned above (0.5 ╬╝M final concentration) and QGreenBlue 2├Ś Green qPCR Master Mix (CellSafe Bio, Inc., Yongin, Korea). The SYBR Green qPCRs were performed in a CFX96 real-time PCR system (Bio-Rad Laboratories). The SYBR Green real-time PCR amplification conditions were as follows: initial denaturation of at 95┬░C for 30 s; 40 cycles at 95┬░C for 5 s, 65┬░C for 30 s, and a melting curve analysis from 65 to 95┬░C with an increment of 0.5┬░C per 5 s. The standard curve of P. odoriferum was created by plotting the qPCR cycle threshold (Ct) values conducted using 10-fold serial dilutions of genomic DNA, cloned DNA (pGEM-T easy vector containing the 360 bp species-specific amplicon) and a bacterial cell suspension of targeted microbe. The copy number of the template was calculated using the previously described formula (Kang et al., 2016; Whelan et al., 2003):
The Bio-Rad CFX Maestro version 1.1 software suite automatically performed thermal cycling, data collection, and standard amplification. A non-template negative control and standard amplification were also included to confirm the SYBR Green real-time PCR quality. The amplification efficiency (E) was calculated using the following formula.
In order to detect and quantify pathogen in Kimchi cabbage leaves infected with P. odoriferum, the bacterial cell suspension (2.47 ├Ś 107 cfu/ml, 50 ╬╝l/inoculation site) was injected in two places on the lower leaf veins of four healthy Kimchi cabbage leaves. After three days of post-inoculation, soft root disease symptoms were confirmed, and samples were collected at five locations (A-E, 20 mm interval) by distance along the leaf vein from the site of disease progression. Each sample (leaf pieces about 1 ├Ś 1 cm) was collected using a sterilized instrument and immersed in a 2 ml tube containing 1 ml of sterile water for about 30 min, and 1 ╬╝l of the immersion solution was used for real-time qPCR. The limit of detection (LOD) corresponds to undetected amplification when Ct Ōēź 37, and the limit of quantitation (LOQ) corresponds to a Ct value when the threshold standard is not met or the standard deviation value is 1.0 Ct Ōēź 36 that not meet the threshold standard in 3 replicates or a standard deviation value of 1.0 or greater. For quantitative analysis, the density of pathogens by distance from symptom was estimated by referring to the cell suspension standard curve results.
The selected gene and oligonucleotide primer set (Table 2) from P. odoriferum were evaluated and confirmed via a combination of Bioinformatics tools, including the Lasergene PreimerSelet program (version 7.2.1, DNASTAR Inc.) and NCBI BLAST search engines (http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/cgi).
