 |
 |
| Plant Pathol J > Volume 34(3); 2018 > Article |
Abstract
Commercial biocontrol of microbial plant diseases and plant pests, such as nematodes, requires field-effective formulations. The isolate Pseudomonas chlororaphis O6 is a Gram-negative bacterium that controls microbial plant pathogens both directly and indirectly. This bacterium also has nematocidal activity. In this study, we report on the efficacy of a wettable powder-type formulation of P. chlororaphis O6. Culturable bacteria in the formulated product were retained at above 1 × 108 colony forming units/g after storage of the powder at 25 °C for six months. Foliar application of the diluted formulated product controlled leaf blight and gray mold in tomato. The product also displayed preventative and curative controls for root-knot nematode (Meloidogyne spp.) in tomato. Under laboratory conditions and for commercially grown melon, the control was at levels comparable to that of a standard commercial chemical nematicide. The results indicated that the wettable powder formulation product of P. chlororaphis O6 can be used for control of plant microbial pathogens and root-knot nematodes.
The formulation of biocontrol microbes is a key design element in strategies against plant diseases caused by microbes and pests such as nematodes. Products containing Bacillus sp. are commercialized world-wide as alternatives for chemical pesticides or as a component of integrated pest management programs. These effectively limit plant disease (Schisler et al., 2004) and afford insect control (Burges, 1998). However, formulations of gram-negative control agents are less utilized, in part because, unlike the Bacillus isolates, they do not form spores that prolong the effective shelf life of products. Existing pseudomonad products control damping-off in cotton (Ardakani et al., 2010; Samavat et al., 2014), Fusarium wilt in tomato (Manikandan et al., 2010), dirty panicle disease in rice (Prathuangwong et al., 2013), and Fusarium wilt and spiral nematode (Helicotylenchus muticinctus) in banana (Selvaraj et al., 2014). The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) registered P. chlororaphis 63-28 as a biological control agent for root rot and wilt diseases and P. chlororaphis TX-1 for the control of several turf-grass diseases (http://www.epa.gov).
Root-knot nematodes (Meloidogyne spp.) are obligate plant pathogenic parasites that cause severe economic losses world-wide (Jones et al., 2013). Various species of the Meloidogyne genus cause damage to crops, as they colonize roots and form galls (Rich et al., 2009). Tomatoes, cucumbers, peppers, cabbages, sweet potatoes, and melons are among the crops that are affected by root-knot nematodes (Jones et al., 2013). Consequently, control of nematodes is needed to limit crop damage (Moens et al., 2009). Current commercial products include chemical-based nematicidal products such as Oxycom™, which induces tolerance of crops to root-knot nematodes (Anwar et al., 2003), and synthetic non-fumigant chemicals, such as ilmicyafos (Wada et al., 2011). Soil sterilization by solarization or methyl bromide application (Abawi and Widmer, 2000) has limited use, because of the non-target toxicity, high cost effectiveness, and long term ecological problems with application (Abawi and Widmer, 2000). Microbial bioproducts, such as oxalic acid from Aspergillus niger F22 (Jang et al., 2016), and organic acids (Seo and Kim, 2014), are formulated into other more environmentally friendly treatments.
The biological control of root-knot nematodes has attracted much interest as an alternative to chemical methods of control. Recently formulated bioproducts include Paecilomyces lilacinus, neem cake, Pseudomonas fluorescens, and Pochonia chlamydosporia; they provide nematode control comparable to the chemical nematicide, carbofuran (Saha and Khan, 2016). Other potential biocontrol microbes include spore-forming Gram-positive Bacillus (Chinheya et al., 2017; Radwan et al., 2012; Rao et al., 2017) and Streptomyces isolates (Oh et al., 2016; Ruanpanun et al., 2011; Zeng et al., 2013). Fungal isolates, such as Trichoderma harzianum (Radwan et al., 2012; Sahebani and Hadavi, 2008) and A. niger (Jang et al., 2016), also are effective control agents.
The potential for nematode control is displayed by Gramnegative bacteria, such as Pseudomonas isolates (Lee et al., 2011; Siddiqui et al., 2006; Thiyagarajan and Kuppusamy, 2014) and chitinolytic bacteria (Ha et al., 2014). The production of hydrogen cyanide (HCN) is highly correlated with the biocontrol of nematodes (Kang et al., 2018; Lee et al., 2011; Nandi et al., 2015; Siddiqui et al., 2006; Thiyagarajan and Kuppusamy, 2014). Larval growth and root-knot symptom formation are effectively controlled in tomatoes treated with the root-colonizing strain Pseudomonas chlororaphis, strain O6 (Lee et al., 2011). A P. chlororaphis O6 mutant lacking HCN production displays reduced biocontrol potential against root-knot nematodes (Kang et al., 2018). However, to date, no formulations of the Pseudomonas strain have been developed for control of the root-knot nematodes.
The objective of this study was to develop a wet-table powder (WP) of P. chlororaphis O6. This microbe was selected because it also protects plants against an array of microbial pathogens, through the synthesis an array of different pesticidal compounds that affect the pathogen directly, or through the activation of induced systemic resistance in the plant (Anderson and Kim, 2018). We assessed the efficacy of the formulation in maintaining the viability of P. chlororaphis O6 cells. We also examined whether the wettable powder was efficacious against foliar fungal pathogens. Further, we examined its control of nematodes in tomato in pot studies, and compared its effect in commercially grown melon to a commercial chemical nematicide. These studies were conducted in greenhouses, where melon was grown in root-knot nematode-infested soils under normal commercial cultivation.
P. chlororaphis strain O6 was isolated from the roots of matured wheat plants grown commercially under dryland farming conditions in Utah, USA (Radtke et al., 1994). Fresh cultures were generated from −80°C deep freezer stocks prepared in 15% sterile glycerol from cells grown on King’s B (KB) (King et al., 1954) agar medium (Difco Inc. Sparks, MD, USA).
For the preparation of the wettable powder formulation, cells from the frozen culture stocks were grown in 50 ml Luria Broth medium for 24 h at 25°C. These cells were further transferred to 1 l of LB broth, incubated at 25°C, and shaken at 150 rpm for 12 h. Subsequently, 1 ml of the culture was transferred to 300 l of a fermentation medium (KMB medium) held in a 500 l pilot fermenter (KoBioTech, Incheon, Korea). The KMB medium contained 20 g of yeast extract, 1 g of K2HPO4, 1.5 g of MgSO4·7H2O, and 45 ml of glycerol/l distilled water. The chemicals used in the preparation of the fermentation medium were obtained from Duksan Pure Chemicals, Ansan, Korea. Cultures were grown for 39 h at 25°C, and shaken at 80 rpm with an aeration rate of 0.3 vvm.
