 |
 |
| Plant Pathol J > Volume 35(1); 2019 > Article |
Abstract
A great variable response was observed when PP-3 and PP-J encumbered with 116 populations of root knot nematode (RKN) at two different temperatures (25 ┬▒ 2┬░C and 30 ┬▒ 2┬░C) and concentrations (104 and 105 spores/ml). The PCR reaction amplified intergenic region between cytochrome oxidase subunit II gene (COII) and large subunit of rRNA gene (lrRNA) of the mitochondrial genome of different RKN species. The primer C2F3 and 1108 identified M. incognita with the highest frequency (52.6%) followed by M. javanica (36.8%) and M. arenaria (10.5%). The sizes of PCR products were 1.7 kb for M. incognita and M. javanica populations while populations of M. arenaria produced 1.1 kb fragment. The digestion with Hinf I yielded three different fragment length patterns on 1.5 % agarose gel. From current research it is concluded that intra-Meloidogyne genetic variability exist in RKN populations which have better encumbrance with P. penetrans.
Pasteuria penetrans has potential for its development as a biological control agent of economically important root knot nematodes (Sayre and Starr, 1985). These hyperparasites start their infection by adhering to the cuticle of infective juveniles (J2s), then penetrate the body wall to enter the host root, usually after the nematode has set up a feeding site (Chen et al., 1997). They either act as restraining the nematode migration toward the roots or by reducing their reproduction (Brown and Smart, 1985; Davies et al., 1988).
Adhesion of spores to the cuticle plays a vital role in the activity of the pathogen when it is used as a biological nematicide (Stirling et al., 1986). Attachment studies of isolates of Pasteuria to different populations and strains of RKN showed a high degree of variation and it is host specific (Davies et al., 1988; Espanol et al., 1997).
This obligate parasitic bacterium exhibits host specificity at two stages in the nematode life cycle; firstly, endospore isolates differ in their ability to encumber the J2s of particular species and strains of root-knot nematodes (Davies, 2005; Davies et al., 2001) and second, endospore populations differ in adhesion to different life stages of the same strain as exemplified by differential attachment to males (Davies and Williamson, 2006).
Identification of RKN is a prerequisite to develop an effective cropping system, resistant cultivars and biocontrol agents (Cenis, 1993). Molecular approaches have made significant contribution to the detection and identification of RKNs (Randig et al., 2002; Ward et al., 2004). Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) based techniques are a strong diagnostic tool for accurate detection of pathogens and have also been widely used for the identification of nematodes (Han et al., 2004; Henson and French, 1993; Martin et al., 2000; Schaad and Frederick, 2002). However, no comprehensive study has been conducted for genetic variability assessment in RKN in Pakistan using molecular tools. Hence, the present study was aimed to in-vitro encumbrance of P. penetrans with different RKN populations at different temperatures and concentrations, and to identify intra-Meloidogyne genetic variability in RKN populations which have better encumbrance with P. penetrans, collected from different ecological regions of Pakistan through PCR-RFLP of an intergenic region between cytochrome oxidase subunit II (COII) and 16S ribosomal mitochondrial genes.
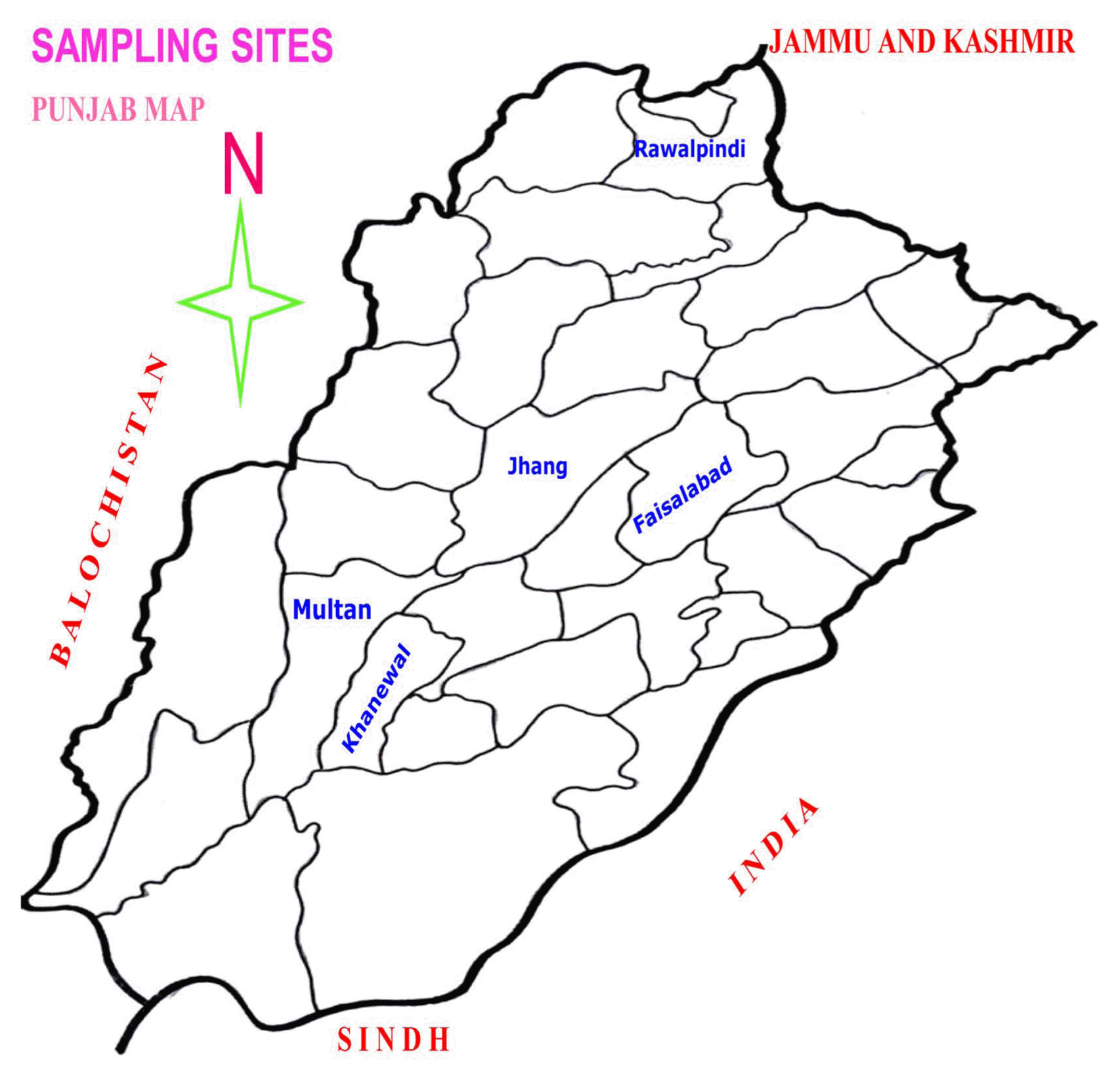
A systematic survey was conducted for a reliable estimation of infestation of root knot nematode major vegetable production area of five Districts of Punjab Province [Faisalabad, Jhang, Khanewal, Multan and Rawalpindi (Fig. 1)]. From each sampling site ten samples were collected at random. Root samples were carefully lifted with trowel up to 15-20 cm depth from the rhizosphere of tomato and cucumber plants together with approximately 1 kg of adhering soil. Samples were put in polythene bags and data on host, locality and soil type etc. was recorded.
A total of 700 samples were collected from two vegetable hosts i.e. tomato and cucumber (350 samples from each host). These samples were transported in Nematology Laboratory of Plant Pathology Department, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad-Pakistan and were stored in refrigerator at 5┬░C (40┬░F) until processing.
A total of 116 populations of RKN (two population/sampling site) were selected for their encumbrance to two isolates of Pasteuria (PP-3 and PP-J). The selection of these populations was made on the basis of RKN incidence in different sampling sites of five District of Punjab, Pakistan on two hosts (tomato and cucumber). During survey 27 out of 35 sampling sites were infested with RKN in case of tomato while in case of cucumber 31 out of 35 sampling sites were infested with RKN, hence 54 RKN populations (27 ├Ś 2 = 54, two RKN populations/sampling site) were selected from tomato and 62 RKN populations (31 ├Ś 2 = 62, two RKN populations/sampling site) were selected from cucumber.
All RKN populations were purified by single egg mass culture and maintained on susceptible tomato cv. Money maker throughout the experiment. Root system bearing egg masses of each Meloidogyne population was washed, cut into pieces and treated with 1% Sodium hypochlorite (to facilitate the release of eggs from egg masses) two days before setting experiment (Hussey and Barker, 1973). The resulting egg suspension was placed in extraction dishes and incubated at 28┬░C for hatching. The newly hatched juveniles were collected after 2 days of incubation period and used in attachment studies.
Dry root powder (100 mg) containing mature endospores of two isolates of Pasteuria (PP-3 and PP-J) were grinded with a pestle and mortar in two ml of water. More water was added and sieved through 38 ╬╝m sieve (Stirling and Wachtel, 1980) and two suspensions of Pasteuria endospores were prepared in water (104 and 105 spores/ml) using Haemocytometer. Dilutions of the suspension were made using the following formula;
One ml of the spore suspension was pipetted to each Petri dish (5 cm in diameter) containing one ml of nematode suspension (50 J2s/ml). To facilitate the counting suspension was diluted by adding one ml of water. Each treatment was replicated ten times, completely randomized and incubated at 25 ┬▒ 2┬░C. Similarly, another set was prepared and incubated at 30 ┬▒ 2┬░C in an incubator.
The Petri dishes were checked after one hour of exposure time and the number of spores attached/J2s on first 10 nematodes was counted under the microscope at 400├Ś magnification. The mean of ten counts was calculated as one observation for each replication. Same procedure was repeated for each nematode population isolated from different hosts.
A total of 19 RKN populations (from tomato and cucumber) were subjected to PCR based analysis of intra-Meloidogyne genetic variability. The populations were selected on the basis of their encumbrance to two isolates of P. penetrans in the in-vitro encumbrance experiments (Table 1). Seventeen RKN populations were selected on the basis of their maximum encumbrance. Two populations which produced minimum encumbrance as compared to all the Meloidogyne populations were also included in the study.
Total genomic DNA was extracted from single J2 using worm lysis buffer (WLB) [50 mM KCl, 10 mM Tris pH 8.3, 2.5 mM MgCl2, 0.45% Tween 20 (Sigma-Aldrich, UK), 0.01% gelatine, 60 ╬╝g/ml proteinase K (Fermentas, USA)]. An individual J2 was placed in 10 ╬╝l of WLB on a sterilized glass microscopic slide, cut into half with sterile micropipette tip, pressed, and lysate was transferred into 0.5 ml PCR tube. The tubes were frozen at ŌłÆ20┬░C for 10 min, incubated at 65┬░C for one hour followed by 95┬░C for 10 min and then immediately placed on ice. An aliquot of 5 ╬╝l of the suspension was used in PCR.
The molecular characterization was conducted following protocol reported by Powers and Harris (1993). A fragment of intergenic region between COII and large subunit of rRNA gene (lr-RNA) of the mitochondrial genome was amplified using forward primer C2F3 (5ŌĆ▓-GGTCAATGTTCAGAAATTTGTGG-3ŌĆ▓) and reverse primer 1108 (5ŌĆ▓-TACCTTTGACCAATCACGCT-3ŌĆ▓). Detailed description of primer design is given in Fig. 2. Polymerase chain reaction was performed in 20 ╬╝l reaction volume in 0.2 ml PCR tubes in a thermal cycler (Mastercycler gradient, Eppendorf Germany). Composition of the reaction mixture and temperature cycles is given in Table 2 and 3, respectively.
The PCR products were resolved on 1.5% agarose gel. In brief, agarose powder was dissolved completely in by sprinkling slowly over the stirring 1├Ś Tris-Borate-EDTA (TBE) buffer and melted completely by heating in microwave oven in short intervals avoiding excessive foam formation and spitting out of the flask. Ethidium bromide was added at 0.5 ╬╝g/ml after cooling the solution to ~60┬░C and the solution was poured into the gel casting tray. After polymerization, the gel was placed in electrophoresis tank. The 6├Ś DNA loading dye was added to the products and 10 ╬╝l of the mixture was pipetted into wells. First and last well of the gels were loaded with 1 kb DNA ladder (Fermentas, USA) for determination of exact size of amplicons. Electrophoresis was performed in 1├Ś TBE buffer at 80 V for 1 h. Gels were visualized and documented using gel documentation system (NYXTECH-NIK, UK).
The PCR products of 1.7 kb in size were further subjected to restriction analysis to discriminate between M. incognita and M. javanica species through digestion with Hinf I enzyme. A 20 ╬╝l restriction reaction was assembled using 10 ╬╝l of amplified product, 7 ╬╝l of nucleases free water, 2 ╬╝l of 10├Ś buffer R [10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.5), 10 mM MgCl2, 100 mM KCl, 0.1 mg/ml BSA] and 1 ╬╝l (10 units) of Hinf I enzyme (Fermentas, USA). Contents were gently mixed, briefly centrifuged and incubated at 60┬░C for two hours. An aliquot of 10 ╬╝l of the restriction mixture was resolved on 1.5% agarose gel, stained with ethidium bromide and visualized through gel documentation system as described above.
A great variable response was observed when PP-3 encumbered with different populations of RKN at two different temperatures (ambient and 30 ┬▒ 2┬░C) and concentrations (104 and 105 spores/ml). The encumbrance level of 54 populations of RKN isolated from tomato varied significantly (Table 4). Interspecific and intraspecfic variability in encumbrance of PP-3 with different populations of RKN was demonstrated. The encumbrance of PP-3 at concentration of 104 spores per ml at ambient temperature was as low as below ten spores attached to different populations of RKN collected from five District of Punjab. Rate of spore attachment at 105 spores per ml was approximately double that at 104 spores/ml (Table 4). At 30 ┬▒ 2┬░C, the encumbrance level also increased in all the RKN populations. The results revealed that with the increase in temperature and spore concentration the mean encumbrance level of Pasteuria with J2 cuticle increased. At least one population of RKN was selected from each District having maximum encumbrance with PP-3. These populations were FSD/T8 (Faisalabad), JNG/T11 (Jhang), KHW/T6 (Khanewal), MUL/T3 (Multan) and RWP/T3 (Rawalpindi).