For a HAD family hydrolase-coding gene (accession no. CP034938.1, 3809023-3809706, protein ID: QHP81543.1) of P. odoriferum JK2.1, the BLASTn searches presented no substantial match to the recognized reference sequences of other Pectobacterium species. The BLASTx results using the predicted protein sequence presented that the most relevant protein to our HAD family hydrolase gene was a P. carotovorum subsp. carotovorum 2-deoxyglucose-6-phosphatase (identity = 99.12%, score = 468 bits [1,205], and expected = 1e-166).
Genomic DNA samples from Pectobacterium, Dickeya, Pantoea, Erwinia, and Musicola strains covering the type strains of each targeted species were used to validate the specificity of the microbe-targeting oligonucleotide primer set via a conventional PCR test.
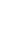
The specificity of the PeOd360F/R primer set was tested by conventional PCR using 29 different bacterial genomic DNA (Table 1). The target gene, expected size of 360 bp, was amplified only in the P. odoriferum strains (Fig. 1). In addition, SYBR Green-based real-time PCR correctly generated PeOd360F/R primer pair-specific fluorescence signals in all P. odoriferum strains (Fig. 2). On the other hand, other bacteria species had no fluorescence signal (Fig. 2, lanes 7-13 and 15-28). In addition, the melting peak showed reproducible single peaks at 88┬░C.
SYBR Green-based real-time PCR was conducted with PeOd360F/R primers to generate a standard curve by plotting the mean threshold cycle (Ct) value (n = 3). The concentration of genomic DNA, cloned DNA, and density of the bacterial cells were 5 ├Ś 10ŌłÆ15 to 5 ├Ś 10ŌłÆ9 g/╬╝l, 1.35 ├Ś 102 to 1.35 ├Ś 109 copies/╬╝l and 2.47 ├Ś 101 to 2.47 ├Ś 107 cfu/ml, respectively (Table 3). The standard curves showed that there are linear-correlation between the Ct values and the concentration of genomic DNA (R2 = 0.999, slope = ŌłÆ3.688, and y-int = 38.709), cloned DNA (R2 = 0.999, slope = ŌłÆ3.928, and y-int = 29.093), and cell suspension (R2 = 0.998, slope = ŌłÆ3.995, and y-int = 44.407). The efficiencies were 86.7%, 79.7%, and 78.0% for each genomic DNA, cloned DNA, and cell suspension (Fig. 3). The LOD results showed that the fluorescence signal could be detected when the genomic DNA and cell suspension were diluted to 50 fg and 2.47 ├Ś 103 cfu/ml, but could not be detected when diluted to 5 fg and 2.47 ├Ś 102 cfu/ml. Therefore, the LOQ of cloned DNA by real-time PCR was confirmed to be 1.35 ├Ś 102 copies. The LOQ of genomic DNA and cell suspension by real-time PCR was confirmed to be 50 fg and 2.47 ├Ś 104 cfu/ml, respectively (Table 3).
