 |
 |
| Plant Pathol J > Volume 36(1); 2020 > Article |
|
Abstract
Ralstonia solanacearum (Rso) is a causal agent of bacterial wilt in Solanaceae crops worldwide including Republic of Korea. Rso virulence predominantly relies on type III secreted effectors (T3Es). However, only a handful of Rso T3Es have been characterized. In this study, we investigated subcellular localization of and manipulation of plant immunity by 8 Rso T3Es predicted to harbor a nuclear localization signal (NLS). While 2 of these T3Es elicited cell death in both Nicotiana benthamiana and N. tabacum, only one was dependent on suppressor of G2 allele of skp1 (SGT1), a molecular chaperone of nucleotide-binding and leucine-rich repeat immune receptors. We also identified T3Es that differentially regulate flg22-induced reactive oxygen species production and gene expression. Interestingly, several of the NLS-containing T3Es translationally fused with yellow fluorescent protein accumulated in subcellular compartments other than the cell nucleus. Our findings bring new clues to decipher Rso T3E function in planta.
Plants have evolved a sophisticated immune system to protect themselves from pathogen infection. Perception of conserved microbial molecules termed pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs), such as bacterial flagellin, leads to pattern-triggered immunity (PTI). PAMP recognition at the cell surface induces downstream responses including production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and expression of defense-related genes, which ultimately restrict pathogen infection (Couto and Zipfel, 2016). To overcome PTI, successful pathogens secrete virulence proteins termed effectors. In turn, plants have developed another layer of the immune system, effector-triggered immunity (ETI), which relies on the recognition of effector presence by intracellular nucleotide-binding and leucine-rich repeat receptors (NLRs). ETI leads to amplified defense responses and is often accompanied by a form of programmed cell death at the infection site known as the hypersensitive response (HR) (Jones and Dangl, 2006).
Ralstonia solanacearum (Rso) is a devastating pathogen that causes bacterial wilt in a wide range of crops worldwide. Rso can inject more than 70 effectors or Ralstonia-injected proteins (Rip) into plant cells by type III secretion system. Rips play a crucial role in the pathogenicity (Deslandes and Genin, 2014; Genin and Denny, 2012; Peeters et al., 2013b). Biological and molecular functions of several Rso type III-dependent effectors (T3Es) have been characterized and are so far mainly related to the suppression of the plant immune system (Fujiwara et al., 2016; Mukaihara et al., 2016; Nakano et al., 2017; Sang et al., 2018; Sun et al., 2019; Wei et al., 2017). However, most functions of Rso T3Es remain to be characterized.
Functional studies on T3Es from different bacterial pathogens revealed that one of major roles of T3Es is to suppress PTI response (Macho and Zipfel, 2015). However, T3Es also target multiple cellular pathways such as signal transduction, phytohormone biosynthesis, cytoskeleton function, and development in plant cells (Büttner, 2016). Manipulation of these processes may result in indirect suppression of plant immunity and contribute to pathogen virulence (Macho, 2016). Therefore, identifying the mode of action by which T3Es hijack host target processes is important to better understand how pathogens overcome host defense and cause disease.
After delivery into plant cells, T3Es localize to different subcellular compartments where they act as plant proteins, mimicking or/and interacting with host proteins (Hogenhout et al., 2009). In order to act on specific host targets and to exert their biochemical activities, localization at specific subcellular compartments is critical (Hicks and Galan, 2013). Certain T3Es may possess eukaryotic organelle-targeting signals (Khan et al., 2018). For example, AvrBs3 from Xanthomonas euvesicatoria and PopP2 (RipP2) from Rso are nuclear-localized T3Es that subvert host transcription to promote pathogen virulence (Deslandes and Rivas, 2011; Le Roux et al., 2015; Marois et al., 2002; Sarris et al., 2015). Interestingly, the homologs of AvrBs3, transcriptional activator-like (RipTAL) T3Es across the Rso species complex possess multiple nuclear localization signal (NLS) and localize to the nucleus when transiently expressed in N. benthamiana (Li et al., 2013). Similarly, PopP2 localizes to the nucleus in host cells and harbors an NLS in the N-terminal region, although this motif is not strictly required for nuclear import (Deslandes et al., 2003; Sarris et al., 2015). In the nucleus, PopP2 interacts with WRKY transcription factors to impair defense signaling (Le Roux et al., 2015; Sarris et al., 2015). Furthermore, given the importance of nuclear trafficking in plant immune signaling, presence of eukaryotic NLS in T3Es might be indicative of virulence function (Motion et al., 2015).
In this study, we characterized 8 predicted NLS-containing Rso T3Es by Agrobacterium-mediated transient expression in N. benthamiana. These T3Es were screened for their ability to induce cell death or to suppress PTI responses. In addition, subcellular localization of the T3Es was examined, and interestingly, several of them localized outside the nucleus in different cell compartments. We expect that this work will help to elucidate biological functions of these T3Es in order to develop bacterial wilt-resistant crops.
All T3E sequences of the reference strain GMI1000 were extracted from R. solanacearum T3E database (Peeters et al., 2013a) and searched for NLS using two prediction programs cNLS Mapper and NLStradamus (Kosugi et al., 2009; Nguyen Ba et al., 2009). Sequences of selected NLS-containing T3Es were divided into 1 to 1.5 kb modules. Module DNA was amplified from GMI1000 genomic DNA with the flanking BsaI site-containing primers listed in Supplementary Table 1. PCR products were ligated into the entry vector pICH41021 and each module construct was verified by Sanger sequencing. Entry modules were assembled into the binary vector pICH86988 in fusion with a C-terminal 3×FLAG tag or yellow fluorescent protein (YFP) under the Cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter using the Golden Gate cloning method (Engler and Marillonnet, 2014). Assemblies confirmed by restriction analysis were mobilized into Agrobacterium tumefaciens AGL1 strain. To generate a lipid body marker, the coding sequence of AtLDIP (lipid drop-associated protein 3-interacting protein, At5g16550) (Pyc et al., 2017) was amplified from Arabidopsis thaliana Col-0 cDNA and assembled into the vector pICH86988 in fusion with C-terminal mCherry fluorescent tag. Recombinant plasmids for the plastid, nucleus, and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) markers fused with mCherry are described in Park et al. (2017).
Agrobacterium-mediated transient transformation of N. benthamiana leaf was carried out as described previously (Newman et al., 2019). A. tumefaciens AGL1 cells contacting T3E constructs were grown on Luria-Bertani medium with selective antibiotics. Cells grown overnight were centrifuged and resuspended in infiltration medium (10 mM MgCl2 and 10 mM MES-KOH, pH 5.6) to reach OD600nm 0.4. The suspensions were infiltrated into fully expanded leaves of 5-week-old N. benthamiana plants using a blunt end syringe.
Electrolyte leakage assays were carried out as described previously (Jayaraman et al., 2017). Agrobacterium infiltration was carried out as described above and two leaf discs were taken for each sample (n = 4) at 0 and 3 days post infiltration (dpi) using an 8 mm diameter cork borer. Leaf discs were floated on 2 ml deionized water in 12-well tissue culture plate with shaking at 150 rpm for 2 h. Water conductivity in each well was measured using a Horiba B-771 LAQUA twin compact conductivity meter (Horiba, Kyoto, Japan).
