Chung, E.-K., Zhang, X.-Z., Yeoung, Y.-R. and Kim, B.-S. 2003. Screening of effective control agents against bacterial soft rot on Chinese cabbage in alpine area. Korean J. Pestic. Sci. 7:32-37.
Cui, W., He, P., Munir, S., He, P., He, Y., Li, X., Yang, L., Wang, B., Wu, Y. and He, P. 2019. Biocontrol of soft rot of Chinese cabbage using an endophytic bacterial strain.
Front. Microbiol. 10:1471.



De Boer, S. H. and Kelman, A. 1978. Influence of oxygen concentration and storage factors on susceptibility of potato tubers to bacterial soft rot (
Erwinia carotovora).
Potato Res. 21:65-79.


Enya, J., Ikeda, K., Takeuchi, T., Horikoshi, N., Higashi, T., Sakai, T., Iida, Y., Nishi, K. and Kubota, M. 2009. The first occurrence of leaf mold of tomato caused by races 4.9 and 4.9.11 of
Passalora fulva (syn.
Fulvia fulva) in Japan.
J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 75:76-79.


Foster, J. M. and Hausbeck, M. K. 2009. Resistance of pepper to Phytophthora crown, root, and fruit rot is affected by isolate virulence.
Plant Dis. 94:24-30.

Hahm, Y.-I., Kwon, M., Kim, J.-S., Seo, H.-W. and Ahn, J.-H. 1998. Surveys on disease occurrence in major horticultural crops in Kangwon alpine areas. Korean J. Plant Pathol. 14:668-675.
Hibberd, A. M., Bassett, M. J. and Stall, R. E. 1987. Allelism tests of three dominant genes for hypersensitive resistance to bacterial spot of pepper.
Phytopathology 77:1304-1307.

Hirai, M. 2006. Genetic analysis of clubroot resistance in
Brassica crops.
Breed. Sci. 56:223-229.

Hong, S.-M., Park, K.-T., Ten, L. N., Back, C.-G., Kang, I.-K., Lee, S.-Y. and Jung, H.-Y. 2023. First report of soft rot caused by
Pectobacterium brasiliense on cucumber in Korea.
Res. Plant Dis. 29:304-309.


James, R. V. and Williams, P. H. 1980. Clubroot resistance and linkage in
Brassica campestris.
Phytopathology 70:776-779.

Jee, S., Choi, J.-G., Lee, Y.-G., Kwon, M., Hwang, I. and Heu, S. 2020. Distribution of
Pectobacterium species isolated in South Korea and comparison of temperature effects on pathogenicity.
Plant Pathol. J. 36:346-354.




Jee, S., Malhotra, S., Roh, E., Jung, K., Lee, D., Choi, J., Yoon, J. and Heu, S. 2012. Isolation of bacteriophages which can infect Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum. Res. Plant Dis. 18:225-230 (in Korean).
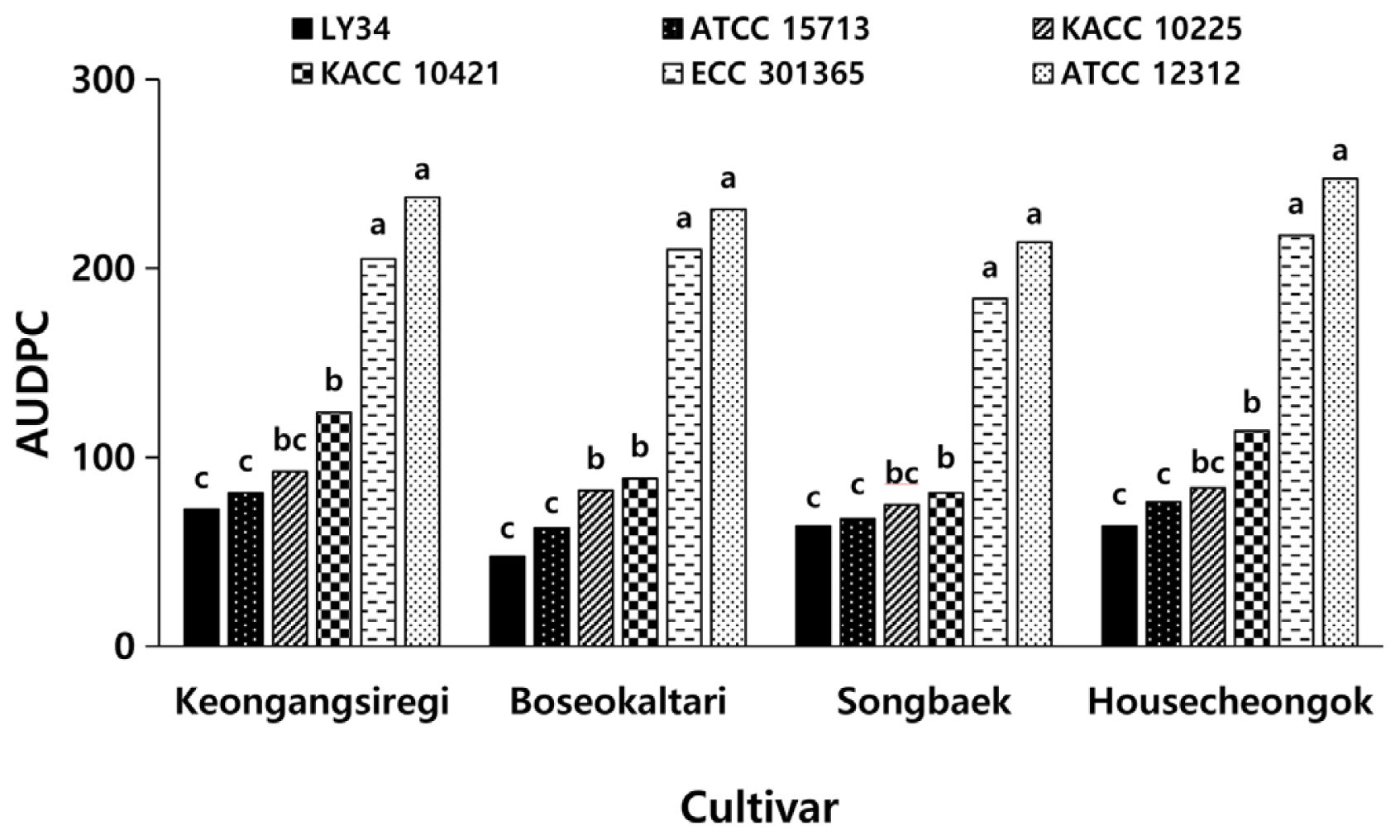
Jeger, M. J. and Viljanen-Rollinson, S. L. H. 2001. The use of the area under the disease-progress curve (AUDPC) to assess quantitative disease resistance in crop cultivars.
Theor. Appl. Genet. 102:32-40.