Direct detection and quantitation of the PeOd360F/R primer set were confirmed by SYBR Green real-time PCR in disease-symptomatic Kimchi cabbage leaf samples. The sample was divided by distance (A-E) from the symptom site and repeated 3 times.
As a result, the Ct values of region ŌĆ£AŌĆØ near the symptom site and region ŌĆ£BŌĆØ close to it were 22.30 ┬▒ 1.14 and 21.46 ┬▒ 0.78, respectively, significantly lower than at other locations somewhat distant from the symptom site. The positive control had a Ct value of 18.29 ┬▒ 0.04 and the negative control had no signal (Fig. 4). In addition, the number of cells was calculated based on the cell suspension standard curve. As a result, region A-E were confirmed to be 7.32 ┬▒ 0.33, 7.57 ┬▒ 0.23, 6.69 ┬▒ 0.88, 6.06 ┬▒ 0.96, and 5.14 ┬▒ 1.29 Log cfu/ml, respectively (Fig. 4D).
The strains P. odoriferum, P. carotovorum, P. brasilience, and P. versatile is currently recognized as the primary the causal agent of bacterial soft rot on storage vegetables in the Republic of Korea (Lee et al., 2014; Park et al., 1999; Roh et al., 2009; Seo et al., 2004). However, the species do not have host specificity (P├®rombelon and Kelman, 1980). Therefore, soft rot disease diagnoses and identifying specific pathogens are economical essential. Furthermore, the microbe genome sequences and genomic analysis techniques can accelerated identification and disease diagnosis. As result, it provides an extended possibility to develop existing detection and quantitation methods by identifying novel target genes.
The methods adopted for rapid and accurate diagnosis include real-time qPCR analysis using SYBR Green-based and FAM-labeled TaqMan probe methods. The specific primer set for qPCR based on SYBR Green in the 16S-23S rRNA internal transcribed spacer (ITS) region was developed to detect and quantify P. carotovorum (Su├Īrez et al., 2022). In addition, the P. brasiliense-specific TaqMan probe-based qPCR assay for detecting and quantifying has been developed by comparing the 16S-23S rRNA ITS and the tRNA-Glu gene region which contain polymorphisms informative for the discrimination of closely related Pectobacterium species (Muzhinji et al., 2020). The specific primers for diagnosing P. odoriferum are currently the only primer sets for conventional PCR and SYBR Green-based qPCR reported by Li et al. (2020). They developed two primer sets based on the srlE gene, encoding sorbitol-specific phosphotransferase, to identify P. odoriferum (Li et al., 2020). However, their study did not show accurate pathogen quantitation values in infected plants. In addition, it requires some effort because DNA is extracted and used from infected plants.