VIGS was performed using a tobacco rattle virus vector as previously described (Choi et al., 2017; Peart et al., 2002). For semi-quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) analysis to confirm NbSGT1 silencing, total RNA was extracted from silenced plants using AccuZol total RNA extraction solution (Bioneer, Daejeon, Korea). cDNA was synthesized from 2.5 μg of RNA with the Maxima First Strand cDNA synthesis kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). cDNA amplification was performed with NbSGT1 and actin specific primers listed in Supplementary Table 1.
Luminol-based measurement of ROS production was carried out as described by Sang and Macho (2017). Leaf discs expressing each effector and GFP were collected using a 5 mm biopsy punch and were floated on 150 μl of deionized water overnight. The water was replaced with 100 μl of assay solution containing 100 μM luminol (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA), 2 μg of horseradish peroxidase, and 100 nM of flg22 (Peptron, Sigma) as elicitor. Luminescence was measured in relative light unit for 75 min using GloMax 96 microplate luminometer (Promega, Madison, WI, USA).
Agrobacterium-infiltrated N. benthamiana leaf discs were collected 24 h post-infiltration and floated on deionized water overnight. Discs were treated with 100 nM flg22 or water for 60 min before RNA extraction. For quantitative RT-PCR, cDNA template was combined with GoTaq qPCR master mix (Promega) and PCRs were performed using the marker gene-specific primers (Segonzac et al., 2011) in triplicate with a CFX connect real-time system (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). Expression was normalized to the reference gene NbEF1α. Primers used for this analysis are listed in Supplementary Table 1.
Equal volumes of A. tumefaciens AGL1 strains carrying T3E-YFP (OD600nm = 0.6), organelle marker-mCherry (OD600nm = 0.6), and silencing suppressor p19 (OD600nm = 0.1) (Qiu et al., 2002) were mixed and infiltrated into 4-week-old N. benthamiana leaves. Microscopic observation was performed 48 h post infiltration. Images were obtained with a confocal laser scanning microscope (+Super-resolution) SP8X (Leica Microsystems, Wetzlar, Germany) using 40× water immersion objective. 514-nm laser and 561-nm white light laser were used for YFP and mCherry excitation, respectively.
Recombinant T3E proteins were detected by immunoblotting as described previously (Newman et al., 2019). Briefly, N. benthamiana leaf expressing each T3E was harvested at 2 dpi and frozen in liquid nitrogen. Total proteins were extracted in protein extraction buffer (10% glycerol, 50 mM Tris-HCL pH 7.5, 2 mM EDTA pH 8, 150 mM NaCl, 5 mM DTT, 0.2-0.5% IGEPAL [Sigma], and 1 tablet of cOmplete mini protease inhibitor cocktail/10 ml [Sigma]). Total proteins were separated by sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, transferred to polyvinylidene difluoride membrane (Merck Millipore, Burlington, MA, USA), and probed with anti-FLAG (Sigma) or anti-GFP antibodies (Santa Cruz Biotech, Dallas, TX, USA) and subsequent anti-mouse horseradish peroxidase secondary antibodies.
Nuclear localization of T3Es plays a crucial role for interaction with key host factors to interrupt defense signaling. To identify T3Es that affect host cellular functions, we screened Rso GMI1000 T3E repertoire sequences for the presence of NLS. Protein sequences of 80 GMI1000 T3Es were downloaded from the database Ralsto T3E (https://iant.toulouse.inra.fr/T3E) and searched with two NLS-prediction programs, NLStradamus and cNLS mapper (Table 1) (Kosugi et al., 2009; Nguyen Ba et al., 2009; Peeters et al., 2013a). Interestingly, about 25% of GMI1000 T3Es (19 out of 80) were predicted to have a putative NLS according to at least one of the two softwares. Among these, we further selected the predicted NLS-containing T3Es based on the coding sequence length (less than 5 kb), %GC content and presence of repeats for simplified cloning. Altogether, we generated recombinant binary constructs for 8 T3Es (RipA1, RipAB, RipAD, RipAF1, RipAO, RipD, RipE1, and RipL) in C-terminal fusion with 3×FLAG or YFP under the control of the constitutive 35S promoter.
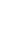
To test whether the predicted NLS-containing T3Es can elicit plant defense response, cell death was monitored in N. benthamiana and N. tabacum leaf transiently expressing each T3E. As a positive control, we used Bcl-2-associated X (BAX), a mammalian proapoptotic regulator which causes programmed cell death when overexpressed in tobacco (Lacomme and Santa Cruz, 1999). As a negative control, we used PopP2 that does not cause cell death in Nicotiana spp. (Sohn et al., 2014). Rapid and robust cell death was induced within 2 days in every leaf spot expressing BAX (Fig. 1). Similarly, RipA1 and RipE1 induced cell death within 2 or 3 days in N. benthamiana and N. tabacum. Consistently, increased electrolyte leakage levels were observed in N. benthamiana leaf cells expressing RipA1 or RipE1 compared to GFP (Supplementary Fig. 1). On the contrary, macroscopic cell death nor electrolyte leakage were observed in N. benthamiana and N. tabacum leaf expressing the negative control PopP2 or any of the 6 other tested T3Es (RipAB, RipAD, RipAF1, RipAO, RipD, and RipL). Protein accumulation and stability were confirmed by immunoblotting with anti-FLAG antibodies (Supplementary Fig. 2). Taken together, our results suggest that RipA1 and RipE1 might be recognized by and elicit activation of the immune system of Nicotiana spp. On another hand, we can hypothesize that the 6 T3Es that did not trigger cell death may exert a virulence function in Nicotiana spp. cells.
The Rso GMI1000 strain is nonpathogenic on Nicotiana spp. due to the presence of two T3Es, AvrA (RipAA) and PopP1 (RipP1) that elicit cell death (Peeters et al., 2013b; Poueymiro et al., 2009). RipA1, previously named AWR1 was shown to trigger a mild necrosis in N. benthamiana (Solé et al., 2012). The robust RipA1-induced cell death observed in our conditions could be due to different Agrobacterium strains, binary construct used, and expression conditions. RipE1 harbors 50% similarity at the amino acid level with T3Es of the AvrPphE (HopX) family (Nimchuk et al., 2007). Interestingly, HopX also elicits cell death in host tissues, dependent on putative catalytic residues conserved in bacterial transglutaminases (Choi et al., 2017; Nimchuk et al., 2007). Of note, RipAB from the R. solanacearum UW551 (phylotype IIB) strain was recently shown to trigger mild necrosis when transiently expressed in N. benthamiana (Zheng et al., 2019). We did not observe any cell death symptoms or significant ion leakage in our experiment with RipAB from GMI1000. However, there are significant differences at the amino acid sequence level, notably in the N-terminal region that could explain the difference in cell death-inducing activities of RipAB variants.
Plant cell death induced by T3E expression could be associated either with necrosis caused by effector-induced cellular toxicity (Alfano and Collmer, 2004) or by HR following T3E recognition by NLR proteins. Suppressor of G2 allele of skp1 (SGT1) is a major stabilizing factor of NLR proteins and is required for T3E-triggered HR (Kadota et al., 2010; Peart et al., 2002). To investigate the SGT1 requirement for RipA1- or RipE1-induced cell death, NbSGT1 expression was knocked-down using VIGS (Choi et al., 2017; Gimenez-Ibanez et al., 2018; Peart et al., 2002). As observed in non-silenced N. benthamiana plants, RipA1 or RipE1 expression triggered cell death in empty vector (EV)-silenced plants (Fig. 2A). Similar to BAX-induced cell death, RipA1-induced cell death was not affected in NbSGT1-silenced plants. Conversely, RipE1 expression did not induce cell death in NbSGT1-silenced plants. Using RT-PCR, we confirmed that NbSGT1 transcript level was significantly reduced in SGT1-silenced plants compared to EV-silenced plants (Fig. 2B). Our results showed that NbSGT1 is required for the cell death induced by RipE1 but not by RipA1 expression, suggesting a possible recognition of RipE1 by an NLR in N. benthamiana.