The same 54 populations of RKN responded differently when encumbered with PP-J isolate of Pasteuria. Its attachment with different populations of RKN at two different temperatures and concentration was almost double than PP-3. The RKN populations which gave maximum encumbrance with PP-J were different from those RKN populations which showed maximum encumbrance with PP-3 (Table 4). Only FSD/T8 (Faisalabad) population showed maximum encumbrance with PP-3 as well as PP-J. The other four populations which gave maximum encumbrance were JNG/T3 (Jhang), KHW/T2 (Khanewal), MUL/T10 (Multan) and RWP/T7 (Rawalpindi).
The encumbrance of 62 populations of RKN also varied with PP-3 at two different temperatures (ambient and 30 ┬▒ 2┬░C) and concentrations (104 and 105 spores per ml). The encumbrance level of PP-3 was maximum at 30 ┬▒ 2┬░C than ambient temperature and spore concentration was also directly related to attachment with nematode cuticle (Table 5). The populations selected on the basis of maximum attachment with PP-3 were FSD/C4 (Faisalabad), JNG/C2 (Jhang), KHW/C9 (Khanewal), MUL/C2 (Multan) and RWP/C10 (Rawalpindi).
A great variability of the number of spores attached to the cuticles of J2 was observed when same 62 populations of RKN were evaluated for encumbrance with PP-J at different temperatures and concentration (Table 5). Two populations showed maximum encumbrance with PP-3 and PP-J were JNG/C2 (Jhang) and MUL/C2 (Multan) while other three populations having maximum encumbrance were FSD/C12 (Faisalabad), KHW/C3 (Khanewal) and RWP/C2 (Rawalpindi). The two RKN populations from cucumber which produced least encumbrance throughout the in-vitro were RWP/C5 (Rawalpindi) and RWP/C6 (Rawalpindi).
The primer set used to amplify intergenic region between CO II and large subunit of rRNA gene (lrRNA) of the mitochondrial genome. It produced single amplicon from each of the 19 samples (Fig. 3). A PCR product of 1.1 kb, expected from M. arenaria species, was obtained from the samples RWP/C5 and RWP/C6 which were chosen on the basis of minimum encumbrance, hence these samples were confirmed as M. arenaria. The seventeen samples, selected on the basis of maximum encumbrance, amplified a product of 1.7 kb related in size expected from M. incognita and M. javanica species (Fig. 3).
The Hinf I restriction analysis of 1.7 kb fragment to differentiate among Meloidogyne species determined single digestion site in samples KHW/T2, RWP/T3, RWP/T7, JNG/C2, KHW/C3, KHW/C9 and MUL/C2, generating two fragments of 1.0 and 0.7 kb (Fig. 4).
These restriction fingerprints related the samples to M. javanica. In rest of 10 samples including FSD/T8, JNG/T3, JNG/T11, KHW/T6, MUL/T3, MUL/T10, FSD/C4, FSD/C12, RWP/C2 and RWP/C10, an additional enzyme digestion site cleaved the 0.7 kb fragment to generate two more fragments of about 0.4 and 0.3 kb (Fig. 4). This restriction pattern related the samples to M. incognita species. In conclusion, M. incognita was found most prevalent in the 19 samples with the highest frequency (52.6%) followed by M. javanica (36.8%) and M. arenaria (10.5%).
Encumbrance of Pasteuria endopsores to the cuticle plays an important role in biological management of root knot nematodes (Channer and Gowen, 1992; Espanol et al., 1997; Stirling, 1984; Stirling et al., 1986; Vagelas et al., 2012; Wishart et al., 2004). Different populations of Pasteuria endospores exhibit different levels of encumbrance to nematode cuticle. These variations have been attributed to differences in the surface composition of different species, races and RKN populations (Davies and Danks, 1992; Davies et al., 2008) and to the heterogenity of the P. penetrans endospore surfaces themselves (Davies et al., 1992). The specificity of endospore encumbrance to J2 cuticle has been studied biochemical and immunological methods. The results showed a high degree of heterogeneity both within and among different populations of P. penetrans (Davies and Redden, 1997; Preston et al., 2003). A carbohydrate-protein mechanism is involved in endospore encumbrance to M. incognita (Davies and Danks, 1993; Persidis et al., 1991) while according to Spiegel et al. (1996) carbohydrate residues, carbohydrate-recognition domains and a 250-kDa antigen on the J2 cuticle of M. javanica were shown to be involved in Pasteuria endospore attachment. According to Davies and Opperman (2006) collagen like proteins on Pasteuria spore core are involved for the adhesion of the endospore to J2 cuticle. These differences in attachment indicated complex interactions between the cuticle of the nematode and the surface of the Pasteuria endospore (Tian et al., 2007).
In current work interspecific and intraspecfic variability in encumbrance was observed with two Pasteuria isolates at different temperatures and concentrations. Temperature is one of several environmental factors that influence the ability of endospore to adhere and to infect Meloidogyne J2 (Hatz and Dickson, 1992). The rate of spore encumbrance to J2 increased with increasing temperature and current results are similar to previous works (Giannakou and Gowen, 2004; Singh and Dhawan, 1990; Stirling et al., 1990; Zareen et al., 2002). Pasteuria penetrans spores attached more readily at 22.5-30┬░C than 15┬░C (Stirling, 1981). However, Giannakou et al. (1997) observed greater attachment at 25 and 30┬░C but the maximum number of endospores was attached at 30┬░C (Ahmed, 1990; Hatz and Dickson, 1992; Orui, 1997). At higher temperature (above 30┬░C) the rate of encumbrance with J2 declined (Hatz and Dickson, 1992). Exposing nematodes to 30┬░C also increased rate of encumbrance. Freitas et al. (1997) pre-exposed M. arenaria J2 in 30┬░C water before exposure to endospores increased J2 receptivity to endospores when compared to treatments at 25┬░C and 35┬░C. The variable encumbrance at different temperatures is due to the fact that it is dependent on nematodesŌĆÖ mobility. At 30┬░C the mobility of nematodes is high while above 35┬░C or below 5┬░C nematodes have little activity (Taylor and Sasser, 1978). ThatŌĆÖs why at these temperatures attachment is decreased. Other reason is that, the bacterium developed more quickly within its host at 30┬░C and 35┬░C than at 25┬░C or below (Hatz and Dickson, 1992).
Encumbrance of Pasteuria endopsores to the J2 cuticle is also dependent on Pasteuria spore densities/concentrations. As the Pasteuria endospores are non-motile and successful encumbrance with J2 cuticle is only achieved when a suitable nematode comes under its vicinity (Chen and Dickson, 1998). The rate of encumbrance to J2 increased approximately five to six times for each 10-fold increase in numbers of Pasteuria endospores in the suspension Hewlett and Dickson (1993). Zareen et al. (2002) reported that encumbrance of Pasteuria endospore to J2 cuticle reduced with increase in dilution factor of spore suspension while Alves et al. (2004) provoked that in order to improve the endospore attachment, endospore concentration of the suspension is more important than to increase the agitation period of the nematodes in the bacterial suspension. Pasteuria endospore concentration in soil is also key factor for its infectivity (Stirling et al., 1990). Endospore densities in soil was positively correlated with percentage of J2 attached and number of spores/J2 (Talavera and Mizukubo, 2003).
The PCR reaction amplified intergenic region between cytochrome oxidase subunit II gene (COII) and large subunit of rRNA gene (lrRNA) of the mitochondrial genome. The primer C2F3 and 1108 identified M. incognita with the highest frequency (52.6%) followed by M. javanica (36.8%) and M. arenaria (10.5%). Heterogeneity in band size was detected in mitochondrial genome of different Meloidogyne species. The sizes of PCR products were 1.7 kb for M. incognita and M. javanica populations while populations of M. arenaria produced 1.1 kb fragment. Therefore, M. arenaria was easily distinguished from M. incognita and M. javanica based on band size of amplified PCR products. No band size variability was detected within species of Meloidogyne. The digestion with Hinf I yielded three different fragment length patterns on 1.5% agarose gel. First, restriction digestion of 1.7 kb M. javanica amplification product determined one enzyme digestion site and resulted in two fragments of 1.0 and 0.7 kb. Second, an additional enzyme digestion site on M. incognita product cleavage the 0.7 kb fragment to generate two more fragments of about 0.4 and 0.3 kb. Third, M. arenaria had no enzyme digestion site by Hinf I digestion.
For precise identification of Meloidogyne species, mitochondrial genome provides good source of genetic markers for identification (Blok et al., 2002; Hu and Glasser, 2006; Hugall et al., 1994; Jeyaprakash et al., 2006). Intraspecfic mitochondrial variation has been observed in a region of multiple nucleotide repeating units in Meloidogyne. Mitochondrial DNA has been applied not only for the identification of Meloidogyne species but also for the molecular differentiation or population genetic study of nematodes (Liu et al., 1999; Szalanski et al., 2000). In the present study intergenic region between cytochrome oxidase subunit II and 16S ribosomal mitochondrial genes have been amplified to determine intra-Meloidogyne genetic variability. The assay successfully differentiated isolates in to three types i.e. M. incognita, M. javanica and M. arenaria based on variation in fragment sizes of the PCR products/their restriction fingerprints. The similar studies have been conducted on characterization of USA (Powers and Harris, 1993) and Korean isolates (Han et al., 2004; Oh et al., 2009) of Meloidogyne species exploiting the same genetic markers. For M. arenaria C2F3/1108 amplified PCR product was of 1.1 kb in USA isolate (Powers and Harris, 1993; Powers et al., 2005) which is of the same size as found in current studies on Pakistani M. arenaria isolates. However, Oh et al. (2009) reported 1.7 kb fragment amplified from Korean M. arenaria isolates. PCR amplification product of Pakistani M. javanica isolates exhibited 1.7 kb product size and on digestion resulted into two band sizes of 1.0 and 0.7 kb which was similar to previous work of Powers and Harris, 1993. However, Hinf I digestion revealed results differing from those of previous study (Oh et al., 2009). Therefore M. incognita, M. javanica and M. arenaria has significant nucleotide variations depending upon different ecological origins.
Fig.┬Ā2
Diagrammatic representation of primer binding sites on the Meloidogyne mitochondrial genome. Primer C2F3 anneals to the coding strand of the cytochrome oxidase subunit II (COII) gene and primer 1108 anneals approximately 450 bp downstream from the start of the lrRNA gene. The intergenic region varies in size among the different Meloidogyne.