In the present study, we used BLAST search to explore for P. odoriferum-specific genes. In addition, we developed the specific primer set based on the HAD family hydrolase gene involved in various cellular processes ranging from amino acid biosynthesis to translation (Koonin and Tatusov, 1994) (Table 2). The advantage of our newly developed assay is that it does not require pre-incubation and DNA extraction for species identification and quantification. In addition, accurate identification of P. odoriferum using conventional PCR and qPCR methods is possible with one primer set. The result of the calculated standard curve shows a small standard error. It ensures that the assay is reproducible and very robust, not only on pathogen gDNA but also on infectious plant suspensions. As a result of measuring the pathogen concentration by distance from the symptom, it was confirmed that the pathogen moved along the leaf veins, and when the infection progressed, the pathogen could be detected even in an area with no symptoms (Fig. 4). The LOD of pathogens is 103 cell units, enabling precise diagnosis.
In conclusion, the newly developed SYBR Green real-time qPCR primer set can perform qPCR directly from plants without DNA extraction. This method is susceptible, saving time, significantly reducing the risk of contamination and cost per reaction, and helping process processing large volumes of samples. The newly developed specific primer set can help in epidemiological study including where this pathogen present by early detection of P. odoriferum.
Acknowledgments
This work was carried out with the support of the National Institute of Agricultural Sciences (Project No. PJ01679902), Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea.
Fig.┬Ā1
Polymerase chain reaction amplification of the HAD family hydrolase gene with the primers. Lane M is the size marker (1 kb DNA plus ladder; Inclon Co., Ltd.) while lanes 1 and 6 were Pectobacterium odoriferum strains, and lanes 7 to 29 included strains from other Pectobacterium, Dickeya, Pantoea, Erwinia, and Musicola species as listed in Table 1.
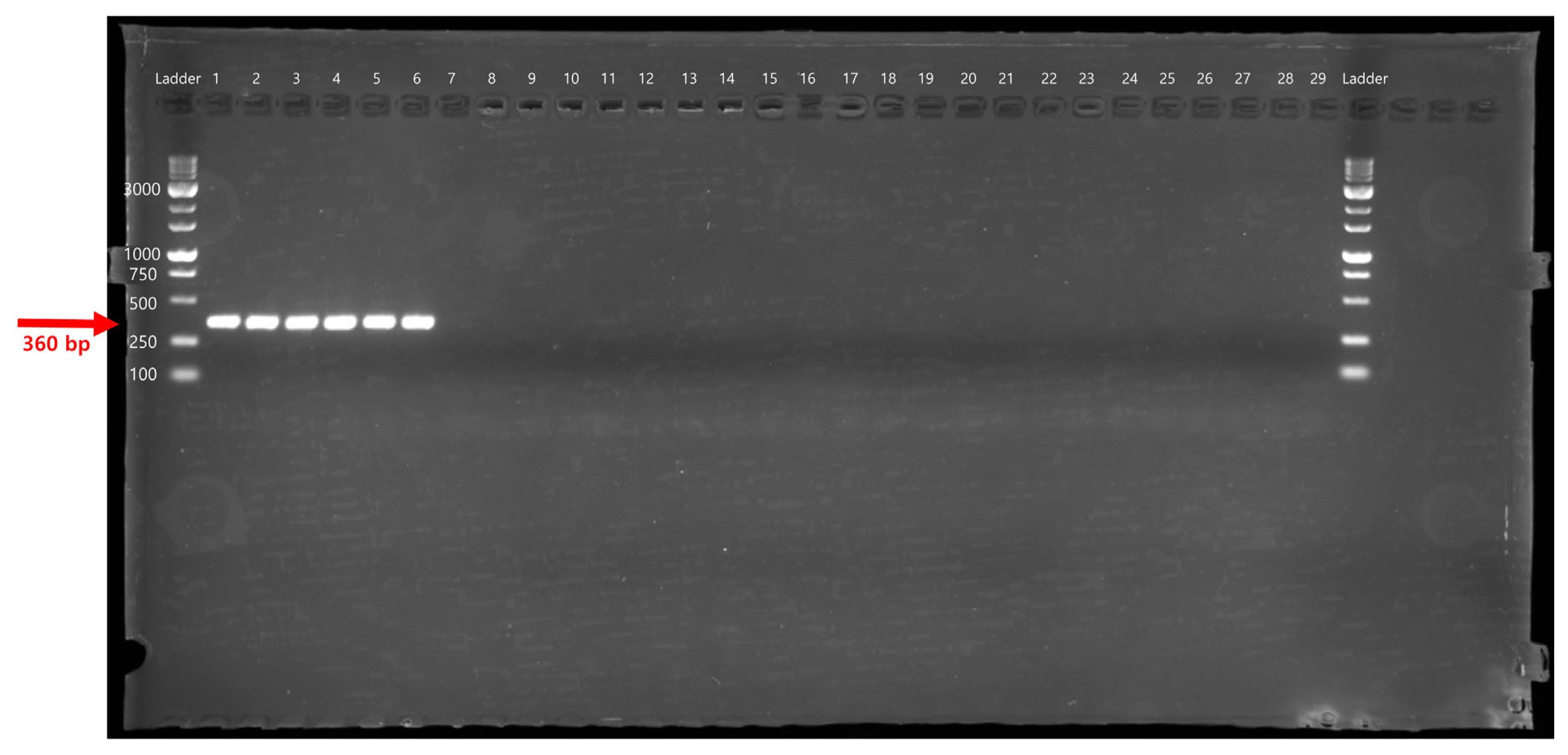
Fig.┬Ā2
Species-specificity assay of the PeOd360F/R primer using real-time polymerase chain reaction. The bacterial strains in lanes 1-29 are described in Table 1. Lane 30, distilled water (n = 3). (A) Amplification curves. (B) Melting curve. (C) Melting peak. The results of the melting peak analysis indicated that the amplified products have a melting temperature (Tm) of approximately 88┬░C. RFU, relative fluorescence units.