Similar to RipA1, several Pseudomonas syringae T3Es induce cell death independent of NbSGT1 (Choi et al., 2017; Gimenez-Ibanez et al., 2018). Although SGT1 might not be required for every NLR function, it is possible that the cell death observed following expression of these T3Es is not related to their recognition by R protein but rather indicative of a form of cellular toxicity.
Rapid generation of apoplastic ROS upon PAMP perception plays an important role in the activation of disease resistance mechanisms in plants (Qi et al., 2017). To test whether the predicted NLS-containing T3Es could suppress innate immunity, the ability to suppress PAMP-triggered ROS production for the 6 T3Es that did not induce cell death was assayed in N. benthamiana. We used flg22, the active epitope of bacterial flagellin perceived by the receptor flagellin sensitive2 (FLS2) in N. benthamiana as an elicitor in this experiment (Hann and Rathjen, 2007; Heese et al., 2007). AvrPto, a T3E from Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato that suppresses flg22-triggered ROS production, was used as a positive control (Hann and Rathjen, 2007). We found that RipAD and RipD suppressed the flg22-induced ROS production to about 17% of GFP control (Fig. 3). RipAF1-expressing leaf tissue consistently showed delayed ROS generation in all experiments; the peak of ROS production was reached about 5 to 10 min later in RipAF1-expressing tissues than in the GFP control. However, RipAF1 expression did not reduce the total ROS production (Fig. 3B). Taken together, RipAD, RipD, and RipAF1 interfered with flg22-triggered ROS production.
At least two other Rso T3Es have been reported to impair or completely suppress flg22-triggered ROS production when expressed in planta (Mukaihara et al., 2016; Nakano et al., 2017; Sang et al., 2018). RipAL localizes to chloroplasts and the conserved catalytic residues of its predicted lipase-like domain are required for flg22-ROS suppression (Nakano et al., 2017). RipAY is a nucleocytoplasmic glutathione-degrading enzyme that associates with regulators of the plant redox balance (Mukaihara et al., 2016; Sang et al., 2018). Although RipD does not possess any conserved domains, it bears significant homology (61% similarity at the amino acid level) with XopB, a Xanthomonas euvesicatoria T3E that also suppresses flg22-ROS production when expressed in Arabidopsis thaliana or N. benthamiana (Priller et al., 2016).
PAMP perception induces defense-oriented transcriptional reprogramming (Navarro et al., 2004; Zipfel et al., 2004). To examine the effect of the selected T3Es on flg22-induced defense gene expression, we monitored expression of the well-characterized PTI marker genes NbCYP71D20, NbACRE31, and NbACRE132 in flg22-treated N. benthamiana (Heese et al., 2007; Le Roux et al., 2015; Segonzac et al., 2011). As previously shown, PopP2 expression significantly impaired the induction of NbCYP71D20 and NbACRE132 (Fig. 4) (Le Roux et al., 2015). Similarly, RipAD, RipAO, and RipD expression caused decreased NbCYP71D20 induction. RipD also reduced the expression of NbACRE31 to about 60% of the GFP control. Our data indicate that these T3Es might affect flg22-induced signaling that leads to the transcriptional reprogramming.
More than 100 genes involved in plant defense are differentially regulated during Rso infection of Arabidopsis roots (Zhao et al., 2019). This could be the result of direct interaction between T3Es and host transcription factors, as demonstrated for PopP2 (Le Roux et al., 2015; Sarris et al., 2015). Indeed, PopP2 acetylates several WRKY transcription factors, altering the expression of the WRKY target genes and thereby contributes to dampen PTI (Le Roux et al., 2015).
To correlate immuno-suppressive activity of the predicted NLS-containing T3E with subcellular localization, each T3E fused with YFP at the C-terminus was transiently expressed in N. benthamiana leaves. At 2 dpi, the T3E-YFP proteins were visualized by confocal microscopy (Fig. 5). RipAB and RipAO exclusively localized in the nucleus of epidermal cells. RipAF1 localized in both cytoplasm and the nucleus. Intriguingly, RipAD was detected in cytosol and chloroplasts, while RipD and RipL localized to vesicle-like structures. To confirm these observations, we co-expressed individual T3E-YFP with organelle markers fused with mCherry (Fig. 5). RipAB and RipAO indeed co-localized with the nucleus-mCherry marker. RipAD co-localized with the chloroplast-mCherry marker in addition to being detected in the cytosol. The vesicular structures marked with RipD-YFP also contained the ER-mCherry marker. The structures highlighted by RipL-YFP were too large to correspond to vesicles within the cytosol. We hypothesized that they could be lipid droplets, the ER-derived structures that store newly synthesized neutral lipids (Guo et al., 2009; Jacquier et al., 2013). Therefore, we cloned “lipid drop-associated protein 3-interacting protein” (AtLIDP), a gene whose product is known to localize in the lipid droplets, in fusion with C-terminal mCherry (Pyc et al., 2017). Strikingly, the RipL-YFP and AtLIDP-mCherry signals co-localized in N. benthamiana cells (Fig. 5). The stability of the T3E-YFP fusion proteins was confirmed by immunoblotting (Supplementary Fig. 3). These results show that these T3Es are localized in distinct cellular compartments where they might fulfill different functions.
Despite being predicted by two different NLS-prediction tools, it is clear that the presence of a putative NLS is insufficient for nuclear localization of some Rso T3Es. Moreover, proteins smaller than ~100 kD can diffuse passively through the nuclear pore complex independent of an NLS (Wang and Brattain, 2007). On the other hand, it is plausible that the observed localization of the nonnuclear T3Es (RipAD, RipD, and RipL) might be biased by our over-expression system. For example, it is possible that RipD-YFP accumulates in the ER due to improper processing (Strasser, 2018). Nonetheless, both RipAD and RipD suppressed flg22-triggered ROS presumably from the chloroplast and ER compartment, respectively. Therefore, different subcellular localization of the T3Es shown in this study suggests distinct mechanisms of host immune suppression by Rso T3Es.
In conclusion, our data provide an initial framework to investigate the relationships between the subcellular localization and the virulence function of several Rso T3Es. Moreover, the robust cell death-inducing activity of RipA1 and RipE1 provide an opportunity for future research to design new disease resistance strategies to bacterial wilt in Solanaceae crops.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Eunsook Park (University of Wyoming) for the kind gift of the organelle-specific marker recombinant plasmids. This work was carried out with the support of “Cooperative Research Program for Agriculture Science and Technology Development (Project PJ01317502)”, Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea and the support of National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (Project No. 2019R1I1A1A01060721, Basic Research and No. 2018R1A5A1023599, SRC). C.S. is supported by the Research Resettlement Fund for New Faculty and Creative-Pioneering Researchers Program through Seoul National University.
Notes
Electronic Supplementary Material
Supplementary materials are available at The Plant Pathology Journal website (http://www.ppjonline.org/).
References
Alfano, JR and Collmer, A 2004. Type III secretion system effector proteins: double agents in bacterial disease and plant defense. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 42:385-414.