To determine cell density and check for contamination, the fermented cultures were serially diluted with sterile water and spread on KB agar plates. Cells were recovered from the fermenter using a 100 l tubular continuous centrifuge (Hanil Industrial Co., Ltd, Daejeon, Korea). Freeze drying additives comprising 5% skim milk, 7.5% monosodium glutamate, and 0.5% ascorbic acid were added to the pelleted bacterial cells. The mixture was frozen at −45°C for 12 h, before freeze-drying using a F/D 20-kg freeze dryer (PYTFD-20R; ilShin Lab, Seoul, Korea). The temperature was programmed at −20°C for 720 min, −10°C for 720 min, 0°C for 720 min, 10°C for 720 min, and 30°C for 120 min. The lyophilized powder was pulverized using a pulverizer (IKA Co., Königswinter, Germany), and each 10 g of product was mixed with 90 g of diatomaceous earth (EP Minerals, Reno, NV, USA) to generate the wettable powder-type formulation (O6-WP10) for testing. This wettable powder formulation O6-WP10 (registration number-3-5-20, Rural Development Administration, Wanju, Korea) had P. chlororaphis O6 dried cells as the main ingredient, with a minimum guaranteed culturable count of 9.6 × 107 colony forming units (CFU) per gram. No contamination was observed.
To investigate the shelf life and cell culturability of the O6-WP10 formulation, 100 g of the powder was packed and sealed in aluminum packages and stored at 25°C. Samples were removed at one month intervals up to six months, and then at ten months. The powder samples were added to sterile water and serial dilutions were plated onto KB agar to determine the CFUs. The experiment was repeated twice with three different packages.
The culturable cells present in O6-WP10 initially was 5 × 109 cfu/g, but a decrease in this number was observed upon storage of the dry powder in sealed pouches at 25°C. For the first three months, values of more than 109 cfu/g were recorded, and at six months the recovered culturable cell count was approximately 4 × 108 cfu/g (Supplementary Fig. 1). However, the viability of the formulated product was less than 105 cfu/g after ten months of storage at 25°C. These results indicate that the wettable powder formulation O6-WP10 had at shelf life of four to six months at 25°C with > 108 cfu/g.
The biocontrol activity of O6-WP10 was tested in planta against three different foliar plant pathogens, Botrytis cinerea and Phytophthora infestans in tomato, and Colletotrichum coccodes on red pepper. These bioassays were conducted as previously described (Kim et al., 2001). Briefly, plants were grown in vinyl pots in a green-house at 25 ± 5°C for one to four weeks. The plants were sprayed to runoff with different concentrations (50, 10 and 4 g/l) of the O6-WP10 product diluted with Tween® 20 as a wetting agent (0.025%). The O6-WP product kept at 25°C for two months was used to test biocontrol efficacies against plant diseases and root-knot nematodes. The treated plant seedlings were inoculated by foliar spray to run-off with one of the three plant pathogens (3 × 104 sporangia/ml for P. infestans, 5 × 105 spores/ml for B. cinerea, and 3 × 105 spores/ml for C. coccodes) after 24 h of the pre-treatments. Spraying with distilled water and Tween® 20 was used as the negative control. One day after treatment, plants were inoculated by spraying with spore suspensions of each pathogen. The disease index, rated three to seven days after pathogen inoculation, was based on the areas of the infected lesion. The pots were arranged in a randomized complete-block design, with three replicates per treatment, and each replicate consisted of nine plants. The data shown in Fig. 1 are based on three independent studies.
Foliar application of the bioformulated product O6-WP10 at doses from 4 g/l to 50 g/l significantly reduced the symptoms of tomato late blight (P < 0.01) and tomato gray mold (P < 0.05). However, no biocontrol for pepper anthracnose by O6-WP10 was observed (Fig. 1). This result confirmed our previous findings that P. chlororaphis O6 bacterial cultures had biocontrol activity when used directly or indirectly against these tomato diseases (Anderson et al., 2017; Anderson and Kim, 2018; Oh et al., 2013; Park et al., 2011).
Examining the biocontrol of root-knot symptom formations in tomato involved modification of the method described in Lee et al (2011). Tomato seeds were surface sterilized by soaking in 70% ethanol for 30 s, followed by 1% sodium hypochlorite for 10 min. After extensive washing with water, three tomato seeds (Beta Tiny, PPS Seed, Yongin, Korea) were planted into a sterile nursery soil mixture of Bio-Sangto and Vermiculite [125 g/vessel, 7:3 (vol/vol), Seminis Korea Inc., Seoul, Korea] contained in sterile Magenta boxes (77 mm × 77 mm × 97 mm, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA). Seedlings were established in enclosed boxes. The lids were removed after development of the second true leaf of tomato plants, and 5 ml of sterile water was added every two days. These boxes were incubated in chambers with a 16 h light (2,000 lx, 80 μmol photons m−2 s−1) and 8 h darkness cycle at 25 ± 5°C for two weeks.
The preventative and curative potentials of the formulated product on root-knot nematodes were assessed. To evaluate the preventive and curative effects, the bioformulations were applied one week before and one week after the nematode inoculation, respectively. The second-stage (J2) juveniles of the root-knot nematode, M. hapla, were isolated from naturally infested soils at a depth of 0-30 cm from the Subtropical Fruit Experimental Station, Haenam, Jeonnam, Korea (Lee et al., 2011). At least 200 M. hapla J2 juveniles, suspended in 10 ml of sterile water, were applied to each box. To determine the biocontrol efficacy, boxes were drenched with 10 ml of a 10-fold diluted two-day-old bacterial culture of the P. chlororaphis O6 strain, grown in KB broth, or with the O6-WP10 formulation suspended in sterile water at 1, 2, or 5 g/l. As a positive chemical control, the nematicide, Nemakick SL (Kyung Nong Cor., Seoul, Korea; 30% Imicyafos as an active ingredient, standard dose 0.25 ml/l) was applied. Plants were drenched with sterile water as a negative control. The boxes were returned to the growth chamber and after one month, the plant masses were measured and the roots were collected. The numbers of root-knot galls/root were counted. This experiment was conducted three times, with three replicates, each with three plants, per treatment.
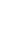
The biocontrol from all tested doses of the O6-WP10 on root-knot nematode infestations of tomato in pot cultures was observed to be similar to that from applications of a 10-fold diluted fresh bacterial culture of P. chlororaphis O6 (Fig. 2). Fresh weights of the tomato roots were lower when plants were infested with nematodes. The root weight was restored to the original level in plants grown without nematodes, and when infested plants were treated with the wettable powder. The gall number/plant was consistently reduced by all doses of the O6-WP10 formulation as effectively as the application of freshly cultured P. chlororaphis O6 cells. These results indicate that the O6-WP10 formulation also had a preventive effect against root-knot nematode in tomato.
When the biological treatments were applied after nematode inoculation, specifically to assess curative potential, there was no effect on fresh root weight (Fig. 3). The chemical pesticide Imicyafos reduced the fresh root weight (Fig. 3) suggesting a negative effect in tomato seedling growth. Reduction in gall numbers was equivalent to that achieved by applications of fresh culture cells of P. chlororaphis O6. The application of O6-WP10 at 2 g/l also provided protection, but at a lower level.