Fig.┬Ā3
Standard curve analysis of real-time polymerase chain reaction performed using a dilution series. A standard curve was generated from the threshold cycles (Ct) also known as crossing points of the Pectobacterium oderiferum standard dilutions. (A) Genomic DNA. (B) Cloned DNA. (C) Bacterial cell suspension. The R2 value of each curve was >0.99.

Fig.┬Ā4
SYBR Green-based real-time polymerase chain reaction for species-specific detection of Pectobacterium odoriferum in samples from Kimchi cabbage leaf. A sample collection by distance from disease symptoms of plant (region A-E). Negative control is healthy Kimchi cabbage leaf, positive control is 5 ng/╬╝l of P. odoriferum KACC 22724 gDNA. (A) Amplification curves. (B, C) Melting curve and melting peak was added to confirm that the target gene was amplified at a specific temperature (88┬░C). (D) The Ct value was converted to Log (cfu/ml) and expressed based on the equation of the standard curve of the Ct value according to the bacterial concentration. Data are shown as mean ┬▒ standard error of mean. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 relative to all treatments; ns, not significant.
Table┬Ā1
List of bacterial strains used in this study
| No. | Scientific name | Sourcea | Hostb | This studyb |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pectobacterium odoriferum | KACC 22724T | Chicory | + |
| 2 | Pectobacterium odoriferum | KACC 22680 | Kimchi cabbage (Korea) | + |
| 3 | Pectobacterium odoriferum | KACC 22677 | White radish (Korea) | + |
| 4 | Pectobacterium odoriferum | GP05 | Potato (Korea) | + |
| 5 | Pectobacterium odoriferum | HNP201716 | Potato (Korea) | + |
| 6 | Pectobacterium odoriferum | PDP201716 | Potato (Korea) | + |
| 7 | Pectobacterium carotovorum | KACC 22723T | Potato | ŌłÆ |
| 8 | Pectobacterium versatile | KACC 22742T | Potato | ŌłÆ |
| 9 | Pectobacterium brasiliense | KACC 22743T | Potato | ŌłÆ |
| 10 | Pectobacterium polaris | KACC 22748T | Potato | ŌłÆ |
| 11 | Pectobacterium quasiaquaticum | KACC 22725T | Water | ŌłÆ |
| 12 | Pectobacterium aquaticum | KACC 22744T | Fresh water | ŌłÆ |
| 13 | Pectobacterium actinidiae | KACC 22717T | Kiwifruit | ŌłÆ |
| 14 | Pectobacterium fontis | KACC 22726T | Fresh water | ŌłÆ |
| 15 | Pectobacterium parmentieri | KACC 22727T | Potato | ŌłÆ |
| 16 | Pectobacterium wasabiae | KACC 22728T | Eutrema wasabi | ŌłÆ |
| 17 | Pectobacterium betavasculorum | KACC 22729T | Beet | ŌłÆ |
| 18 | Pectobacterium atrosepticum | KACC 22730T | Potato | ŌłÆ |
| 19 | Pectobacterium aroidearum | KACC 22731T | Calla Lily | ŌłÆ |
| 20 | Pectobacterium punjabense | KACC 22732T | Potato | ŌłÆ |
| 21 | Dickeya fangzhongdai | KACC 22747T | Peer tree | ŌłÆ |
| 22 | Dickeya dadantii | KACC 22743T | Rose geranium | ŌłÆ |
| 23 | Dickeya chrysnathemi | KACC 22733T | Chrysanthemum | ŌłÆ |
| 24 | Dickeya dadantii subsp. diffenbachiae | KACC 22735T | Dieffenbachia | ŌłÆ |
| 25 | Dickeya zeae | KACC 22736T | Maize | ŌłÆ |
| 26 | Pantoea ananatis | KACC 22739T | Pineapple | ŌłÆ |
| 27 | Erwinia pyrifoliae | KACC 13193T | Peer tree | ŌłÆ |
| 28 | Erwinia rhapontici | KACC 22740T | Rhubarb | ŌłÆ |
| 29 | Musicola paradisiaca | KACC 22741T | Banana | ŌłÆ |
Table┬Ā2
Primer sequences, their targets, and the annealing temperatures used in Pectobacterium odoriferum PCR screens
Table┬Ā3
Mean threshold cycle (Ct) of 10-fold dilution series of Pectobacterium odoriferum KACC 22724 cloned DNA, genomic DNA, and cell suspension determined by real-time PCR
References
Bhat, K.A., Masood, S.D., Bhat, N.A., Bhat, M.A., Razvi, S.M., Mir, M.R., Akhtar, S. and Habib, M. 2010. Current status of post harvest soft rot in vegetables: a review. Asian J. Plant Sci 9:200-208.