Büttner, D 2016. Behind the lines-actions of bacterial type III effector proteins in plant cells. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 40:894-937.



Choi, S, Jayaraman, J, Segonzac, C, Park, H-J, Park, H, Han, S-W and Sohn, KH 2017. Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae type III effectors localized at multiple cellular compartments activate or suppress innate immune responses in Nicotiana benthamiana. Front Plant Sci. 8:2157



Couto, D and Zipfel, C 2016. Regulation of pattern recognition receptor signalling in plants. Nat Rev Immunol. 16:537-552.


de Lange, O, Schreiber, T, Schandry, N, Radeck, J, Braun, KH, Koszinowski, J, Heuer, H, Strauß, A and Lahaye, T 2013. Breaking the DNA-binding code of Ralstonia solanacearum TAL effectors provides new possibilities to generate plant resistance genes against bacterial wilt disease. New Phytol. 199:773-786.


Deslandes, L and Genin, S 2014. Opening the Ralstonia solanacearum type III effector tool box: insights into host cell subversion mechanisms. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 20:110-117.


Deslandes, L, Olivier, J, Peeters, N, Feng, DX, Khounlotham, M, Boucher, C, Somssich, I, Genin, S and Marco, Y 2003. Physical interaction between RRS1-R, a protein conferring resistance to bacterial wilt, and PopP2, a type III effector targeted to the plant nucleus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 100:8024-8029.



Deslandes, L and Rivas, S 2011. The plant cell nucleus: a true arena for the fight between plants and pathogens. Plant Signal Behav. 6:42-48.


Engler, C and Marillonnet, S 2014. Golden Gate cloning. In: DNA cloning and assembly methods, eds. by S Valla and R Lale, 119-131. Humana Press, Totowa, NJ, USA.

Fujiwara, S, Kawazoe, T, Ohnishi, K, Kitagawa, T, Popa, C, Valls, M, Genin, S, Nakamura, K, Kuramitsu, Y, Tanaka, N and Tabuchi, M 2016. RipAY, a plant pathogen effector protein, exhibits robust γ-glutamyl cyclotransferase activity when stimulated by eukaryotic thioredoxins. J Biol Chem. 291:6813-6830.



Genin, S and Denny, T 2012. Pathogenomics of the Ralstonia solanacearum species complex. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 50:67-89.


Gimenez-Ibanez, S, Hann, DR, Chang, JH, Segonzac, C, Boller, T and Rathjen, J 2018. Differential suppression of Nicotiana benthamiana innate immune responses by transiently expressed Pseudomonas syringae type III effectors. Front Plant Sci. 9:688



Guéneron, M, Timmers, AC, Boucher, C and Arlat, M 2000. Two novel proteins, PopB, which has functional nuclear localization signals, and PopC, which has a large leucine-rich repeat domain, are secreted through the hrp-secretion apparatus of Ralstonia solanacearum. Mol Microbiol. 36:261-277.


Guo, Y, Cordes, KR, Farese, RV Jr and Walther, TC 2009. Lipid droplets at a glance. J Cell Sci. 122:749-752.



Hann, DR and Rathjen, J 2007. Early events in the pathogenicity of Pseudomonas syringae on Nicotiana benthamiana. Plant J. 49:607-618.