Fig.┬Ā3
Gel image of C2F3/1108 amplified PCR product of COII/LrRNA of mitochondrial genome. The 1.7 kb sizes of PCR products are characteristics of M. incognita and M. javanica while M. arenaria produce 1.1 kb fragment size. M lanes were loaded with 1 kb ladder.
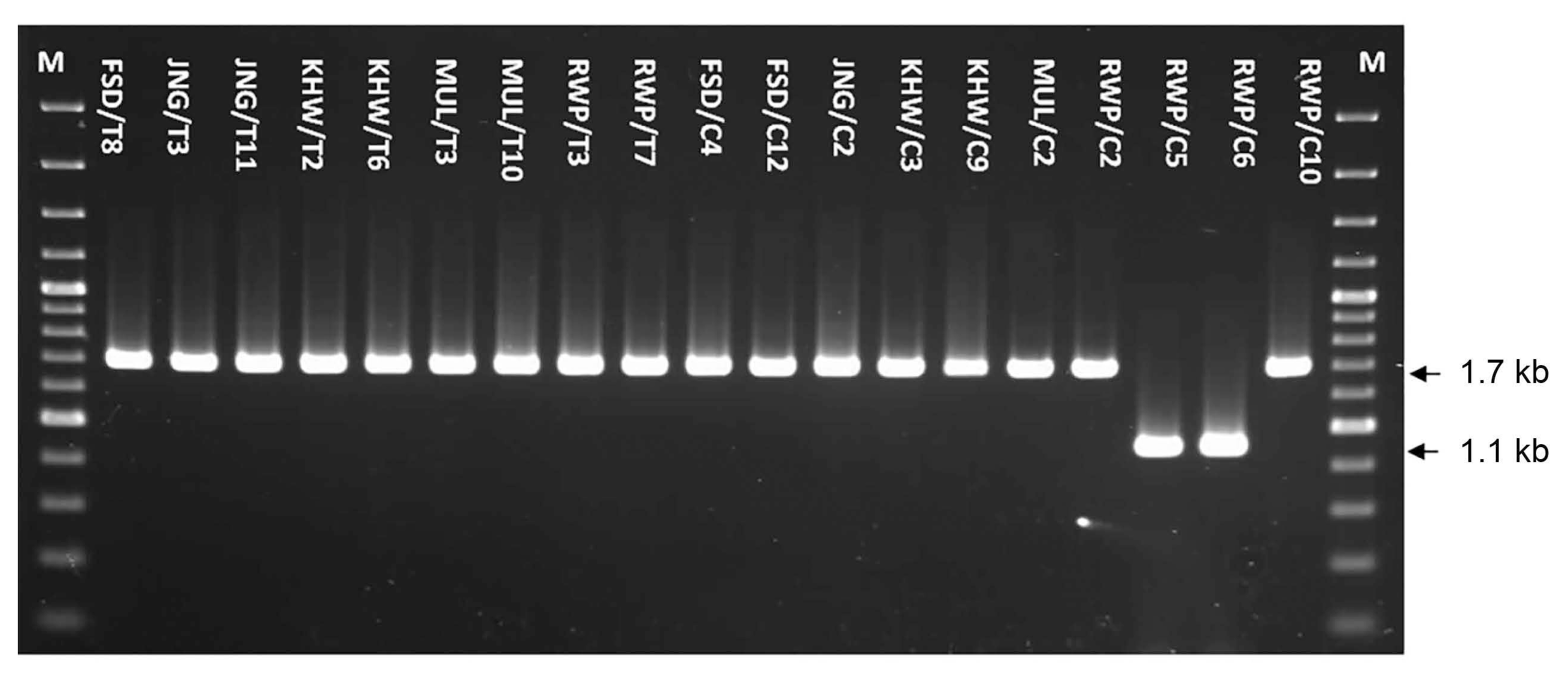
Fig.┬Ā4
Gel image of PCR products from 17 nematode populations restricted with Hinf I enzyme. Lanes showing two fragments of 1.0 and 0.7 kb were related M. javanica whereas lanes with three fragments of 1.0, 0.4 and 0.3 kb were related to M. incognita. The products were resolved on 1.5% agarose gel and stained with ethidium bromide. M lanes were loaded with 1 kb ladder.