To test the efficacy of the P. chlororaphis O6 formulation against root-knot nematode, a field trial of melon grown in commercial greenhouses was conducted in 2015. Because these greenhouses were a commercial enterprise, it was not possible to have a greenhouse without treatments. Three greenhouses, each with an area of 660 m2, were used, and each greenhouse was planted with 1,400 melon seedlings. Each greenhouse had soils with the same chemical and physical properties of a sandy loam (Supplementary Table 1). The powdery mildew resistant variety of melon, ‘EarlsElite’ (Syngenta Korea, Seoul, Korea), was transplanted into the greenhouses on July 1, 2015. Cultivation practices recommended by the Rural Development Administration (RDA, Wanju, Korea) were followed. In the previous year, 30-40% of this melon cultivar when grown in the same soils within the greenhouses was infested with root-knot nematode. This infection rate occurred in spite of the 2014 application of the chemical nematicide Fosthazate GR (active ingredient 5%, 3.5 kg/660 m2) one week prior to transplanting.
In 2015, O6-WP10 at 2 g/l was applied through a drip irrigation system at four different times, 2, 20, 40, and 55 days after transplantation (DAT) of melon, in two of the greenhouses. Fosthiazate GR was applied once in the third greenhouse by dispersal at the recommended rate one week prior to melon transplantation. The nematode density and growth of the melon plants were determined just prior to germination and at 20, 40, 55, and 70 DAT. To determine the nematode populations, soil (300 g) was collected at a radius of 20 cm and 10-20 cm in depth from around the melon plants, with 10 sampling sites per greenhouse. The nematode density was assessed under a stereomicroscope (Leica KL200 LED, Leica, Buffalo, NY, USA) using a Baermann funnel (Southey, 1986). Soils in all three greenhouses had nematodes at the time of transplantation (Fig. 4). The numbers of nematodes declined with time in each greenhouse. At 55 and 70 DAT, there was a statistically significant lower nematode count in the soils from the greenhouse treated with the bacterial formulation (Fig. 4).
The growth of the melons was measured as plant height and stem diameter for 50 plants per greenhouse, randomly selected at the defined DAT. The plant height was measured from the base of the plant to the axil of the youngest leaf, and was expressed in cm. The stem diameter at 5 cm from the base of each plant was measured using a digital caliper. These data are shown in Table 1. The findings illustrate that treatment with the formulation in both greenhouses statistically improved plant growth compared to in the chemical-treated greenhouse, at 70 DAT for height and 55 DAT for stem diameter. There was no evidence of reduced growth in the O6-WP10-treated greenhouses at any sampling time. The numbers of melons marketed were higher for both greenhouses treated with the formulation in 2015 compared to 2014 (Table 1). In contrast, the number of melon was similar in 2015 and 2014 for the greenhouse treated with Fosthiazate GR.
These results show that the formulation of wettable powder O6-WP10 controlled both foliar pathogens in tomato as well as root-knot nematodes under lab and field soil conditions. These findings confirm the efficacy of P. chlororaphis isolates as broad- spectrum biocontrol agents (Anderson and Kim, 2018). Effective root-knot and pathogen biocontrol likely involves the production of HCN (Gallagher and Manoil, 2001; Knowles and Bunch, 1986; Siddiqui et al., 2006; Voisard et al., 1989). HCN and pyrrolnitrin, produced by P. chlororaphis PA23, have been cited as nematode repellents and contributing to fast- and slow-killing of the model nematode, Caenorhabditis elegans (Nandi et al., 2015). Adding glycine to the product or fermentation medium may provide a greater root-knot nematode control efficacy, because this amino acid is a precursor of HCN (Castric, 1977; Lee et al., 2011; Wissing, 1974). The production of biocontrol-related metabolites is regulated by nutrient composition (Duffy and Défago, 1999); in P. chlororaphis O6, glucose in the growth medium reduced pyrrolnitrin production while promoting the synthesis of other antibiotics, such as phenazines (Park et al., 2011). We are currently investigating the effects of different carbon and nitrogen sources, as well as C/N ratio on the biocontrol efficacy of the bioformulated product from P. chlororaphis O6.
In addition to direct control of the root-knot nematode, induction of systemic resistance may also be involved. Many microbial metabolites induce systemic resistance in plants against root-knot nematodes through a salicylic acid-independent pathway (Anita et al., 2004; Choudhary et al., 2007; Siddiqui and Shaukat, 2004). DL-β-Amino-n-butyric acid and jasmonate applications have been reported to induce systemic and local resistance to root-knot nematodes in rice and tomato (Nahar et al., 2011; Oka et al., 1999; Siddiqui and Shaukat, 2004). Root colonization and microbial metabolites, such as phenazines and pyrrolnitrin from P. chlororaphis O6, have also been found to induce systemic resistance against plant diseases and abiotic stresses (Cho et al., 2008, 2012; Han et al., 2006; Kang et al., 2007; Ryu et al., 2007) and, thus, also may contribute to nematode control. The induction of microbial defense by P. chlororaphis O6 is dependent on a ethylene pathway, but is salicylic acid-independent (Spencer et al., 2003).
Unlike the chemical nematicide, Fosthiazate GR, an advantage of biopesticides is their possible use during crop cultivation. More studies are needed to optimize the dose and timing of applications of O6-WP10. Commercial microbial biopesticide formulations must be easy to distribute, inexpensive to produce, and have a long shelf life (Melin et al., 2007). The wettable-powder formulation of O6-WP10, when packaged dry in sealed packages, is easy to transport, and in this formulation it retained effective cell viability for more than three-months. The use of freeze-drying in the preparation of the wettable-powder bioformulation has been shown to be successful in preserving other culturable bacteria (Burges, 1998). The advantages of freeze-dried formulations are minimal contamination, compaction of the product to a small size, long shelf life for bacterial culturability, and easy preparation of suspensions in water before application (Burges, 1998). The formulated product is appropriate for organic farming and integrated pest management programs. The cost effectiveness of the O6-WP10, however, needs to be determined.
In summary, a bioformulated wettable powder, containing cells of P. chlororaphis O6, and its metabolites, conferred protection against microbial diseases and root-knot nematode infestations. Nematode control was observed in melons grown in infested soils in commercial greenhouses as well as in tomatoes grown in pots. However, the greenhouse studies suggested that a combination of treatments will be needed to alleviate the negative consequences in soil heavily infested with root-knot nematodes. For “ecofriendly” control, we suggest that the application of a bioformulated product, such as O6-WP10, could be combined with a nematicidal plant extract.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Korea Institute of Planning and Evaluation for Technology in Food, Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (IPET) through the Agri-Bio Industry Technology Development Program, funded by the Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs (grant no. 314084-3).
Fig. 1
In planta biocontrol efficacies of the formulated Pseudomonas chlororaphis O6 wettable-powder (O6-WP10) against three foliar vegetable diseases. The O6-WP10 product was suspended with Tween® 20 as a wetting agent (0.025%) at 50 g/l (O6-WP10-50), 10 g/l (O6-WP10-100), or 4 g/l (O6-WP10-250) prior to application. TGM, tomato gray mold; TLB, tomato late blight; and PAN, pepper anthracnose. Data are means ± standard deviations of three independent experiments with nine plants/treatment. Bars with different letters for each pathosystem showed significantly different (P < 0.05 or P < 0.01) levels of disease based on Duncan’s multiple range test.