Bustin, S.A. 2008. Molecular medicine, gene-expression profiling and molecular diagnostics: putting the cart before the horse. Biomarkers Med 2:201-207.

Charkowski, A.O. 2018. The changing face of bacterial soft-rot diseases. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol 56:269-288.


Chen, J., Zhang, L., Paoli, G.C., Shi, C., Tu, S.-I. and Shi, X. 2010. A real-time PCR method for the detection of Salmonella enterica from food using a target sequence identified by comparative genomic analysis. Int. J. Food Microbiol 137:168-174.


Czajkowski, R., P├®rombelon, M., Jafra, S., Lojkowska, E., Potrykus, M., Van der Wolf, J. and Sledz, W. 2015. Detection, identification and differentiation of Pectobacterium and Dickeya species causing potato blackleg and tuber soft rot: a review. Ann. Appl. Biol 166:18-38.




Gallois, A., Samson, R., Ageron, E. and Grimont, P.A.D. 1992.
Erwinia carotovora subsp. odorifera subsp. nov., associated with odorous soft rot of chicory (Cichorium intybus L.). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol 42:582-588.

Gao, B., Wang, R.Y., Chen, S.L., Ma, J. and Li, X.H. 2016. First report of Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum and P. carotovorum subsp. odoriferum causing bacterial soft rot of sweetpotato in China. Plant Dis 100:1776.

Glasner, J.D., Marquez-Villavicencio, M., Kim, H.-S., Jahn, C.E., Ma, B., Biehl, B.S., Rissman, A.I., Mole, B., Yi, X., Yang, C.-H., Dangl, J.L., Grant, S.R., Perna, N.T. and Charkowski, A.O. 2008. Niche-specificity and the variable fraction of the Pectobacterium pan-genome. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact 21:1549-1560.


Jee, S., Choi, J.-G., Lee, Y.-G., Kwon, M., Hwang, I. and Heu, S. 2020. Distribution of Pectobacterium species isolated in South Korea and comparison of temperature effects on pathogenicity. Plant Pathol. J 36:346-354.




Kang, B.K., Cho, M.S. and Park, D.S. 2016. Red pepper powder is a crucial factor that influences the ontogeny of Weissella cibaria during Kimchi fermentation. Sci. Rep 6:28232.




Kettani-Halabi, M., Terta, M., Amdan, M., El Fahime, E.M., Bouteau, F. and Ennaji, M.M. 2013. An easy, simple inexpensive test for the specific detection of Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum based on sequence analysis of the pmrA gene. BMC Microbiol 13:176.




Kim, B.-S. and Yeoung, Y.-R. 2004. Suppression of bacterial soft rot on Chinease cabbage by calcium fertilizer treatment. Res. Plant Dis 10:82-85.
Koonin, E.V. and Tatusov, R.L. 1994. Computer analysis of bacterial haloacid dehalogenases defines a large superfamily of hydrolases with diverse specificity: application of an iterative approach to database search. J. Mol. Biol 244:125-132.

Lang, J.M., Hamilton, J.P., Diaz, M.G.Q., Van Sluys, M.A., Burgos, M.R.G., Vera Cruz, C.M., Buell, C.R., Tisserat, N.A. and Leach, J.E. 2010. Genomics-based diagnostic marker development for Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae and X. oryzae pvoryzicola
. Plant Dis 94:311-319.


Lee, D.H., Kim, J.-B., Lim, J.-A., Han, S.-W. and Heu, S. 2014. Genetic diversity of Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. brasiliensis isolated in Korea. Plant Pathol. J 30:117-124.



Lee, S.G., Kim, S.K., Lee, H.J., Choi, C.S. and Park, S.T. 2016. Impacts of climate change on the growth, morphological and physiological responses, and yield of Kimchi cabbage leaves. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol 57:470-477.


Li, X., Fu, L., Chen, C., Sun, W., Tian, Y. and Xie, H. 2020. Characteristics and rapid diagnosis of Pectobacterium carotovorum ssp. associated with bacterial soft rot of vegetables in China. Plant Dis 104:1158-1166.


Ma, B., Hibbing, M.E., Kim, H.-S., Reedy, R.M., Yedidia, I., Breuer, J., Breuer, J., Glasner, J.D., Perna, N.T., Kelman, A. and Charkowski, A.O. 2007. Host range and molecular phylogenies of the soft rot enterobacterial genera Pectobacterium and Dickeya
. Phytopathology 97:1150-1163.