Table┬Ā1
List of 19 root-knot nematode populations selected on the basis of their encumbrance to two Pasteuria isolates (PP-3 and PP-J) and used in species differentiation using PCR-RFLP marker
| Encumbrance | District | Tomato* | Cucumber** | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||||
| PP-3 | PP-J | PP-3 | PP-J | ||
| Faisalabad | FSD/T8 | - | FSD/C4 | FSD/C12 | |
| Jhang | JNG/T11 | JNG/T3 | JNG/C2 | - | |
| Maximum | Khanewal | KHW/T6 | KHW/T2 | KHW/C9 | KHW/C3 |
| Multan | MUL/T3 | MUL/T10 | MUL/C2 | - | |
| Rawalpindi | RWP/T3 | RWP/T7 | RWP/C10 | RWP/C2 | |
| Minimum | Rawalpindi. RWP/C5, RWP/C6 (with same response to PP-3 and PP-J) | ||||
Table┬Ā2
Composition of PCR reaction mixtures assembled for characterization of 19 root-knot nematode populations
Table┬Ā3
Temperature cycles used in PCR performed for characterization of 19 root-knot nematode populations
Table┬Ā4
Encumbrance of two Pasteuria isolates (PP-3 and PP-J) with different populations of Meloidogyne spp. isolated from tomato
| Districts | Locality | Population code | Meloidogyne spp. | PP-3 | PP-J | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||||||||||
| 25 ┬▒ 2┬░C | 30 ┬▒ 2┬░C | 25 ┬▒ 2┬░C | 30 ┬▒ 2┬░C | ||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||
| 104 | 105 | 104 | 105 | 104 | 105 | 104 | 105 | ||||
| Faisalabad | JK farm | FSD/T1 | M. incognita | 3.93 cd1 | 13.70 bcd 12.63 de | 19.87 e | 15.57 ef | 24.73 c | 35.77 d | 37.73 f | |
| FSD/T2 | M. incognita | 4.23 cd | 14.30 bcd 14.87 bc | 21.67 bcd | 18.33 b | 26.27 b | 37.07 c | 44.37 bc | |||
| Jahangir Mor | FSD/T3 | M. incognita | 5.50 bc | 14.80 bc | 15.07 b | 22.57 bc | 16.63 de | 23.73 cd | 32.73 g | 43.00 cd | |
| FSD/T4 | M. incognita | 4.66 cd | 14.30 bcd 14.53 bc | 21.83 bcd | 18.03 bc | 24.47 c | 34.27 ef | 43.33 cd | |||
| Dhasian | FSD/T5 | M. incognita | 3.60 d | 13.73 bcd 13.93 bcd | 21.70 bcd | 14.50 fg | 19.70 fg | 28.00 i | 36.47 f | ||
| FSD/T6 | M. incognita | 6.53 ab | 15.37 ab | 15.30 b | 23.10 b | 19.90 a | 27.83 a | 38.30 b | 45.57 ab | ||
| 204RB | FSD/T7 | M. incognita | 3.93 cd | 12.80 d | 12.47 e | 20.73 de | 17.03 cd | 21.67 e | 33.13 fg | 42.30 de | |
| FSD/T8 | M. incognita | 7.66 a | 16.73 a | 18.17 a | 25.17 a | 20.80 a | 28.70 a | 40.27 a | 46.50 a | ||
| 53GB | FSD/T9 | M. incognita | 3.90 cd | 13.33 cd | 13.90 bcd | 20.90 de | 16.47 de | 20.37 f | 32.27 g | 41.33 e | |
| FSD/T10 | M. incognita | 4.13 cd | 14.40 bcd 14.33 bc | 22.67 bc | 14.80 fg | 19.97 fg | 31.93 g | 42.03 de | |||
| Nathu Chak | FSD/T11 | M. javanica | 6.96 ab | 14.67 bcd 14.50 bc | 22.57 bc | 16.77 de | 23.20 d | 34.60 de | 44.33 bc | ||
| FSD/T12 | M. javanica | 3.73 d | 13.33 cd | 13.57 cde | 21.40 cd | 13.97 g | 19.07 g | 29.53 h | 36.73 f | ||
| LSD | 1.425 | 1.63 | 1.286 | 1.267 | 1.108 | 0.9727 | 1.222 | 1.464 | |||
| Jhang | Al Hafiz Farm | JNG/T1 | M. incognita + M. javanica | 6.20 ab | 15.03 bc | 14.87 abc | 22.93 bcd | 18.53 b | 27.63 a | 39.07 a | 45.30 abc |
| JNG/T2 | M. incognita + M. javanica | 2.96 d | 13.13 f | 13.43 cd | 21.67 def | 15.83 cd | 21.03 f | 33.20 f | 42.43 e | ||
| Chak No.204 JB | JNG/T3 | M. incognita | 4.93 bc | 14.70 cde 15.00 abc | 22.17 cde | 20.53 a | 27.90 a | 40.07 a | 45.87 a | ||
| JNG/T4 | M. incognita | 3.33 d | 13.10 f | 13.10 d | 19.80 g | 18.37 b | 26.87 ab | 37.70 b | 44.50 abcd | ||
| Kosar Abad | JNG/T5 | M. incognita | 3.73 cd | 14.77 bcd 14.20 bcd | 22.50 bcde | 17.73 b | 24.10 e | 35.03 de | 44.17 cd | ||
| JNG/T6 | M. incognita | 6.50 a | 15.10 bc | 15.63 ab | 23.60 abc | 18.53 b | 27.87 a | 39.60 a | 43.90 cd | ||
| Basti Usmana | JNG/T7 | M. javanica | 3.93 cd | 13.70 cdef13.63 cd | 20.47 fg | 18.13 b | 25.53 cd | 37.00 bc | 45.73 ab | ||
| JNG/T8 | M. javanica | 2.90 d | 13.47 def | 13.17 d | 21.03 efg | 15.00 d | 19.93 g | 34.33 ef | 39.90 f | ||
| Kot M.Yar (Shorkot) | JNG/T9 | M. incognita | 5.86 ab | 14.73 bcd 15.00 abc | 21.97 def | 18.33 b | 26.27 bc | 37.07 bc | 44.37 bcd | ||
| JNG/T10 | M. incognita | 3.93 cd | 13.30 ef | 13.60 cd | 21.70 def | 16.60 c | 24.73 de | 36.27 bcd | 43.67 de | ||
| Gulgusht Farm | JNG/T11 | M. incognita | 6.80 a | 16.57 a | 16.27 a | 24.90 a | 15.37 d | 21.03 f | 36.13 cd | 42.47 e | |
| JNG/T12 | M. incognita | 5.96 ab | 15.73 ab | 15.90 a | 23.93 ab | 17.63 b | 25.77 cd | 37.40 bc | 44.27 bcd | ||
| LSD | 1.285 | 1.296 | 1.480 | 1.379 | 1.015 | 1.037 | 1.347 | 1.357 | |||
| Khanewal | Khaliqa Abad | KHW/T1 | M. javanica | 3.53 bc | 14.4 | 15.03 ab | 22.57 ab | 15.70 c | 21.20 d | 33.40 c | 37.63 d |
| KHW/T2 | M. javanica | 4.76 abc14.9 | 15.43 a | 22.57 ab | 19.00 a | 26.63 a | 38.30 a | 45.60 a | |||
| Chak No. 125/15L | KHW/T3 | M. incognita + M. javanica | 3.60 bc | 13.7 | 13.67 bc | 21.43 bcd | 16.30 c | 23.73 b | 36.00 b | 41.00 c | |
| KHW/T4 | M. incognita + M. javanica | 5.30 ab | 14.7 | 15.00 ab | 21.97 bc | 17.57 b | 26.00 a | 36.67 b | 43.63 b | ||
| 10 Kassi | KHW/T5 | M. incognita | 3.03 c | 13.9 | 13.97 bc | 21.03 cd | 13.63 d | 17.77 e | 28.27 d | 35.73 e | |
| KHW/T6 | M. incognita | 5.46 a | 15.0 | 15.53 a | 23.37 a | 16.50 bc | 22.80 bc | 34.23 c | 40.20 c | ||
| Tulamba | KHW/T7 | M. incognita | 3.63 bc | 13.6 | 13.50 c | 20.57 d | 16.63 bc | 22.03 cd | 34.97 bc | 39.90 c | |
| KHW/T8 | M. incognita | 4.03 abc14.0 | 14.27 abc | 22.67 ab | 16.33 c | 23.87 b | 36.33 b | 43.90 b | |||
| LSD | 1.63 | - | 1.333 | 1.237 | 1.131 | 1.166 | 1.620 | 1.299 | |||
| Multan | Kotla Sadat | MUL/T1 | M. incognita | 4.9 | 15.03 ab | 14.93 abcd | 23.13 ab | 17.73 bc | 24.80 cde | 35.80 de | 41.40 c |
| MUL/T2 | M. incognita | 5.8 | 14.97 ab | 15.03 abc | 22.47 abc | 18.53 b | 26.07 abc | 37.37 bc | 45.23 a | ||