Fig. 2
In vitro control of root-knot nematodes in pot-grown tomato seedlings by a wettable-powder bioformulation of Pseudomonas chlororaphis O6 (O6-WP10). Treatments one week before the nematode inoculation were as described in the text. The study was conducted with three replicates per treatment, with three tomato plants for each treatment. Different letters within a column represent significant differences at the 0.05 probability level according to Duncan’s multiple range test.
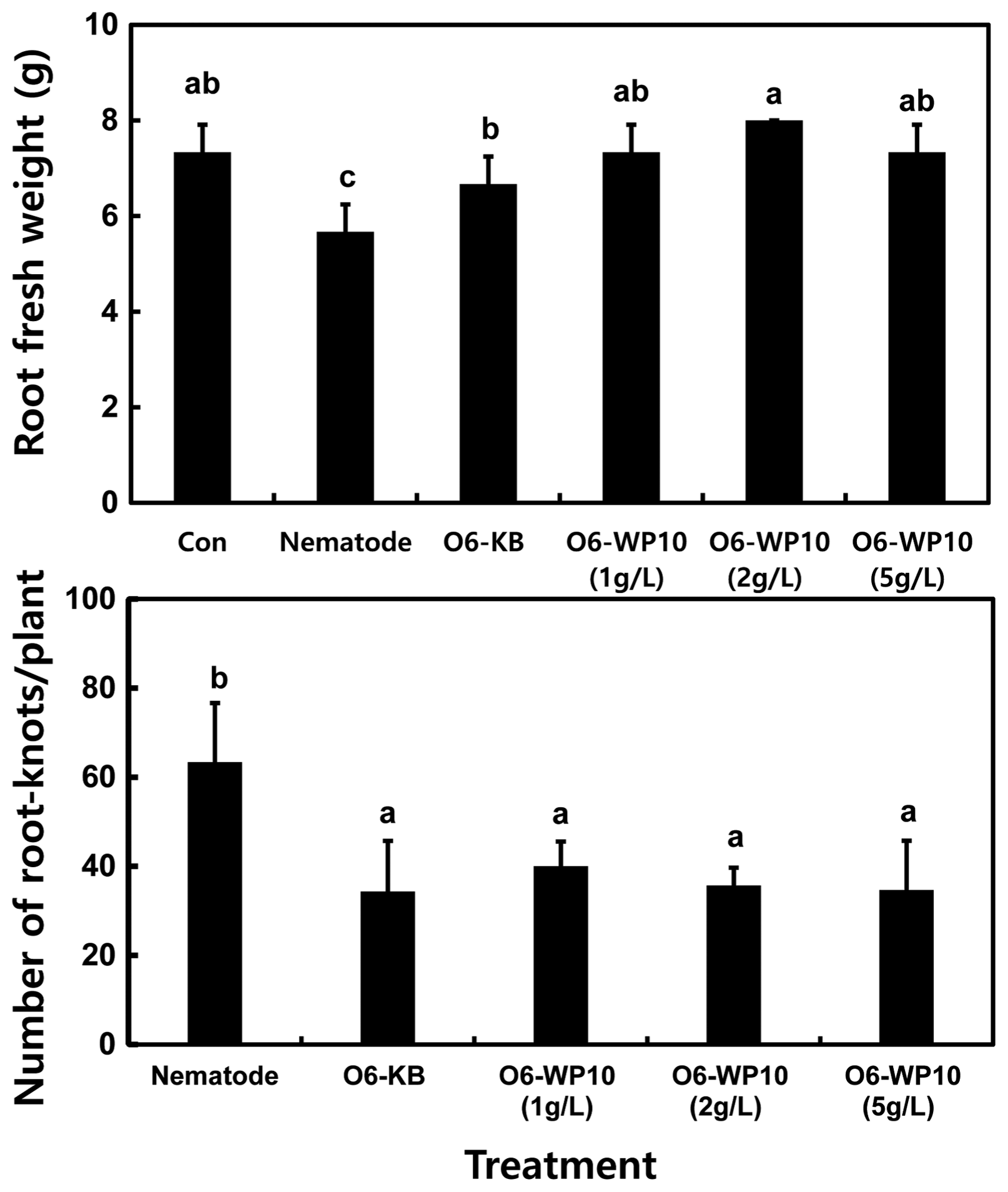
Fig. 3
Curative effects for root-knot nematode in pot grown tomato. Treatments were as described in the text. The chemical nematicide, Imicyafos at 5 ml/20 l was applied as a positive treatment. The study was conducted with three replicates per treatment, with three tomato plants per treatment. Different letters within a column represent significant differences at the 0.05 probability level according to Duncan’s multiple range test.
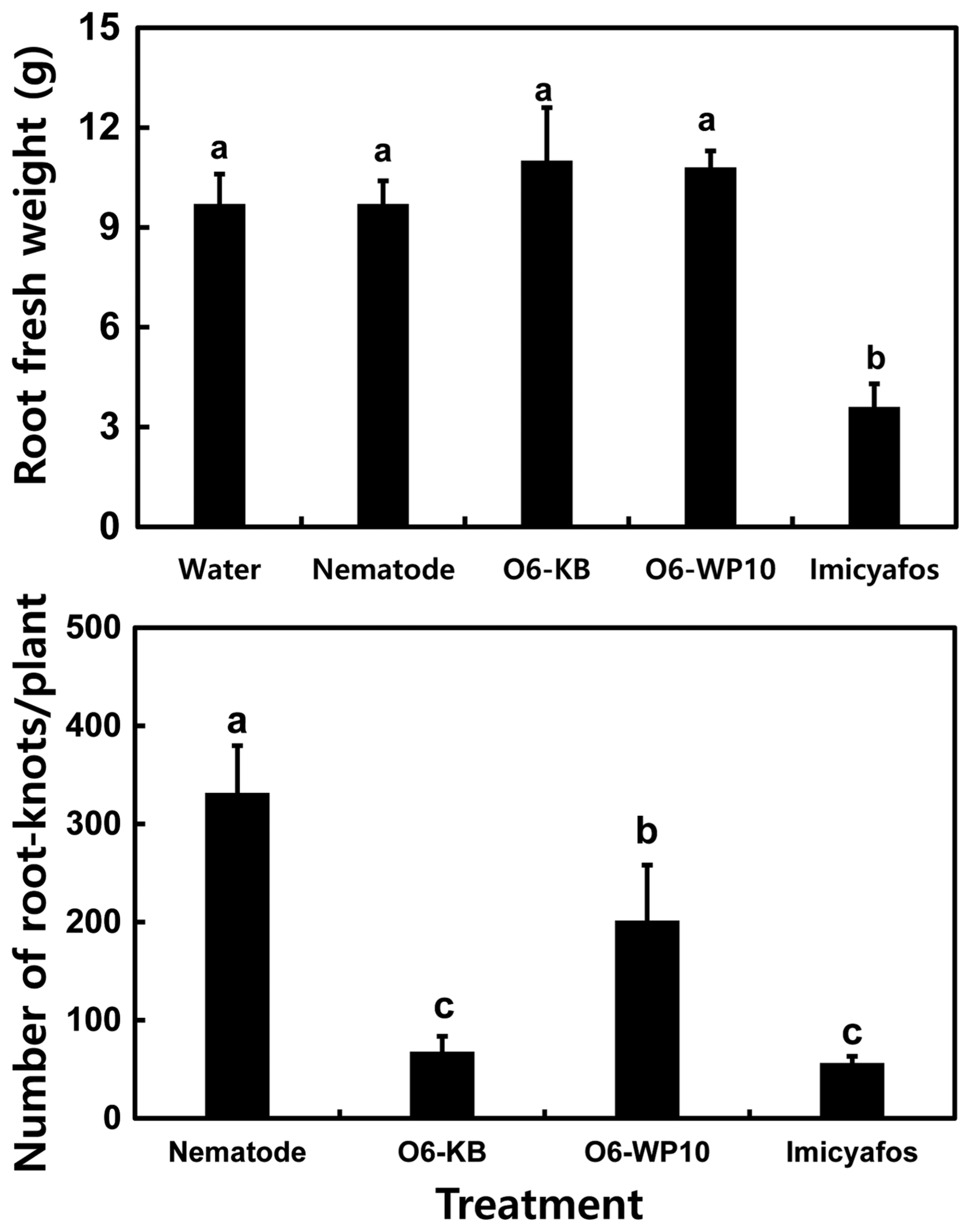
Fig. 4
Control efficacy of the Pseudomonas chlororaphis O6 wettable-powder (O6-WP10) against natural infestations of root-knot nematode in melon. Greenhouses 1 and 2 were treated with O6-WP10 (2 g/l at 2, 20, 40, and 55 DAT) whereas Fosthiazate GR, a chemical pesticide, was applied to Greenhouse 3. Soil samples were collected prior to transplantation and at 20, 40, 55, and 70 DAT, and nematode density was determined. The data are expressed as the means and standard deviations of three replicates per time point. Different letters within a column represent significant differences at the 0.05 probability level according to Duncan’s multiple range test.
Table 1
