 |
 |
| Plant Pathol J > Volume 30(4); 2014 > Article |
Abstract
Leaf scald caused by the infection of Rhynchosporium secalis, is a worldwide crop disease resulting in significant loss of barley yield. In this study, a systematic sequencing of expressed sequence tags (ESTs) was chosen to obtain a global picture of the assembly of genes involved in pathogenesis. To identify a large number of plant ESTs, which are induced at different time points, an amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) display of complementary DNA (cDNA) was utilized. Transcriptional changes of 140 ESTs were observed, of which 19 have no previously described function. Functional annotation of the transcripts revealed a variety of infection-induced host genes encoding classical pathogenesis-related (PR) or genes that play a role in the signal transduction pathway. The expression analyses by a semi-quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) revealed that Rar1 and Rpg4 are defense inducible genes, and were consistent with the cDNA-AFLP data in their expression patterns. Hence, the here presented transcriptomic approach provides novel global catalogue of genes not currently represented in the EST databases.
Rhynchosporium secalis (Oudem.) J. J. Davis, the causal agent of scald, is an important global disease of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.), responsible for large economic losses in cool and humid areas of temperate zones (Wagner, 2008). Crop rotations, fungicides, or resistant cultivars may control it. The latter, however, depends critically on a clear perception of the interaction between host and pathogen, which in turn requires a well-characterized set of differential cultivars or differential isolates (Walters et al., 2012). However, it is highly challenging to control this disease in barley due to a poor understanding of the mechanisms of plant resistance and since no highly resistant barley cultivar is yet available (Bj├Ėrnstad et al., 2002).
Significant advances have been achieved in understanding the molecular basis of plant-pathogen interactions, especially in specific race-cultivar interactions (Looseley, 2012; Wagner, 2008). However, using Amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) display of complementary DNA (cDNA) technique that scrutiny can reveal altered expression of any gene that carries suitable restriction sites leads to an accurate way for understanding plant responses to pathogens (Baldwin et al., 1999; Wendy et al., 2000). The cDNA-AFLP approach, once established, is an efficient and economical method to display whole transcript profiles of single tissues, specific developmental stages or other inducible characters (Bachem et al., 1996).
Transcript profiles and spatial expression patterns of genes provide an important basis for functional analysis of unknown genes by correlating those patterns with biological process of interest (Vuylsteke et al., 2007). In addition, studying global gene expression coordinately expressed genes can help to discover the networks involved in the process (Al-Daoude and Jawhar, 2009).
Stages of R. secalis infection in barley are well characterized (Lehnackers and Knogge, 1990), and each stage is a potential recognition point with the possible release of pathogen or plant-derived signaling molecules. Significant variation occurs, however, at the early stages of infection. Linsell et al. (2011) reported that at early stages of infection, fungal attachment and germination are accompanied by the release of proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, glycoproteins, and peptides from the spores, and many of these molecules can trigger general host defense responses (Steiner-Lange et al., 2003). In addition, primary germ tubes are also capable of breaching host epidermal walls leading to the initiation of cytoplasmic aggregates in underlying host cells (Lehnackers and Knogge, 1990). Therefore, the initial induction of defense responses most likely occurs at the early stages of infection and is possibly the result of synergistic effects of recognition of multiple pathogen-derived molecules.
However, in spite of the fact that scald disease exerts a substantial impact on barley production in many regions of the world; limited information is available about the genetic background and regulation of interaction mechanisms in resistant scald barley genotypes during the early phase of infection. Therefore, the primary objective of this research was to monitor the global response of the assembly of barley genes differentially expressed during early interaction stages between the fungal pathogen R. secalis and the barley resistant genotype Banteng, via cDNA-AFLP method.
The Syrian pathotype R. secalis (Rs46) used in the study was the most virulent of 115 isolates collected in 1997 and 2006 from naturally infected barley in different regions of Syria, as described by Arabi et al. (2010). The fungal mycelia were transferred from a stock culture into Petri dishes containing lima bean agar (LBA) with 13 mg/l kanamycin sulphate and incubated for 2 weeks at 15 ┬▒ 1┬░C in the dark. Then, conidia were collected with 10 ml of sterile distilled water. The conidial suspension was adjusted to 0.5├Ś106 conidia/ml using hemacytometer counts of conidia to provide estimates of the inoculum concentration. A surfactant (polyoxyethylene-20-sorbitan monolaurate) was added (100 ╬╝l/l) to the conidial suspension to facilitate dispersion of the inoculum over the leaf surfaces.