| Qadarpur Raan | MUL/T3 | M. incognita | 5.9 | 15.73 a | 15.47 a | 23.90 a | 18.07 b | 25.57 bcd | 36.57 cd | 43.13 b | |
| MUL/T4 | M. incognita | 4.5 | 14.60 abc | 15.17 ab | 23.20 ab | 16.07 de | 20.73 g | 33.63 fg | 36.50 e | ||
| Kambir Pur | MUL/T5 | M. incognita + M. javanica | 4.2 | 14.63 abc | 13.93 bcd | 22.77 ab | 17.97 b | 23.33 ef | 34.80 ef | 37.67 de | |
| MUL/T6 | M. incognita + M. javanica | 3.1 | 13.63 c | 13.57 d | 20.83 c | 15.07 ef | 20.90 g | 33.13 g | 37.37 de | ||
| Kian Pur | MUL/T7 | M. incognita | 4.9 | 15.20 ab | 15.03 abc | 23.27 ab | 17.80 bc | 27.00 ab | 38.40 b | 46.00 a | |
| MUL/T8 | M. incognita | 4.4 | 14.57 bc | 14.33 abcd | 21.83 bc | 15.87 def | 22.00 fg | 34.50 ef | 38.20 d | ||
| Abu-Al-Fatah Kotla | MUL/T9 | M. incognita | 4.0 | 13.70 c | 14.03 abcd | 22.03 bc | 14.70 f | 17.90 h | 29.37 h | 37.00 de | |
| MUL/T10 | M. incognita | 4.3 | 14.97 ab | 14.93 abcd | 22.63 ab | 19.70 a | 27.57 a | 39.77 a | 46.23 a | ||
| Saqiqque Abbad | MUL/T11 | M. incognita | 4.1 | 13.73 c | 13.67 cd | 21.77 bc | 16.60 cd | 25.00 cde | 35.60 de | 40.90 c | |
| MUL/T12 | M. incognita | 4.9 | 14.60 abc | 14.70 abcd | 22.37 abc | 17.57 bc | 24.00 de | 35.33 de | 40.50 c | ||
| LSD | - | 1.005 | 1.244 | 1.556 | 1.160 | 1.610 | 1.261 | 1.447 | |||
| Rawalpindi | Kango Juma | RWP/T1 | M. incognita | 5.80 a | 15.70 ab | 15.43 ab | 23.60 ab | 18.17 ab | 25.30 ab | 36.30 bc | 42.30 b |
| RWP/T2 | M. incognita | 5.03 abc | 15.00 bc | 15.17 abc | 22.77 bc | 15.03 de | 19.97 d | 32.67 e | 36.70 c | ||
| Kango Bahadur | RWP/T3 | M. javanica | 6.16 a | 16.20 a | 16.50 a | 24.53 a | 17.73 ab | 25.57 ab | 37.37 b | 42.47 b | |
| RWP/T4 | M. javanica | 3.03 d | 13.63 d | 12.77 e | 20.20 f | 14.63 e | 18.03 e | 30.00 f | 36.20 c | ||
| Qazi Abad | RWP/T5 | M. incognita | 4.10 bcd | 13.90 d | 13.60 cde | 21.77 cde | 18.07 ab | 24.40 b | 35.83 c | 41.07 b | |
| RWP/T6 | M. incognita | 4.03 cd | 14.00 cd | 14.43 bcde | 22.20 cd | 17.10 bc | 22.57 c | 34.53 d | 37.33 c | ||
| Odiala | RWP/T7 | M. javanica | 5.93 a | 15.73 ab | 15.03 abc | 22.93 bc | 18.60 a | 26.40 a | 38.60 a | 44.83 a | |
| RWP/T8 | M. javanica | 3.76 cd | 13.80 d | 13.20 de | 20.67 ef | 15.20 de | 18.40 e | 31.03 f | 36.60 c | ||
| Sawan | RWP/T9 | M. incognita | 4.73 abc | 14.70 bcd | 14.43 bcde | 21.90 cd | 16.33 cd | 20.77 d | 32.50 e | 37.20 c | |
| RWP/T10 | M. incognita | 5.53 ab | 15.63 ab | 14.63 bcd | 21.40 de | 18.33 ab | 25.77 ab | 36.47 bc | 41.60 b | ||
| LSD | 1.32 | 0.9869 | 1.619 | 1.074 | 1.318 | 1.478 | 1.221 | 1.405 | |||
Table┬Ā5
Encumbrance of two Pasteuria isolates (PP-3 and PP-J) with different populations of Meloidogyne spp. isolated from cucumber.
| District | Locality | n | Meloidogyne spp. | PP-3 | PP-J | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||||||||||
| 25 ┬▒ 2┬░C | 30 ┬▒ 2┬░C | 25 ┬▒ 2┬░C | 30 ┬▒ 2┬░C | ||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||
| 104 | 105 | 104 | 105 | 104 | 105 | 104 | 105 | ||||
| Faisalabad | JK Farm | FSD/C1 | M. incognita | 4.63 cde1 | 11.00 e | 13.70 de | 18.00 g | 14.87 de | 22.20 c | 34.00 cd | 37.27 d |
| FSD/C2 | M. incognita | 5.26 abcde | 13.80 cd | 15.70 bc | 21.73 de | 16.47 bc | 22.43 c | 35.23 bc | 38.60 c | ||
| Jahangir Mor | FSD/C3 | M. incognita | 5.93 abc | 14.70 bc | 16.27 abc | 23.10 bc | 17.03 abc | 25.07 b | 36.93 ab | 41.00 b | |
| FSD/C4 | M. incognita | 6.86 a | 16.23 a | 17.73 a | 24.80 a | 17.77 ab | 26.30 ab | 36.90 ab | 41.17 ab | ||
| Chak. No 496 | FSD/C5 | M. incognita | 5.63 abc | 13.43 d | 14.87 cd | 19.70 f | 14.67 de | 20.00 def | 25.57 f | 36.57 de | |
| FSD/C6 | M. incognita | 6.50 ab | 15.57 ab | 15.60 bc | 24.27 ab | 17.30 ab | 25.93 ab | 36.70 ab | 40.17 b | ||
| Chak No.54 | FSD/C7 | M. incognita | 3.70 e | 8.967 f | 12.70 e | 16.37 h | 13.87 ef | 18.80 f | 24.93 f | 35.53 ef | |
| FSD/C8 | M. incognita | 4.90 bcde | 13.93 cd | 15.87 bc | 20.80 ef | 15.73 cd | 20.27 de | 30.30 e | 35.90 ef | ||
| Dhasian | FSD/C9 | M. incognita | 5.83 abc | 13.90 cd | 17.00 ab | 19.90 f | 16.37 bc | 23.23 c | 36.27 ab | 40.50 b | |
| FSD/C10 | M. incognita | 5.53 abcd | 13.40 d | 16.70 ab | 23.83 ab | 15.63 cd | 20.77 d | 32.90 d | 36.60 de | ||
| 204RB | FSD/C10 | M. incognita | 4.00 de | 10.63 e | 13.20 e | 18.13 g | 12.83 f | 18.93 ef | 25.97 f | 35.23 f | |
| FSD/C12 | M. incognita | 6.40 ab | 14.83 bc | 17.03 ab | 22.33 cd | 18.33 a | 26.67 a | 37.57 a | 42.27 a | ||
| LSD | 1.42 | 1.10 | 1.32 | 1.26 | 1.32 | 1.27 | 1.55 | 1.17 | |||
| Jhang | Al Hafiz Farm | JNG/C1 | M. javanica | 4.7 | 12.90 ef | 14.23 e | 17.33 g | 14.30 fg | 20.53 fgh | 32.27 efg | 37.50 de |
| JNG/C2 | M. javanica | 7.2 | 16.57 a | 18.03 a | 23.47 b | 19.37 a | 27.53 a | 38.23 a | 43.63 a | ||
| Chak No.204 | JNG/C3 | M. incognita | 5.8 | 13.93 cde | 15.73 d | 23.23 b | 17.80 b | 25.37 b | 36.93 ab | 41.20 b | |
| JNG/C4 | M. incognita | 5.0 | 13.87 cde | 17.20 abc | 22.00 cd | 16.23 de | 22.40 de | 33.20 def | 37.83 d | ||
| Kosar Abad | JNG/C5 | M. javanica | 5.5 | 14.97 bc | 17.87 a | 22.60 bcd | 14.90 efg | 20.03 gh | 27.67 i | 36.37 de | |
| JNG/C6 | M. javanica | 5.6 | 14.17 cd | 17.73 ab | 24.63 a | 17.67 bc | 24.60 bc | 35.30 bc | 40.23 bc | ||
| Bahsti Usmana | JNG/C7 | M. incognita | 4.6 | 13.30 def | 16.63 bcd | 20.63 e | 13.67 g | 19.43 h | 29.37 h | 37.50 de | |
| JNG/C8 | M. incognita | 5.1 | 12.63 f | 15.97 d | 21.73 d | 16.03 de | 21.27 efg | 33.60 cde | 39.93 bc | ||
| Kot M. Yar | JNG/C9 | M. incognita + M. javanica | 5.3 | 14.60 bc | 17.73 ab | 22.63 bcd | 15.63 def | 20.67 efgh | 30.93 gh | 36.17 e | |
| JNG/C10 | M. incognita + M. javanica | 5.6 | 15.43 b | 17.50 abc | 22.87 bc | 17.87 b | 23.40 cd | 34.37 cd | 39.53 c | ||