Effects of the formulated product O6-WP10 on melon growth in commercial cultivation greenhouses heavily infected with root-knot nematodes in Gokseong, Korea in 2015a
| Melon growth parameters at days after transplantation (d)b | Greenhouse 1 treated with O6-WP10 | Greenhouse 2 treated with O6-WP10 | Greenhouse 3 treated with Fosthiazate GR |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plant height (cm) | |||
| 20 | 13.7 ± 1.5 a | 12.7 ± 0.6 a | 12.8 ± 0.8 a |
| 40 | 131.0 ± 5.6 a | 124.7 ± 7.2 a | 121.3 ± 14.0 a |
| 55 | 137.7 ± 2.5 a | 135.0 ± 6.1 a | 132.0 ± 7.8 a |
| 70 | 146.7 ± 2.9 a | 143.3 ± 5.8 a | 131.7 ± 7.6 b |
| Main stem diameter (mm) | |||
| 20 | 6.4 ± 0.4 a | 5.7 ± 0.6 a | 6.4 ± 0.4 a |
| 40 | 11.3 ± 1.2 a | 11.0 ± 0.7 a | 10.7 ± 1.5 a |
| 55 | 11.3 ± 0.6 ab | 11.7 ± 0.6 a | 10.3 ± 0.6 b |
| 70 | 11.7 ± 0.6 a | 11.7 ± 0.6 a | 10.7 ± 0.6 a |
| Total number of harvested fruit (2015/2014) | 1,000/800 | 1,240/1,000 | 1,000/960 |
a Two greenhouses were treated in 2015 with O6-WP10, whereas the third was treated with the nematicide, Fosthiazate GR.
b Plant height and stem diameter were measured at the defined days after transplantation. The total harvested number of melons was compared in between 2015 and 2014 in the same greenhouses. The growth data are presented as the means and standard deviations of three replicates, with 50 randomly selected plants at each time point. Different letters within a column represent significant differences at the 0.05 probability level according to Duncan’s multiple range test.
References
Abawi, GS and Widmer, TL 2000. Impact of soil health management practices on soilborne pathogens, nematodes and root diseases of vegetable crops. Appl Soil Ecol. 15:37-47.