Heese, A, Hann, DR, Gimenez-Ibanez, S, Jones, AM, He, K, Li, J, Schroeder, JI, Peck, SC and Rathjen, J 2007. The receptor-like kinase SERK3/BAK1 is a central regulator of innate immunity in plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 104:12217-12222.



Hicks, SW and Galán, JE 2013. Exploitation of eukaryotic subcellular targeting mechanisms by bacterial effectors. Nat Rev Microbiol. 11:316-326.


Hogenhout, SA, Van der Hoorn, RA, Terauchi, R and Kamoun, S 2009. Emerging concepts in effector biology of plant-associated organisms. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact. 22:115-122.


Jacquier, N, Mishra, S, Choudhary, V and Schneiter, R 2013. Expression of oleosin and perilipins in yeast promotes formation of lipid droplets from the endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Sci. 126:5198-5209.


Jayaraman, J, Choi, S, Prokchorchik, M, Choi, DS, Spiandore, A, Rikkerink, EH, Templeton, MD, Segonzac, C and Sohn, KH 2017. A bacterial acetyltransferase triggers immunity in Arabidopsis thaliana independent of hypersensitive response. Sci Rep. 7:3557



Kadota, Y, Shirasu, K and Guerois, R 2010. NLR sensors meet at the SGT1-HSP90 crossroad. Trends Biochem Sci. 35:199-207.


Khan, M, Seto, D, Subramaniam, R and Desveaux, D 2018. Oh, the places they’ll go! A survey of phytopathogen effectors and their host targets. Plant J. 93:651-663.


Kosugi, S, Hasebe, M, Tomita, M and Yanagawa, H 2009. Systematic identification of cell cycle-dependent yeast nucleocytoplasmic shuttling proteins by prediction of composite motifs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 106:10171-10176.



Lacomme, C and Santa Cruz, S 1999. Bax-induced cell death in tobacco is similar to the hypersensitive response. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 96:7956-7961.



Le Roux, C, Huet, G, Jauneau, A, Camborde, L, Trémousaygue, D, Kraut, A, Zhou, B, Levaillant, M, Adachi, H, Yoshioka, H, Raffaele, S, Berthomé, R, Couté, Y, Parker, JE and Deslandes, L 2015. A receptor pair with an integrated decoy converts pathogen disabling of transcription factors to immunity. Cell. 161:1074-1088.


Li, L, Atef, A, Piatek, A, Ali, Z, Piatek, M, Aouida, M, Sharakuu, A, Mahjoub, A, Wang, G, Khan, S, Fedoroff, NV, Zhu, J-K and Mahfouz, MM 2013. Characterization and DNA-binding specificities of Ralstonia TAL-like effectors. Mol Plant. 6:1318-1330.



Macho, A 2016. Subversion of plant cellular functions by bacterial type-III effectors: beyond suppression of immunity. New Phytol. 210:51-57.


Macho, AP and Zipfel, C 2015. Targeting of plant pattern recognition receptor-triggered immunity by bacterial type-III secretion system effectors. Curr Opin Microbiol. 23:14-22.


Marois, E, Van den Ackerveken, G and Bonas, U 2002. The Xanthomonas type III effector protein AvrBs3 modulates plant gene expression and induces cell hypertrophy in the susceptible host. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact. 15:637-646.


Motion, GB, Amaro, TM, Kulagina, N and Huitema, E 2015. Nuclear processes associated with plant immunity and pathogen susceptibility. Brief Funct Genomics. 14:243-252.



Mukaihara, T, Hatanaka, T, Nakano, M and Oda, K 2016. Ralstonia solanacearum type III effector RipAY is a glutathione-degrading enzyme that is activated by plant cytosolic thioredoxins and suppresses plant immunity. mBio. 7:e00359-16.




Nakano, M, Oda, K and Mukaihara, T 2017. Ralstonia solanacearum novel E3 ubiquitin ligase (NEL) effectors RipAW and RipAR suppress pattern-triggered immunity in plants. Microbiology. 163:992-1002.


Navarro, L, Zipfel, C, Rowland, O, Keller, I, Robatzek, S, Boller, T and Jones, JDG 2004. The transcriptional innate immune response to flg22. Interplay and overlap with Avr gene-dependent defense responses and bacterial pathogenesis. Plant Physiol. 135:1113-1128.



Newman, TE, Lee, J, Williams, SJ, Choi, S, Halane, MK, Zhou, J, Solomon, P, Kobe, B, Jones, JDG, Segonzac, C and Sohn, KH 2019. Autoimmunity and effector recognition in Arabidopsis thaliana can be uncoupled by mutations in the RRS1-R immune receptor. New Phytol. 222:954-965.


Nguyen Ba, AN, Pogoutse, A, Provart, N and Moses, AM 2009. NLStradamus: a simple Hidden Markov Model for nuclear localization signal prediction. BMC Bioinformatics. 10:202



Nimchuk, ZL, Fisher, EJ, Desveaux, D, Chang, JH and Dangl, JL 2007. The HopX (AvrPphE) family of Pseudomonas syringae type III effectors require a catalytic triad and a novel N-terminal domain for function. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact. 20:346-357.


Park, E, Lee, H-Y, Woo, J, Choi, D and Dinesh-Kumar, SP 2017. Spatiotemporal monitoring of Pseudomonas syringae effectors via type iii secretion using split fluorescent protein fragments. Plant Cell. 29:1571-1584.



Peart, JR, Cook, G, Feys, BJ, Parker, JE and Baulcombe, DC 2002. An EDS1 orthologue is required for N-mediated resistance against tobacco mosaic virus. Plant J. 29:569-579.


Peeters, N, Carrère, S, Anisimova, M, Plener, L, Cazalé, A-C and Genin, S 2013a. Repertoire, unified nomenclature and evolution of the Type III effector gene set in the Ralstonia solanacearum species complex. BMC Genomics. 14:859


Peeters, N, Guidot, A, Vailleau, F and Valls, M 2013b. Ralstonia solanacearum, a widespread bacterial plant pathogen in the post-genomic era. Mol Plant Pathol. 14:651-662.


Poueymiro, M, Cunnac, S, Barberis, P, Deslandes, L, Peeters, N, Cazale-Noel, A-C, Boucher, C and Genin, S 2009. Two type III secretion system effectors from Ralstonia solanacearum GMI1000 determine host-range specificity on tobacco. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact. 22:538-550.