| Gulghasht Farm | JNG/C11 | M. incognita | 4.5 | 12.80 ef | 16.37 cd | 19.70 f | 16.43 cd | 21.83 def | 32.00 efg | 37.90 d | |
| JNG/C12 | M. incognita | 4.9 | 13.90 cde | 16.63 bcd | 20.73 e | 15.30 def | 21.23 efg | 31.60 fg | 36.97 de | ||
| LSD | - | 1.07 | 1.06 | 0.84 | 1.28 | 1.58 | 1.68 | 1.44 | |||
| Khanewal | Raees Abad | KHW/C1 | M. incognita | 3.83 cd | 7.30 f | 11.57 f | 16.00 fg | 14.70 c | 19.37 e | 30.40 e | 35.63 f |
| KHW/C2 | M. incognita | 5.33 ab | 14.33 abcd | 16.83 ab | 24.00 a | 17.00 ab | 21.53 d | 32.33 d | 38.57 bc | ||
| Khaliqa Abad | KHW/C3 | M. javanica | 5.56 ab | 14.93 ab | 16.87 ab | 23.63 ab | 18.23 a | 26.83 a | 37.63 a | 42.20 a | |
| KHW/C4 | M. javanica | 4.60 bcd | 13.47 bcd | 16.47 bc | 22.37 c | 15.10 c | 20.10 e | 30.50 e | 36.33 ef | ||
| Chak 125/15L | KHW/C5 | M. incognita | 5.53 ab | 14.73 abc | 16.97 ab | 23.67 ab | 17.57 a | 24.90 b | 35.30 bc | 40.90 a | |
| KHW/C6 | M. incognita | 4.93 ab | 13.53 bcd | 16.70 abc | 22.97 bc | 15.80 bc | 21.70 d | 34.47 c | 38.20 c | ||
| Dass Kassi | KHW/C7 | M. incognita | 3.63 d | 10.03 e | 12.10 ef | 15.63 g | 13.03 d | 19.20 e | 30.87 de | 36.57 def | |
| KHW/C8 | M. incognita | 4.73 abc | 12.97 d | 12.57 e | 16.60 f | 15.43 c | 19.83 e | 31.97 de | 37.20 cde | ||
| Kacha Koh | KHW/C9 | M. javanica | 5.83 a | 15.77 a | 17.43 a | 24.30 a | 17.83 a | 25.97 ab | 37.37 a | 41.27 a | |
| KHW/C10 | M. javanica | 5.60 ab | 14.00 bcd | 15.90 c | 20.73 d | 17.17 a | 23.37 c | 36.70 ab | 39.57 b | ||
| Tulamba | KHW/C11 | M. incognita | 5.00 ab | 13.27 cd | 14.60 d | 19.57 e | 15.00 c | 20.20 e | 32.40 d | 37.83 cd | |
| KHW/C12 | M. incognita | 5.30 ab | 14.33 abcd | 17.03 ab | 23.97 a | 15.80 bc | 21.77 d | 31.27 de | 36.20 ef | ||
| LSD | 0.99 | 1.34 | 0.81 | 0.87 | 1.22 | 1.27 | 1.47 | 1.27 | |||
| Multan | Kotla Saadat | MUL/C1 | M. javanica | 4.83 bc | 13.77 bc | 16.67 ab | 21.63 ab | 16.27 c | 22.00 ef | 32.77 e | 37.57 de |
| MUL/C2 | M. javanica | 6.56 a | 15.20 a | 17.23 a | 22.80 a | 18.50 a | 26.80 a | 38.03 a | 41.63 a | ||
| Qadir pur Raan | MUL/C3 | M. incognita | 5.60 ab | 13.90 bc | 16.30 ab | 21.40 ab | 14.87 d | 20.70 fg | 31.80 ef | 38.17 de | |
| MUL/C4 | M. incognita | 5.86 ab | 14.20 abc | 16.80 ab | 22.13 ab | 17.97 ab | 25.13 bc | 36.33 b | 39.67 bc | ||
| Kambir pur | MUL/C5 | M. incognita | 3.90 c | 12.20 d | 11.43 e | 16.73 e | 13.10 e | 20.17 gh | 30.80 f | 36.90 e | |
| MUL/C6 | M. incognita | 4.70 bc | 13.13 cd | 13.73 cd | 19.00 c | 16.67 bc | 22.00 ef | 33.17 de | 38.90 cd | ||
| Kian pur | MUL/C7 | M. incognita | 5.76 ab | 13.93 bc | 15.30 bc | 20.93 b | 14.53 d | 20.67 fg | 31.87 ef | 37.97 de | |
| MUL/C8 | M. incognita | 5.06 bc | 13.47 bc | 14.27 cd | 18.53 cd | 17.23 abc | 23.97 cd | 34.90 c | 38.57 cd | ||
| Abu Al-Fatah Kotla | MUL/C9 | M. incognita + M. javanica | 3.93 c | 11.00 e | 11.77 e | 16.03 e | 13.90 de | 19.00 h | 30.97 f | 37.47 de | |
| MUL/C10 | M. incognita + M. javanica | 5.03 bc | 13.53 bc | 13.40 d | 17.13 de | 16.40 c | 22.80 de | 34.50 cd | 38.17 de | ||
| Saddique Abad | MUL/C11 | M. javanica | 4.56 bc | 13.87 bc | 14.07 cd | 18.63 cd | 14.67 d | 20.97 fg | 34.17 cd | 37.97 de | |
| MUL/C12 | M. javanica | 5.66 ab | 14.47 ab | 16.90 ab | 20.77 b | 18.03 ab | 25.73 ab | 36.33 b | 40.53 ab | ||
| LSD | 1.16 | 1.11 | 1.61 | 1.44 | 1.26 | 1.29 | 1.32 | 1.32 | |||
| Rawalpindi | Kango Juma | RWP/C1 | M. incognita | 4.16 bcde | 12.73 de | 13.03 def | 18.03 e | 16.17 cd | 21.63 d | 33.63 c | 38.57 cd |
| RWP/C2 | M. incognita | 5.70 ab | 14.87 a | 17.30 ab | 23.60 a | 18.90 a | 26.70 a | 37.73 a | 42.00 a | ||
| Kango Bhadur | RWP/C3 | M. incognita | 4.76 abcd | 13.73 bcd | 16.13 bc | 21.33 b | 16.90 bc | 23.83 b | 35.90 b | 39.17 c | |
| RWP/C4 | M. incognita | 5.06 abc | 13.33 cde | 15.97 c | 20.43 bcd | 15.47 de | 21.13 d | 32.27 cde | 38.23 cd | ||
| Qazi Abad | RWP/C5 | M. arenaria | 3.23 de | 5.06 h | 7.30 h | 9.16 h | 5.66 g | 8.800 g | 9.83 g | 12.93 h | |
| RWP/C6 | M. arenaria | 2.90 e | 5.50 gh | 6.46 h | 8.26 h | 6.00 g | 8.23 g | 9.40 g | 12.60 h | ||
| Mathian | RWP/C7 | M. incognita | 4.86 abc | 12.97 cde | 13.80 de | 19.83 cd | 14.50 e | 18.73 ef | 32.03 de | 36.90 ef | |
| RWP/C8 | M. incognita | 4.56 bcd | 12.50 e | 12.57 ef | 21.33 b | 12.90 f | 18.13 ef | 30.97 e | 36.17 fg | ||
| Bunny | RWP/C9 | M. incognita | 5.20 abc | 14.53 ab | 16.67 abc | 22.83 a | 16.80 bc | 23.43 bc | 35.67 b | 39.57 bc | |
| RWP/C10 | M. incognita | 6.20 a | 15.17 a | 17.70 a | 23.77 a | 17.67 b | 24.77 b | 36.20 b | 40.60 b | ||
| Sawan | RWP/C11 | M. incognita | 4.73 abcd | 12.50 e | 12.73 def | 19.70 d | 15.90 cd | 19.43 e | 32.30 cde | 37.50 de | |
| RWP/C12 | M. incognita | 3.26 de | 6.43 g | 10.37 g | 15.40 g | 12.03 f | 17.57 f | 27.30 f | 34.93 g | ||
| Odiala | RWP/C13 | M. incognita | 3.76 cde | 11.30 f | 12.00 f | 16.63 f | 16.90 bc | 22.27 cd | 33.33 cd | 38.90 c | |
| RWP/C14 | M. incognita | 5.00 abc | 13.83 bc | 13.83 d | 21.03 bc | 15.13 de | 18.73 ef | 31.40 e | 35.87 fg | ||
| LSD | 1.39 | 0.96 | 1.13 | 1.15 | 1.16 | 1.31 | 1.38 | 1.25 | |||
References
Ahmed, R 1990. Studies on the efficacy of Pasteuria penetrans for the biological control of Meloidogyne species. PhD thesis. University of Reading, Reading, UK.
Alves, FR, Freitas, LG, Martinelli, PRP, Campos, AVS, Oliveira, RL and Ferraz, S 2004. Influence of endospore concentration and agitation period of the suspension on the attachment of Pasteuria penetrans to Meloidogyne javanica. Nematol Bras. 28:235-237.
Blok, VC, Wishart, J, Fargette, M, Berthier, K and Phillips, MS 2002. Mitochondrial differences distinguishing Meloidogyne mayaguensis from the major species of tropical rootknot nematodes. Nematology. 4:773-781.