Anderson, AJ and Kim, YC 2018. Biopesticides produced by plant-probiotic Pseudomonas chlororaphis isolates. Crop Prot. 105:62-69.

Anderson, AJ, Kang, BR and Kim, YC 2017. The Gac/Rsm signaling pathway of a biocontrol bacterium, Pseudomonas chlororaphis O6. Res Plant Dis. 23:212-227.

Anita, B, Rajendran, G and Samiyappan, R 2004. Induction of systemic resistance in tomato against root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne incognita by Pseudomonas fluorescens. Nematol Mediterr. 32:47-51.
Anwar, SA, McKenry, MV, Yang, KY and Anderson, AJ 2003. Induction of tolerance to root-knot nematode by oxycom. J Nematol. 35:306-313.


Ardakani, SS, Heydari, A, Khorasani, N and Arjmandi, R 2010. Development of new bioformulations of Pseudomonas fluorescens and evaluation of these products against dampingoff of cotton seedlings. J Plant Pathol. 92:83-88.
Burges, HD 1998. In: Formulation of microbial pesticides: beneficial microorganisms, nematodes and seed treatments, eds. by HD Burges, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, Nederlands.
Castric, PA 1977. Glycine metabolism by Pseudomonas aeruginosa: hydrogen cyanide biosynthesis. J Bacteriol. 130:826-831.