Moussa, H.B., P├®dron, J., Bertrand, C., Hecquet, A. and Barny, M.-A. 2021.
Pectobacterium quasiaquaticum sp. nov., isolated from waterways. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol 71:005042.
Muzhinji, N., Dube, J.P., de Haan, E.G., Woodhall, J.W. and van der Waals, J.E. 2020. Development of a TaqMan PCR assay for specific detection and quantification of Pectobacterium brasiliense in potato tubers and soil. Eur. J. Plant Pathol 158:521-532.


Nabhan, S., Wydra, K., Linde, M. and Debener, T. 2012. The use of two complementary DNA assays, AFLP and MLSA, for epidemic and phylogenetic studies of pectolytic enterobacterial strains with focus on the heterogeneous species Pectobacterium carotovorum
. Plant Pathol 61:498-508.

Naum, M., Brown, E.W. and Mason-Gamer, R.J. 2008. Is 16S rDNA a reliable phylogenetic marker to characterize relationships below the family level in the Enterobacteriaceae? J. Mol. Evol 66:630-642.



Oskiera, M., Kałużna, M., Kowalska, B. and Smolińska, U. 2017.
Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. odoriferum on cabbage and Chinese cabbage: identification, characterization and taxonomic relatedness of bacterial soft rot causal agents. J. Plant Pathol 99:149-160.
Park, D.H., Kim, J.S., Lee, H.G., Hahm, Y. and Lim, C.K. 1999. Black leg of potato plants by Erwinia carotovora subspatroseptica
. Plant Dis. Agric 5:64-66.
Pasanen, M., Waleron, M., Schott, T., Cleenwerck, I., Misztak, A., Waleron, K., Pritchard, L., Bakr, R., Degefu, Y., van der Wolf, J., Vandamme, P. and Pirhonen, M. 2020.
Pectobacterium parvum sp. nov., having a Salmonella SPI-1-like Type III secretion system and low virulence. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol 70:2440-2448.



P├®rombelon, M.C.M. and Kelman, A. 1980. Ecology of the soft rot Erwinias. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol 18:361-387.

Portier, P., P├®dron, J., Taghouti, G., Dutrieux, C. and Barny, M.-A. 2020. Updated taxonomy of Pectobacterium genus in the CIRM-CFBP bacterial collection: when newly described species reveal ŌĆ£oldŌĆØ endemic population. Microorganisms 8:1441.



Portier, P., P├®dron, J., Taghouti, G., Fischer-Le Saux, M., Caullireau, E., Bertrand, C., Laurent, A., Chawki, K., Oulgazi, S., Moumni, M., Andrivon, D., Dutrieux, C., Faure, D., H├®lias, V. and Barny, M.-A. 2019. Elevation of Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. odoriferum to species level as Pectobacterium odoriferum sp. nov., proposal of Pectobacterium brasiliense sp. nov. and Pectobacterium actinidiae sp. nov., emended description of Pectobacterium carotovorum and description of Pectobacterium versatile sp. nov., isolated from streams and symptoms on diverse plants. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol 69:3207-3216.


Roh, E., Lee, S., Lee, Y., Ra, D., Choi, J., Moon, E. and Heu, S. 2009. Diverse antibacterial activity of Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum isolated in Korea. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol 19:42-50.

Seo, S.-T., Koo, J.-H., Hur, J.-H. and Lim, C.-K. 2004. Characterization of Korean Erwinia carotovora strains from potato and Chinese cabbage. Plant Pathol. J 20:283-288.

Staley, J.T. 2006. The bacterial species dilemma and the genomic-phylogenetic species concept. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci 361:1899-1909.




Su├Īrez, M.B., Diego, M., Feria, F.J., Mart├Łn-Robles, M.J., Moreno, S. and Palomo, J.L. 2022. New PCR-based assay for the identification of Pectobacterium carotovorum causing potato soft rot. Plant Dis 106:676-684.


Waleron, M., Waleron, K. and Lojkowska, E. 2014. Charaterization of Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. odoriferum causing soft rot of stored vegetables. Eur. J. Plant Pathol 139:457-469.


- TOOLS



 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Full text via PMC
Full text via PMC Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print