Brown, SM and Smart, GC 1985. Root penetration by Meloidogyne incognita juveniles infected with Bacillus penetrans. J Nematol. 17:123-126.


Cenis, JL 1993. Identification of four major Meloidogyne spp. by random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD-PCR). Phytopathology. 83:76-80.

Channer, AGDR and Gowen, SR 1992. Selection for increased host resistance and increased pathogen specificity in the Meloidogyne-Pasteuria penetrans interaction. Fundam Appl Nematol. 15:331-339.
Chen, ZX, Dickson, DW, Mitchell, DJ, McSorley, R and Hewlett, TE 1997. Suppression mechanisms of Meloidogyne arenaria race 1 by Pasteuria penetrans. J Nematol. 29:1-8.


Chen, ZX and Dickson, DW 1998. Review of Pasteuria penetrans: biology, ecology and biological control potential. J Nematol. 30:313-340.


Davies, KG 2005. Interactions between nematodes and microorganisms: bridging ecological and molecular approaches. Adv Appl Microbiol. 57:53-78.


Davies, KG, Kerry, BR and Flynn, CA 1988. Observations on the pathogenicity of Pasteuria penetrans, a parasite of root-knot nematodes. Ann Appl Biol. 112:491-501.

Davies, KG and Danks, C 1992. Interspecific differences in the nematode surface coat between Meloidogyne incognita and M. arenaria related to the adhesion of the bacterium Pasteuria penetrans. Parasitology. 105:475-480.

Davies, KG, Robinson, MP and Laird, V 1992. Proteins involved in the attachment of a hyperparasite, Pasteuria penetrans, to its plant parasitic nematode host, Meloidogyne incognita. J Invertebr Pathol. 59:18-23.

Davies, KG and Danks, C 1993. Carbohydrate/protein interactions between the cuticle of infective juveniles of Meloidogyne incognita and spores of the obligate hyperparasite Pasteuria penetrans. Nematologica. 39:53-64.

Davies, ILG and Redden, M 1997. Diversity and partial characterization of putative virulence determinants in Pasteuria penetrans, the hyperparasitic bacterium of root-knot nematodes (Meloidogyne spp). J Appl Microbiol. 83:227-235.