After an extensive screening for several years in the greenhouse and laboratory experiments, the German cv. Banteng was proved to be the most resistant genotype to all scald isolates available so far. Therefore, it was selected for the cDNA-AFLP analysis. Inoculation tests of Rs46 isolate was performed using the method described by Arabi et al. (2010). Seeds were surface-sterilized with 5% sodium hypochlorite solution for 5 min, washed three times in sterile distilled water, then planted in plastic flats (60├Ś40├Ś8 cm) filled with sterilized peatmoss, and arranged in a randomized complete block design with three replicates. Each experimental unit consisted of two rows of 18 seedlings. Flats were placed in a growth chamber at 22┬▒1┬║C (day) and 17┬▒1┬║C (night) with a day length of 12 h and a relative humidity of 80-90%. Seedlings were irrigated with KnopŌĆÖs nutrient solution (1g NaNO3; 0.25 g KNO3; 0.25 g MgSO4 7H2O; 0.25 g KH2PO4; and 10 mg FeCl3 per 1000 ml of water).
Plants were inoculated at growth stage 13 (Zadoks et al., 1974) by uniformly spraying each flat with 25 ml of conidial suspension with a hand-held spray bottle. After inoculation, plants were maintained in the dark at 95-100% R.H. for the first 18 h. Non-inoculated control plants were sprayed with distilled water.
Leaf samples for RNA isolation were taken at different time points post inoculation (2, 3, 4 and 5 days) according to the developmental stages of the fungus during infection (Table 1). Leaves were collected at each time point from 20 individual plants, labeled and immediately frozen in liquid N2 before they were stored at ŌłÆ80┬║C till needed. As controls, mRNA was extracted from water-treated leaves incubated under the same conditions and at the same time points. mRNA was extracted from samples (100-200 mg) with the Nucleotrap mRNA mini kit (Macherey-Nagel, MN, Germany) following the manufacturerŌĆÖs protocol.
The cDNA-AFLP protocol was performed according to the method described by Breyne et al. (2002) with minor modifications which permit the visualization of one single cDNA fragment for each messenger originally present in the sample, thus reducing the redundancy of sequences obtained. Briefly, double-stranded cDNA was synthesized from 1 ╬╝g mRNA using the Superscript II reverse transcription kit (Invitrogen, UK) and a biotinylated oligo-dT primer (Roche). The cDNA was digested with BstYI (restriction site RGATCY), and the 3ŌĆ▓ ends of the fragments were captured on streptavidin magnetic beads (Dynal). Digestion with MseI yielded fragments that were ligated to adapters for amplification (BstYI-Forw: 5ŌĆ▓-CTC GTA GAC TGC GTA GT-3ŌĆ▓; BstYI_Rev: 5ŌĆ▓-GAT CAC TAC GCA GTC TAC-3ŌĆ▓; MseI-Forw: 5ŌĆ▓-GAC GAT GAG TCC TGA G-3ŌĆ▓; MseI-Rev: 5ŌĆ▓-TAC ATC AGG ACT CAT-3ŌĆ▓). Pre-amplification was performed with an MseI primer (Mse0: 5ŌĆ▓-GAT GAG TCC TGA GTA A-3ŌĆ▓), combined with a BstYI primer carrying either a T or a C at the 3ŌĆ▓ end (BstT0: 5ŌĆ▓-GAC TGC GTA GTG ATC T-3ŌĆ▓; BstC0: 5ŌĆ▓-GAC TGC GTA GTG ATC C-3ŌĆ▓). Pre-amplification PCR conditions were as follows: 5 min denaturation at 94┬║C and then 30 s denaturation at 94┬║C, 60 s annealing at 56┬║C, 60 s extension at 72┬║C (25 cycles), followed by 5 min at 72┬║C. After preamplification, the mixture was diluted 100 folds and 4 ╬╝l was used for selective amplification with 14 primer combinations, carried out with two selective nucleotides on the MseI primer. Touch-down PCR conditions for selective amplifications were as follows: 5 min denaturation at 94┬║C, followed by 30 s denaturation at 94┬║C, 30 s annealing at 65┬║C, 60 s extension at 72┬║C (13 cycles, scale down of 0.7┬║C per cycle); 30 s denaturation at 94┬║C, 30 s annealing at 56┬║C, 60 s extension at 72┬║C (23 cycles) and 5 min at 72┬║C. Selective amplification products were separated on a 6% polyacrylamide gel in a Sequi-Gen GT Sequencing Cell (38 ├Ś 50 cm) (Bio-Rad, USA) running for 2.5 h at 105 W and 50┬║C, and silver stained (Silver Sequence kit, Promega, Cat. Q4132).