Priller, JPR, Reid, S, Konein, P, Dietrich, P and Sonnewald, S 2016. The Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria type-3 effector XopB inhibits plant defence responses by interfering with ROS production. PLoS ONE. 11:e0159107



Pyc, M, Cai, Y, Gidda, SK, Yurchenko, O, Park, S, Kretzschmar, FK, Ischebeck, T, Valerius, O, Braus, GH, Chapman, KD, Dyer, JM and Mullen, RT 2017. Arabidopsis lipid droplet-associated protein (LDAP) - interacting protein (LDIP) influences lipid droplet size and neutral lipid homeostasis in both leaves and seeds. Plant J. 92:1182-1201.


Qi, J, Wang, J, Gong, Z and Zhou, J-M 2017. Apoplastic ROS signaling in plant immunity. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 38:92-100.


Qiu, W, Park, J-W and Scholthof, HB 2002. Tombusvirus p19-mediated suppression of virus-induced gene silencing is controlled by genetic and dosage features that influence pathogenicity. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact. 15:269-280.


Sang, Y and Macho, A 2017. Analysis of PAMP-triggered ROS burst in plant immunity. In: Plant pattern recognition receptors, eds. by L Shan and P He, 143-153. Humana Press, New York NY, USA.

Sang, Y, Wang, Y, Ni, H, Cazalé, A-C, She, Y-M, Peeters, N and Macho, A 2018. The Ralstonia solanacearum type III effector RipAY targets plant redox regulators to suppress immune responses. Mol Plant Pathol. 19:129-142.


Sarris, PF, Duxbury, Z, Huh, SU, Ma, Y, Segonzac, C, Sklenar, J, Derbyshire, P, Cevik, V, Rallapalli, G, Saucet, SB, Wirthmueller, L, Menke, FLH, Sohn, KH and Jones, JDG 2015. A plant immune receptor detects pathogen effectors that target WRKY transcription factors. Cell. 161:1089-1100.


Schandry, N, de Lange, O, Prior, P and Lahaye, T 2016. TALE-like effectors are an ancestral feature of the Ralstonia solanacearum species complex and converge in DNA targeting specificity. Front Plant Sci. 7:1225



Segonzac, C, Feike, D, Gimenez-Ibanez, S, Hann, DR, Zipfel, C and Rathjen, J 2011. Hierarchy and roles of pathogen-associated molecular pattern-induced responses in Nicotiana benthamiana. Plant Physiol. 156:687-699.



Sohn, KH, Segonzac, C, Rallapalli, G, Sarris, PF, Woo, JY, Williams, SJ, Newman, TE, Paek, KH, Kobe, B and Jones, JDG 2014. The nuclear immune receptor RPS4 is required for RRS1SLH1-dependent constitutive defense activation in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS Genet. 10:e1004655



Solé, M, Popa, C, Mith, O, Sohn, KH, Jones, JDG, Deslandes, L and Valls, M 2012. The awr gene family encodes a novel class of Ralstonia solanacearum type III effectors displaying virulence and avirulence activities. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact. 25:941-953.


Strasser, R 2018. Protein quality control in the endoplasmic reticulum of plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 69:147-172.



Sun, Y, Li, P, Shen, D, Wei, Q, He, J and Lu, Y 2019. The Ralstonia solanacearum effector RipN suppresses plant PAMP-triggered immunity, localizes to the endoplasmic reticulum and nucleus, and alters the NADH/NAD+ ratio in Arabidopsis. Mol Plant Pathol. 20:533-546.



Wang, R and Brattain, MG 2007. The maximal size of protein to diffuse through the nuclear pore is larger than 60kDa. FEBS Lett. 581:3164-3170.



Wei, Y, Sang, Y and Macho, A 2017. The Ralstonia solanacearum type III effector RipAY is phosphorylated in plant cells to modulate its enzymatic activity. Front Plant Sci. 8:1899.

Zhao, C, Wang, H, Lu, Y, Hu, J, Qu, L, Li, Z, Wang, D, He, Y, Valls, M, Coll, NS, Chen, Q and Lu, H 2019. Deep sequencing reveals early reprogramming of Arabidopsis root transcriptomes upon Ralstonia solanacearum infection. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact. 32:813-827.


Zheng, X, Li, X, Wang, B, Cheng, D, Li, Y, Li, W, Huang, M, Tan, X, Zhao, G, Song, B, Macho, AP, Chen, H and Xie, C 2019. A systematic screen of conserved Ralstonia solanacearum effectors reveals the role of RipAB, a nuclear-localized effector that suppresses immune responses in potato. Mol Plant Pathol. 20:547-561.