Jo, S.-J., Shim, S.-A., Jang, K. S., Choi, Y. H., Kim, J.-C. and Choi, G. J. 2014. Resistance of chili pepper cultivars to isolates of
Phytophthora capsici.
Korean J. Hortic. Sci. Technol. 32:66-76 (in Korean).

Jo, E. J., Jang, K. S., Choi, Y. H., Ahn, K. G. and Choi, G. J. 2016. Resistance of cabbage plants to isolates of
Plasmodiophora brassicae.
Korean J. Hortic. Sci. Technol. 34:442-452 (in Korean).

Kim, H., Jo, E. J., Choi, Y. H., Jang, K. S. and Choi, G. J. 2016. Pathotype classification of
Plasmodiophora brassicae isolates using clubroot-resistant cultivar of Chinese cabbage.
Plant Pathol. J. 32:423-430.


Korean Society of Plant Pathology 2022. List of Plant Disease in Korea. Radish. 6th ed. Korean Society of Plant Pathology. Seoul, Korea. pp. 165-168.
Kuginuki, Y., Yoshikawa, H. and Hirai, M. 1999. Variation in virulence of Plasmodiophora brassicae in Japan tested with clubroot-resistant cultivars of Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa L. ssp. pekinensis). Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 105:327-332.
Lee, J. H., Lee, J. and Oh, D.-G. 2018a. Resistance of pepper cultivars to
Ralstonia solanacearum isolates from major cultivated areas of chili peppers in Korea.
Hortic. Sci. Technol. 36:569-576.

Lee, S. M., Choi, Y. H., Jang, K. S., Kim, H., Lee, S.-W. and Choi, G. J. 2018b. Development of an efficient bioassay method for testing resistance to bacterial soft rot of radish.
Res. Plant Dis. 24:193-201 (in Korean).


Lee, S. M., Lee, J. H., Jang, K. S., Choi, Y. H., Kim, H. and Choi, G. J. 2020. Resistance of commercial radish cultivars to strains of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. raphani. Hortic. Sci. Technol. 38:97-106.
Madden, L. V., Hughes, G. and van den Bosch, F. 2007. The study of plant disease epidemics. APS Press, St. Paul, MN, USA. pp. 421.
Park, D. H., Seo, S. T., Lee, H. G., Choi, G. S. and Lim, C. K. 1999. Bacterial soft rot of radish by Erwinia chrysanthemi. Plant Dis. Agric. 5:61-63.
Park, K.-T., Hong, S.-M., Back, C.-G., Cho, Y.-J., Lee, S.-Y., Ten, L. N. and Jung, H.-Y. 2023a. First report of
Pectobacterium versatile as the causal pathogen of soft rot in kimchi cabbage in Korea.
Res. Plant Dis. 29:72-78.