Chinheya, CC, Yobo, KS and Laing, MD 2017. Biological control of the root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne javanica (Chitwood) using Bacillus isolates, on soybean. Biol Control. 109:37-41.

Cho, SM, Kang, BR, Kim, JJ and Kim, YC 2012. Induced systemic drought and salt tolerance by Pseudomonas chlororaphis O6 root colonization is mediated by ABA-independent stomatal closure. Plant Pathol J. 28:202-206.

Cho, SM, Kang, BR, Han, SH, Anderson, AJ, Park, JY, Lee, YH, Cho, BH, Yang, KY, Ryu, CM and Kirn, YC 2008. 2R,3R-butanediol, a bacterial volatile produced by Pseudomonas chlororaphis O6, is involved in induction of systemic tolerance to drought in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact. 21:1067-1075.


Choudhary, DK, Prakash, A and Johri, BN 2007. Induced systemic resistance (ISR) in plants: mechanism of action. Indian J Microbiol. 47:289-297.


Duffy, BK and Défago, G 1999. Environmental factors modulating antibiotic and siderophore biosynthesis by Pseudomonas fluorescens biocontrol strains. Appl Environ Microbol. 65:2429-2438.

Gallagher, LA and Manoil, C 2001. Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 kills Caenorhabditis elegans by cyanide poisoning. J Bacteriol. 183:6207-6214.



Ha, WJ, Kim, YC, Jung, H and Park, SK 2014. Control of the root-knot nematode (Meloidogyne spp.) on cucumber by a liquid bio-formulation containing chitinolytic bacteria, chitin and their products. Res Plant Dis. 20:112-118.

Han, SH, Lee, SJ, Moon, JH, Park, KH, Yang, KY, Cho, BH, Kim, KY, Kim, YW, Lee, MC, Anderson, AJ and Kim, YC 2006. GacS-dependent production of 2R, 3R-butanediol by Pseudomonas chlororaphis O6 is a major determinant for eliciting systemic resistance against Erwinia carotovora but not against Pseudomonas syringae pv. tabaci in tobacco. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact. 19:924-930.


Jang, JY, Choi, YH, Shin, TS, Kim, TH, Shin, K-S, Park, HW, Kim, YH, Kim, H, Choi, GJ and Jang, KS 2016. Biological control of Meloidogyne incognita by Aspergillus niger F22 producing oxalic acid. PLoS One. 11:e0156230



Jones, JT, Haegeman, A, Danchin, EG, Gaur, HS, Helder, J, Jones, MG, Kikuchi, T, Manzanilla-Lopez, R, Palomares-Rius, JE, Wesemael, WM and Perry, RN 2013. Top 10 plant-parasitic nematodes in molecular plant pathology. Mol Plant Pathol. 14:946-961.



Kang, BR, Anderson, AJ and Kim, YC 2018. Hydrogen cyanide produced by Pseudomonas chlororaphis O6 exhibits nematicidal activity against Meloidogyne hapla. Plant Pathol J. 34:35-43.



Kang, BR, Han, S-H, Zdor, RE, Anderson, AJ, Spencer, M, Yang, KY, Kim, YH, Lee, MC, Cho, BH and Kim, YC 2007. Inhibition of seed germination and induction of systemic disease resistance by Pseudomonas chlororaphis O6 requires phenazine production regulated by the global regulator, GacS. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 17:586-593.

Kim, JC, Choi, GJ, Park, JH, Kim, HT and Cho, KY 2001. Activity against plant pathogenic fungi of phomalactone isolated from Nigrospora sphaerica. Pest Manag Sci. 57:554-559.


King, EO, Ward, M and Raney, D 1954. Two simple media for the demonstration of pyocyanin and fluorescein. J Lab Clin Med. 44:301-307.

Lee, JH, Ma, KC, Ko, SJ, Kang, BR, Kim, IS and Kim, YC 2011. Nematicidal activity of a nonpathogenic biocontrol bacterium, Pseudomonas chlororaphis O6. Curr Microbiol. 62:746-751.


Manikandan, R, Saravanakumar, D, Rajendran, L, Raguchander, T and Samiyappan, R 2010. Standardization of liquid formulation of Pseudomonas fluorescens Pf1 for its efficacy against Fusarium wilt of tomato. Biol Control. 54:83-89.

Melin, P, Hakansson, S and Schnurer, J 2007. Optimisation and comparison of liquid and dry formulations of the biocontrol yeast Pichia anomala J121. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 73:1008-1016.


Moens, M, Perry, RN and Starr, JL 2009. Meloidogyne species-a diverse group of novel and important plant parasites. In: Root-knot nematodes, 1:eds. by RN Perry, M Moens and JL Starr, 1-17. CABI Publishing, Wallingford, UK.

Nahar, K, Kyndt, T, De Vleesschauwer, D, Höfte, M and Gheysen, G 2011. The jasmonate pathway is a key player in systemically induced defense against root knot nematodes in rice. Plant Physiol. 157:305-316.



Nandi, M, Selin, C, Brassinga, AKC, Belmonte, MF, Fernando, WD, Loewen, PC and De Kievit, TR 2015. Pyrrolnitrin and hydrogen cyanide production by Pseudomonas chlororaphis strain PA23 exhibits nematicidal and repellent activity against Caenorhabditis elegans. PLoS One. 10:e0123184



Oh, M, Han, JW, Choi, JS, Choi, YH, Jang, KS, Choi, GJ and Kim, H 2016. Nematicidal activity of Streptomyces flavogriseus KRA15-528 to Meloidogyne incognita. Res Plant Dis. 22:227-235.