Davies, KG, Fargette, M, Balla, G, Daudi, A, Duponnois, R, Gowen, SR, Mateille, T, Phillips, MS, Sawadogo, A, Trivino, C, Vouyoukalou, E and Trudgill, DL 2001. Cuticle heterogeneity as exhibited by Pasteuria spore attachment is not linked to the phylogeny of parthenogenetic root-knot nematodes (Meloidogyne spp.). Parasitology. 122:111-120.


Davies, KG and Opperman, CH 2006. A potential role for collagen in the attachment of Pasteuria penetrans to nematode cuticle. In: Multitrophic interactions in soil and integrated control, eds. by JM Raaijmakers and RA Sikora, 11-15. General Secretariat IOBC/WPRS, Dijon, France.
Davies, KG and Williamson, VM 2006. Host-specificity exhibited by populations of endospores of Pasteuria penetrans to the juvenile and male cuticles of Meloidogyne hapla. Nematology. 8:475-476.

Davies, KG, Rowe, JA and Williamson, VM 2008. Interand intra-specific cuticle variation between amphimictic and parthenogenetic species of root-knot nematode (Meloidogyne spp.) as revealed by a bacterial parasite (Pasteuria penetrans). Int J Parasitol. 38:851-859.


Espanol, M, Verdejo-Lucas, S, Davies, KG and Kerry, BR 1997. Compatibility between Pasteuria penetrans and Meloidogyne populations from Spain. Biocontrol Sci Technol. 7:219-230.

Freitas, LG, Mitchell, DJ and Dickson, DW 1997. Temperature Effects on the Attachment of Pasteuria penetrans Endospores to Meloidogyne arenaria Race 1. J Nematol. 29:547-555.


Giannakou, IO, Pembroke, B, Gowen, SR and Davies, KG 1997. Effects of long-term storage and above normal temperatures on spore adhesion of Pasteuria penetrans and infection of the root-knot nematodes Meloidogyne javanica. Nematologica. 43:185-192.

Giannakou, IO and Gowen, SR 2004. Factors affecting biological control effectiveness of Pasteuria penetrans in Meloidogyne javanica and the bacterial development in the nematode body. Nematropica. 34:153-163.
Han, H, Cho, MR, Jeon, HY, Lim, CK and Jang, HI 2004. PCR-RFLP Identification of three major Meloidogyne species in Korea. J Asia Pac Entomol. 7:171-175.

Hatz, B and Dickson, DW 1992. Effect of temperature on attachment, development, and interactions of Pasteuria penetrans on Meloidogyne arenaria. J Nematol. 24:512-521.


Henson, JM and French, R 1993. The polymerase chain reaction and plant disease diagnosis. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 31:81-109.


Hewlett, TE and Dickson, DW 1993. A centrifugation method for attaching endospores of Pasteuria spp. to nematodes. J Nematol. 25:785-788.


Hu, M and Gasser, RB 2006. Mitochondrial genomes of parasitic nematodes - progress and perspectives. Trends Parasitol. 22:78-84.


Hugall, A, Moritz, C, Stantont, J and Wolstenholme, DR 1994. Low, but strongly structured mitochondrial DNA diversity in root knot nematodes (Meloidogyne). Genetics. 136:903-912.



Hussey, RS and Barker, KR 1973. A comparison of methods of collecting inocula of Meloidogyne spp. including a new technique. Plant Dis Rep. 57:1025-1028.
Jeyaprakash, A, Tigano, MS, Brito, J, Carneiro, RMDG and Dickson, DW 2006. Differentiation of Meloidogyne floridensis from M. arenaria using high-fidelity PCR amplified mitochondrial AT-rich sequences. Nematropica. 36:1-12.
Liu, J, Berry, RE and Blouin, MS 1999. Molecular differentiation and phylogeny of entomopathogenic nematodes (Rhabditida: Heterorhabditidae) based on ND4 gene sequences of mitochondrial DNA. J Parasitol. 85:709-715.


Martin, RR, James, D and L├®vesque, CA 2000. Impacts of molecular diagnostic technologies on plant disease management. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 38:207-239.


Oh, HK, Bae, CH, Kim, MI, Wan, X, Oh, SH, Han, YS, Lee, HB and Kim, I 2009. Molecular biological diagnosis of Meloidogyne species occurring in Korea. Plant Pathol J. 25:247-255.

Orui, Y 1997. Effect of spore sonication on attachment and host-attachment range of P. penetrans to the root-knot nematode. Appl Entomol Zool. 32:101-107.

Persidis, A, Lay, JG, Manousis, T, Bishop, AH and Ellar, DJ 1991. Characterization of potential adhesions of the bacterium Pasteuria penetrans, and of putative receptors on the cuticle of Meloidogyne incognita, a nematode host. J Cell Sci. 100:613-622.

Powers, TO and Harris, TS 1993. A polymerase chain reaction method for identification of five major Meloidogyne species. J Nematol. 25:1-6.


Powers, TO, Mullin, PG, Harris, TS, Sutton, LA and Higgins, RS 2005. Incorporating molecular identification of Meloidogyne spp. into a large-scale regional nematode survey. J Nematol. 37:226-235.


Preston, JF, Dickson, DW, Maruniak, JE, Nong, G, Brito, JA, Schmidt, LM and Giblin-Davis, RM 2003. Pasteuria spp: systematics and phylogeny of these bacterial parasites of phytopathogenic nematodes. J Nematol. 35:198-207.


Randig, O, Bongiovanni, M, Carniero, RMDG, Sarah, J and Castagnone-Sereno, P 2002. A species-specific satellite DNA family in the genome of the coffee root-knot nematode Meloidogyne exigua: application to molecular diagnostics of the parasite. Mol Plant Pathol. 3:431-437.


Sayre, RM and Starr, MP 1985. Pasteuria penetrans (ex Thorne, 1940) nom. rev., comb. n., sp. n., a mycelia and endospore-forming bacterium parasitic in plant parasitic nematodes. Proc helminthol Soc Wash. 52:149-165.
Schaad, NW and Frederick, RD 2002. Real-time PCR and its application for rapid plant disease diagnostics. Can J Plant Pathol. 24:250-258.

Singh, B and Dhawan, SC 1990. A new bacterial strain of Pasteuria penetrans, its host range and effect of temperature on spore attachment to second-stage juveniles of pigeon-pea cyst nematode, Heterodera cajani. Indian J Nematol. 20:161-166.
Spiegel, Y, Mor, M and Sharon, E 1996. Attachment of Pasteuria penetrans endospores to the surface of Meloidogyne javanica second-stage juveniles. J Nematol. 28:328-334.


Stirling, GR 1981. Effect of temperature on infection of Meloidogyne javanica by Bacillus penetrans. Nematologica. 27:458-462.

Stirling, GR 1984. Biological control of Meloidogyne javanica with Bacillus penetrans. Phytopathology. 74:55-60.

Stirling, GR and Wachtel, MF 1980. Mass production of Bacillus penetrans for the biological control of root-knot nematodes. Nematologica. 26:308-312.

Stirling, GR, Bird, AF and Cakurs, AB 1986. Attachment of Pasteuria penetrans spores cuticles of root-knot nematodes. Revue Nematol. 9:251-260.
Stirling, GR, Sharma, RD and Perry, J 1990. Attachment of Pasteuria penetrans spores to the root-knot nematode Meloidogyne javanica in soil and its effects on infectivity. Nematologica. 36:246-252.

Szalanski, AL, Tayor, DB and Mullin, PG 2000. Assessing nuclear and mitochondrial DNA sequence variation within Steinernema (Rhabditida: Steinernematidae). J Nematol. 32:229-233.


Talavera, M and Mizukubo, T 2003. Influence of soil conditions, spore densities and nematode age on Pasteuria penetrans attachment to Meloidogyne incognita. Spanish J Agric Res. 1:57-63.

Taylor, A and Sasser, J 1978. Biology, identification and control of root-knot nematodes (Meloidogyne species. North Carolina State University Graphics, Raleigh, NC, USA. 111.
Tian, B, Yang, J and Zhang, KQ 2007. Bacteria used in the biological control of plant-parasitic nematodes: populations, mechanisms, and future prospects. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 61:197-213.


Vagelas, I, Leontopoulos, S, Pembroke, B and Gowen, S 2012. Poisson and negative binomial modeling techniques for better understanding Pasteuria penetrans spore attachment on rootknot nematode juveniles. J Agric Sci Technol. 2:273-277.
Ward, E, Foster, SJ, Fraaije, BA and Mccartney, HA 2004. Plant pathogen diagnostics: immunological and nucleic acid-based approaches. Ann Appl Biol. 145:1-16.

- TOOLS



 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Full text via PMC
Full text via PMC Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print