Park, K.-T., Hong, S.-M., Back, C.-G., Kang, I.-K., Lee, S.-Y., Ten, L. N. and Jung, H.-Y. 2023b.
Pectobacterium brasiliense as a causative agent for soft rot of radish in Korea.
Res. Plant Dis. 29:64-71.


Park, K.-T., Hong, S.-M., Ten, L. N., Back, C.-G., Lee, S.-Y., Kang, I.-K. and Jung, H.-Y. 2023c. First report of
Pectobacterium aroidearum causing soft rot on
Zamioculcas zamiifolia.
Res. Plant Dis. 29:445-451.


Park, K.-T., Ten, L. N., Back, C.-G., Hong, S.-M., Lee, S.-Y., Han, J.-S. and Jung, H.-Y. 2023d. First report of melon soft rot disease caused by
Pectobacterium brasiliense in Korea.
Res. Plant Dis. 29:310-315.


Park, K.-T., Ten, L. N., Hong, S.-M., Back, C.-G., Lee, S.-Y. and Jung, H.-Y. 2023e. First report of
Pectobacterium brasiliense causing bitter melon soft rot disease in Korea.
Res. Plant Dis. 29:452-458.


Park, Y. W., Lim, S. T. and Yun, H. D. 1998. Cloning and characterization of a CMCase gene, celB, of
Erwinia carotovra subsp.
carotovora LY34 and its comparison to
celA.
Mol. Cells 8:280-285.

Perombelon, M. C. M. and Salmond, G. P. C. 1995. Bacterial soft rot. In: Pathogenesis and host specificity in plant diseases, Vol. 1. Prokaryotes, eds. by U. S. Singh, R. P. Singh and K. Kohmoto, pp. 1-20. Pergamon, Oxford, UK.
Ramirez-Villupadua, J., Endo, R. M., Bosland, P. and Williams, P. H. 1985. A new race of
Fusarium oxysporum f. sp.
conglutinans that attacks cabbage type A resistance.
Plant Dis. 69:612-613.

Rimmer, S. R. 2007. Bacterial soft rot. In: Compendium of Brassica disease, eds. by S. R. Rimmer, V. I. Shattuck and L. Buchwaldt, pp. 59-60. APS Press, St. Paul, MN, USA.
Risser, G., Banihashemi, Z. and Davis, D. W. 1976. A proposed nomenclature of
Fusarium oxysporum f. sp.
melonis races and resistance genes in
Cucumis melo.
Phytopathology 66:1105-1106.

Shrestha, A., Kim, E. C., Lim, C. K., Cho, S., Hur, J. H. and Park, D. H. 2009. Biological control of soft rot on Chinese cabbage using beneficial bacterial agents in greenhouse and field. Korean J. Pestic. Sci. 13:325-331.
Takken, F. L. W., Schipper, D., Nijkamp, H. J. J. and Hille, J. 1998. Identification and
Ds-tagged isolation of a new gene at the
Cf-4 locus of tomato involved in disease resistance to
Cladosporium fulvum race 5.
Plant J. 14:401-411.



Taylor, J. D., Conway, J., Roberts, S. J., Astley, D. and Vincente, J. G. 2002. Sources and origin of resistance to
Xanthomonas campestris pv.
campestris in Brassica genomes.
Phytopathology 92:105-111.


Tsuda, K., Tsuji, G., Higashiyama, M., Ogiyama, H., Umemura, K., Mitomi, M., Kubo, Y. and Kosaka, Y. 2016. Biological control of bacterial soft rot in Chinese cabbage by
Lactobacillus plantarum strain BY under field conditions.
Biol. Control 100:63-69.

Vijeth, S., Dhaliwal, M. S., Jindal, S. K. and Sharma, A. 2018. Evaluation of tomato hybrids for resistance to leaf curl virus disease and for high-yield production.
Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 59:699-709.


Wright, P. J., Triggs, C. M. and Burge, G. K. 2005. Control of bacterial soft rot of calla (
Zantedeschia spp.) by pathogen exclusion, elimination and removal.
N. Z. J. Crop Hortic. Sci. 33:117-123.

Yang, S. S., Sung, N. K., Choi, D. I. and Kim, C. H. 1989. Pathogenic variation of Phytophthora capsici Leonian on red-pepper in Korea. Korean J. Plant Pathol. 5:370-376.
Yerasu, S. R., Murugan, L., Halder, J., Prasanna, H. C., Singh, A. and Singh, B. 2019. Screening tomato genotypes for resistance to early blight and American serpentine leafminer.
Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 60:427-433.


Yoshikawa, H. 1993. Studies on breeding of clubroot resistance in cole (Cruciferae) crop. Bull. Natl. Res. Inst. Veg. Ornam. Plants Tea Ser. A. 7:1-165.






 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print