Oh, SA, Kim, JS, Han, SH, Park, JY, Dimkpa, C, Edlund, C, Anderson, AJ and Kim, YC 2013. The GacS-regulated sigma factor RpoS governs production of several factors involved in biocontrol activity of the rhizobacterium Pseudomonas chlororaphis O6. Can J Microbiol. 59:556-562.


Oka, Y, Cohen, Y and Spiegel, Y 1999. Local and systemic induced resistance to the root-knot nematode in tomato by DL-β-amino-n-butyric acid. Phytopathology. 89:1138-1143.


Park, JY, Oh, SA, Anderson, AJ, Neiswender, J, Kim, JC and Kim, YC 2011. Production of the antifungal compounds phenazine and pyrrolnitrin from Pseudomonas chlororaphis O6 is differentially regulated by glucose. Lett Appl Microbiol. 52:532-537.


Prathuangwong, S, Athinuwat, D, Chuaboon, W, Chatnaparat, T and Buensanteai, N 2013. Bioformulation Pseudomonas fluorescens SP007s against dirty panicle disease of rice. Afr J Microbiol Res. 7:5274-5283.

Radtke, C, Cook, WS and Anderson, A 1994. Factors affecting antagonism of the growth of Phanerochaete chrysosporium by bacteria isolated from soils. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 41:274-280.

Radwan, MA, Farrag, SAA, Abu-Elamayem, MM and Ahmed, NS 2012. Biological control of the root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne incognita on tomato using bioproducts of microbial origin. Appl Soil Ecol. 56:58-62.

Rao, MS, Kamalnath, M, Umamaheswari, R, Rajinikanth, R, Prabu, P, Priti, K, Grace, GN, Chaya, MK and Gopalakrishnan, C 2017. Bacillus subtilis IIHR BS-2 enriched vermicompost controls root knot nematode and soft rot disease complex in carrot. Sci Hortic. 218:56-62.

Rich, JR, Brito, JA, Kaur, R and Ferrell, JA 2009. Weed species as hosts of Meloidogyne: a review. Nematropica. 39:157-185.
Ruanpanun, P, Laatsch, H, Tangchitsomkid, N and Lumyong, S 2011. Nematicidal activity of fervenulin isolated from a nematicidal actinomycete, Streptomyces sp. CMU-MH021, on Meloidogyne incognita. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 27:1373-1380.


Ryu, CM, Kang, BR, Han, SH, Cho, SM, Kloepper, JW, Anderson, AJ and Kim, YC 2007. Tobacco cultivars vary in induction of systemic resistance against Cucumber mosaic virus and growth promotion by Pseudomonas chlororaphis O6 and its gacS mutant. Eur J Plant Pathol. 119:383-390.

Saha, T and Khan, MR 2016. Evaluation of bioformulations for management of root knot nematode (Meloidogyne incognita) infecting tuberose. Pak J Zool. 48:651-656.
Sahebani, N and Hadavi, N 2008. Biological control of the root-knot nematode Meloidogyne javanica by Trichoderma harzianum. Soil Biol Biochem. 40:2016-2020.

Samavat, S, Heydari, A, Zamanizadeh Hamid, R, Rezaee, S and Aliabadi Ali, A 2014. Application of new bioformulations of Pseudomonas aureofaciens for biocontrol of cotton seedling damping-off. J Plant Prot Res. 54:334-339.

Schisler, DA, Slininger, PJ, Behle, RW and Jackson, MA 2004. Formulation of Bacillus spp. for biological control of plant diseases. Phytopathology. 94:1267-1271.


Selvaraj, S, Ganeshamoorthi, P, Anand, T, Raguchander, T, Seenivasan, N and Samiyappan, R 2014. Evaluation of a liquid formulation of Pseudomonas fluorescens against Fusarium oxysporum f. sp cubense and Helicotylenchus multicinctus in banana plantation. BioControl. 59:345-355.

Seo, Y and Kim, YH 2014. Control of Meloidogyne incognita using mixtures of organic acids. Plant Pathol J. 30:450-455.



Siddiqui, IA and Shaukat, SS 2004. Systemic resistance in tomato induced by biocontrol bacteria against the root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne javanica is independent of salicylic acid production. J Phytopathol. 152:48-54.

Siddiqui, IA, Shaukat, SS, Sheikh, IH and Khan, A 2006. Role of cyanide production by Pseudomonas fluorescens CHA0 in the suppression of root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne javanica in tomato. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 22:641-650.

Southey, JF 1986. Laboratory methods for work with plant and soil nematodes. H.M.S.O. Books, Norfolk, UK.
Spencer, M, Ryu, CM, Yang, KY, Kim, YC, Kloepper, JW and Anderson, AJ 2003. Induced defence in tobacco by Pseudomonas chlororaphis strain O6 involves at least the ethylene pathway. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol. 63:27-34.

Thiyagarajan, SS and Kuppusamy, H 2014. Biological control of root knot nematodes in chillies through Pseudomonas fluorescens’s antagonistic mechanism. J Plant Sci. 2:152-158.

Voisard, C, Keel, C, Haas, D and Dèfago, G 1989. Cyanide production by Pseudomonas fluorescens helps suppress black root rot of tobacco under gnotobiotic conditions. EMBO J. 8:351-358.



Wada, S, Toyota, K and Takada, A 2011. Effects of the nematicide imicyafos on soil nematode community structure and damage to radish caused by Pratylenchus penetrans. J Nematol. 43:1-6.





 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Full text via PMC
Full text via PMC Download Citation
Download Citation Supplement
Supplement Print
Print