Fig. 1
RipA1 and RipE1 induce cell death in Nicotiana spp. N. benthamiana (N.b) and N. tabacum (N.t) leaves were infiltrated with Agrobacterium tumefaciens AGL1 strain carrying C-terminally 3×FLAG-tagged T3E, BAX, or PopP2. Photographs were taken 4 days post-infiltration. The number of patches showing cell death out of total infiltrated patches for that treatment in more than three independent experiments is indicated under each photograph panel.
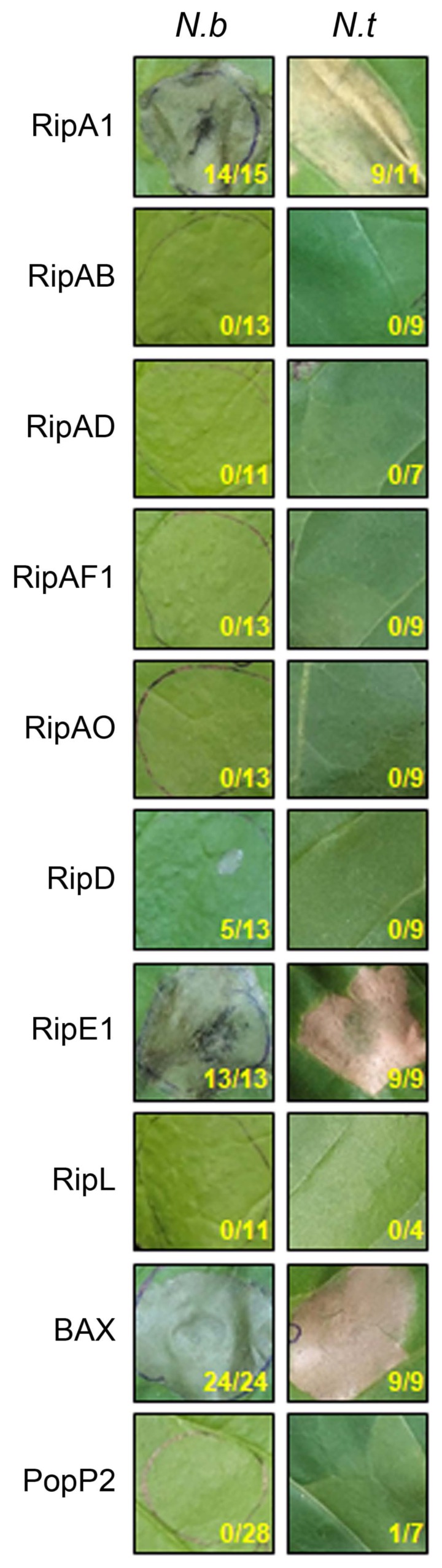
Fig. 2
NbSGT1 is required for cell death triggered by RipE1. (A) Effector-triggered cell death in silenced plants. Nicotiana benthamiana plants silenced for EV or NbSGT1 were infiltrated with Agrobacterium tumefaciens AGL1 strain carrying RipA1, RipE1, BAX, or GFP (as in Fig. 1). Photographs were taken 7 days post-infiltration. The number of patches showing cell death out of total infiltrated patches for that treatment in three independent experiments is indicated under each photograph panel. (B) Analysis of NbSGT1 gene expression in silenced plants. NbSGT1 and NbActin gene-specific fragments were amplified by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction..
Fig. 3
RipAD, RipAF1, and RipD impair flg22-induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. ROS production upon treatment with 100 nM flg22 was continuously recorded for 75 min for Nicotiana benthamiana leaf tissue expressing T3E, GFP, or AvrPto. (A) ROS production curve over duration of the experiment, and (B) total ROS production for the experiment. Data presented in (A) are mean ± standard error of mean (SEM; n = 16) of relative light units (RLU) from one representative experiment. Total ROS production (B) is presented as mean percentage relative to total ROS production in GFP from one representative experiment. A statistically significant difference compared to GFP-expressing leaf is indicated by asterisks (Student’s t-test, ***P < 0.001).

Fig. 4
RipAD, RipAO, and RipD impair flg22-induced defense gene expression. Induction of defense marker gene expression in Nicotiana benthamiana leaf tissue expressing T3E or GFP was monitored 60 min after 100 nM flg22 treatment. Mock treatment (water) in GFP-expressing leaf is included as a negative control. Gene expression was normalized by NbEF1α expression and is shown as the ratio of expression level (%) compared to flg22-treated GFP sample. Data presented are the mean of three independent experiments ± standard error of mean (n = 3). Statistical significance compared to GFP-expressing leaf is indicated by asterisks (Student’s t-test, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001).
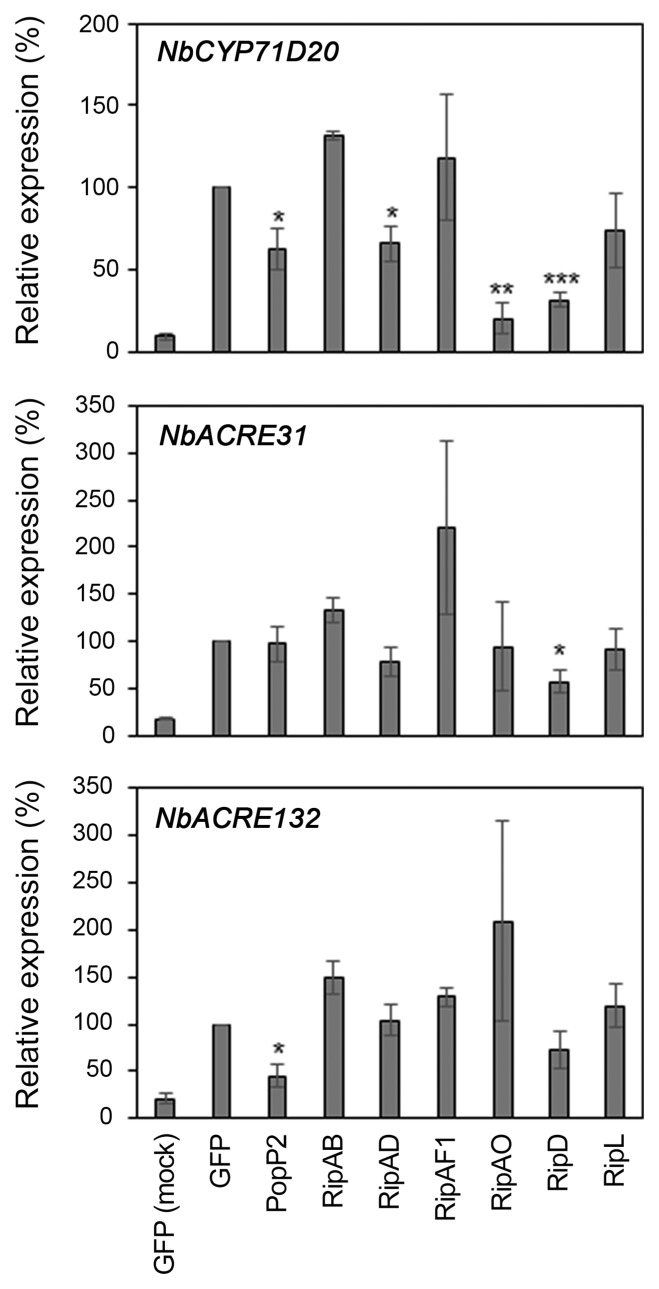
Fig. 5
Subcellular localization of the predicted nuclear localization signal-containing T3Es. Nicotiana benthamiana leaves were infiltrated with Agrobacterium tumefaciens AGL1 strain carrying YFP-tagged T3E and different organelle markers fused with mCherry (-mC) as indicated. Fluorescence was observed 2 days post-infiltration by confocal microscopy. Pictures are representative of three independent experiments. Scale bars = 25 μm (RipAD, RipAB, RipAO, and RipD), 50 μm (RipL), 10 μm (RipAF1).
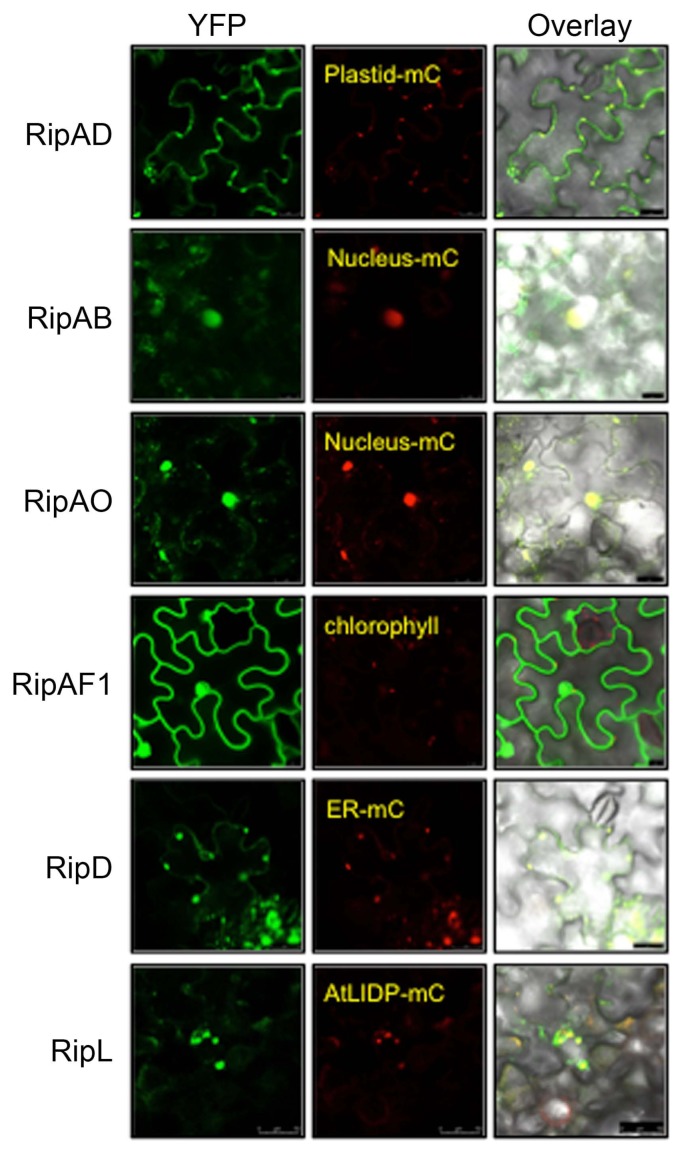
Table 1
Ralstonia solanacearum type III effectors with predicted NLS
| Name | Gene IDa | Protein lengthb | Predicted NLS | Description | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
||||||
| NLStradamusc | cNLS Mapper (score)d | |||||
| RipAI | RSp0838 | 170 | 61 - KRRRKPETRQRLHRLRK - 77 | - | - | - |
| RipAB | RSp0876 | 174 | 112 - GKKKKKR - 118 | 93 - SGGKRKRDDE -112 (8); 112 - GKKKKKRDDE - 121 (5) | NLS harboring protein | Guéneron et al. (2000), Zheng et al. (2019) |
| RipAD | RSp1601 | 310 | 114 - ARAKSGKK - 121 | - | ||
| RipAF1 | RSp0822 | 350 | 33 - PPRRPKNR - 40 | - | Putative ADPribosyltransferase | |
| RipAY | RSp1022 | 416 | 26 - PRKKNGSPPRRA - 37 | - | γ-glutamyl cyclotransferase | Fujiwara et al. (2016), Mukaihara et al. (2016), Wei et al. (2017), Sang et al. (2018) |
| RipE1 | RSc3369 | 425 | 407 - RRRARRAALGK - 417 | - | - | - |
| RipAO | RSp0879 | 498 | 210 - RPAPMRQAARPAPPPARAP - 228 | - | - | - |
| RipD | RSp0304 | 643 | 184 - PRRKPS - 189 | - | - | - |
| RipH1 | RSc1386 | 765 | 466 - RPAGASGGMRRKHRKPGMR - 484 | - | - | - |
| RipA1 | RSc2139 | 1,063 | 91 - KPAPRRMRPPAAPGRKH - 107 | - | AWR motif | Solé et al. (2012) |
| RipA2 | RSp0099 | 1,127 | 88 - PKAP - 91 | - | AWR motif | Solé et al. (2012) |
| RipTAL | RSc1815 | 1,245 | 185 - RSARARR - 191; 980 - RIRR - 983 | 1107 - PHRKRPAETAI - 1117 (5.5) | Transcription activator-like protein | de Lange et al. (2013), Li et al. (2013), Schandry et al. (2016) |
| RipA4 | RSp0847 | 1,330 | 35 - KAPRK - 39; 832 - KRRLRHKLR - 840 | 683 - RKRQAVVEF - 691 (8); 829 - DQRKRRLRHK - 838 (6) | AWR motif | Solé et al. (2012) |
| RipL | RSp0193 | 1,403 | 1387 - QPSKSKGKGTKGKGKAK - 1403 | - | Pentatricopeptide Repeats | - |
| RipR | RSp1281 | 1,742 | 190 - KGKIRVKAR - 198; 944 - GRRKQRRPAKAK - 955 | - | - | - |
| RipS1 | RSc3401 | 2,353 | 27 - SKPQGHRAPRAR - 38 | 2311 - RERLLKKMRDA - 2321 (5) | - | - |
| RipS2 | RSp1374 | 2,483 | 93 - APRRQRSDREPPARQAKRARHDRDAIRTETGRARTAPAPA- 133; 135 - ARDRH - 139; 142 - SDARRRAP - 149 | 26 - HPRKRNRDP - 34 (5); 59 -PAPKRQRVS - 67 (7.5); 106 -RQAKRARHD - 114 (9); 2235 - PQVNKRRAQAK - 2245 (5) | SKWP repeats | - |
| RipS3 | RSp0930 | 2,291 | 1554 - RKKRRGQQRSFKPRK - 1568 | 108 - RIPLKRKREAG - 117 (10); 1550- VMDDRKKRRGQQRSF - 1564 (6) | SKWP repeats | - |
| RipS4 | RSc1839 | 2,570 | 2551 - PHRPQRPERPQQGKRAGHRP - 2570 | SKWP repeats | - | |
a From GMI1000 in Ralsto T3E database (https://iant.toulouse.inra.fr/T3E).
c Predicted by NLStradamus (www.moseslab.csb.utoronto.ca/NLStradamus), prediction cutoff = 0.6.
d Predicted by cNLS mapper (http://nls-mapper.iab.keio.ac.jp), cutoff score = 5.




 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Full text via PMC
Full text via PMC Download Citation
Download Citation Supplement
Supplement Print
Print