Bands of interest were excised from gels with a surgical blade and eluted in 100 ╬╝l of sterile distilled water. An aliquot of 5 ╬╝l was used as a template for reamplification using non-labeled primers identical to those employed for selective AFLP amplification. PCR products were purified with MultiScreen PCR ╬╝96 plates (Millipore) and sequenced directly (BMR Genomics). Prior to sequencing, PCR products were purified with QIAgen gel extraction kit according to the manufacturerŌĆÖs recommendations. Sequencing was carried out on a Genetic Analyzer (ABI 310, Perklin-elmer, Applied Biosystems, USA). Each sequence was identified by homology search using the Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST) program (Altschul et al., 1997) against the GenBank no redundant public sequence database using an E-value (BLASTX expectation values [E] of <10ŌłÆ5) to database entries with assigned identities.
A portion of seedling leaves was used for semi-quantitative RT-PCR analysis to validate the expression patterns detected by cDNA-AFLP. Gene specific oligonucleotides were designed from the conserved regions of plant defense related genes using sequences available in the NCBI Genbank database (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov); Rar1F: CAGGCGCCAGTAAAGAATGC; Rar1R: TGCTTGGCACTTCTACCGTT. Rpg4F: GCGTCGTCCATATTGTACAC; Rpg4R: TTGATCCGTTCGTGCTTTGG. EF1╬▒F: CCTGGTATGGTTGTGACCTTTGG; EF1╬▒R: GGGCTTGGTGGGAATCATCTTC. RT-PCR conditions were as follows: initial denaturation at 94┬║C for 5 min, followed by 20 to 25 cycles of 94┬║C for 1 min denaturation, 55┬║C for 1 min annealing and 72┬║C for 1 min extension. Final extension was carried out at 72┬║C for 7 min. The annealing temperature was varied according to the sequence of the oligonucleotide used. PCR products were visualized on 1.5% agarose gel by electrophoresis in TAE buffer system. Template used for this analysis was the cDNA from uninoculated and inoculated with R. secalis 2, 3, 4 and 5 days post inoculation.
In this study, a systematic sequencing of expressed sequence tags (ESTs) was chosen to document the early resistant barley response to R. secalis infection (Looseley, 2012). It demonstrated differential gene expression in barley leaves during the early phase of infection, before any visible symptoms are apparent in the tissues (Table 2). cDNA-AFLP analysis carried out on mRNA samples of infected leaves at different points of time, and on water-sprayed leaves (healthy control), as described by Breyne et al. (2002). Different sampling points were chosen to cover early barley responses to scald which leads within 5 days to a visible hypersensitive cell death on a resistant genotype. For each of the 8 primer combinations, 20-35 transcript derived fragments (TDFs) were visualized as bands, 50-700 bp in size, representing approximately 140 transcripts overall. Only 19 transcripts showed a differential expression pattern with cDNA-AFLP results (accession numbers in NCBI databases are given in Table 2). To determine the reproducibility of these profiles, the experiments were repeated using additional samples of a biological replicate
Based on the assumption that disease resistance involves the early recognition of the invading pathogen and the activation of defense response genes, the cDNA-AFLP patterns of resistant plants were screened for expressed fragments which occur 2, 3, 4 and 5 days after fungal attack (Fig. 1). The time points for taking samples for RNA isolation in the first experiments were chosen for captivating mRNA samples to wrap up barley response to R. secalis invasion, taking into account the findings of Xi et al. (2000) on the production of barley scald symptoms. Differentially-expressed transcripts were visually scored relative to the first sampling time point which was arbitrarily attributed a zero value.
BlastX score to sequences on the database were presented in this study (Table 2). The majority of genes were observed to be related to either metabolism or cellular defense. Among these, fragments 3 and 5 with high similarities (high BlastX scores) to barley pathogenically-induced genes including HOX1 (JZ714795) and the Rpg4 (JZ714796) appeared two days post inoculation. Moreover, fragment 140 showed strong similarities to the barley Rpg5 gene (JZ714811). The Rpg4 and Rpg5 genes are known from barley to be involved in resistance against Puccinia graminis (Wang et al., 2013). They are located on the long arm of chromosome 5H where Looseley (2012) reported a QTL in connection with barley-R. seclais symptom expression. Furthermore, over expression of particular PR-5 proteins delays or halts the onset of disease symptoms of fungal pathogens in rice (Datta et al., 1999). Additionally, Rym4 (JZ714808) appeared at 2 days of inoculation, which is the recessive bymovirus resistance locus in barley corresponding to the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E gene (Kanyuka et al., 2005). The percents of similarity are given in Table 2.
The study also identified genes believed to be involved in the signal transduction pathway. Several genes encoding for transcription factors placed in this category appeared 3 days post inoculation, including fragments that showed homology with LK2 (JZ714810), SCARECROW (JZ714803), and RIRE2 (JZ714806) (Table 2).
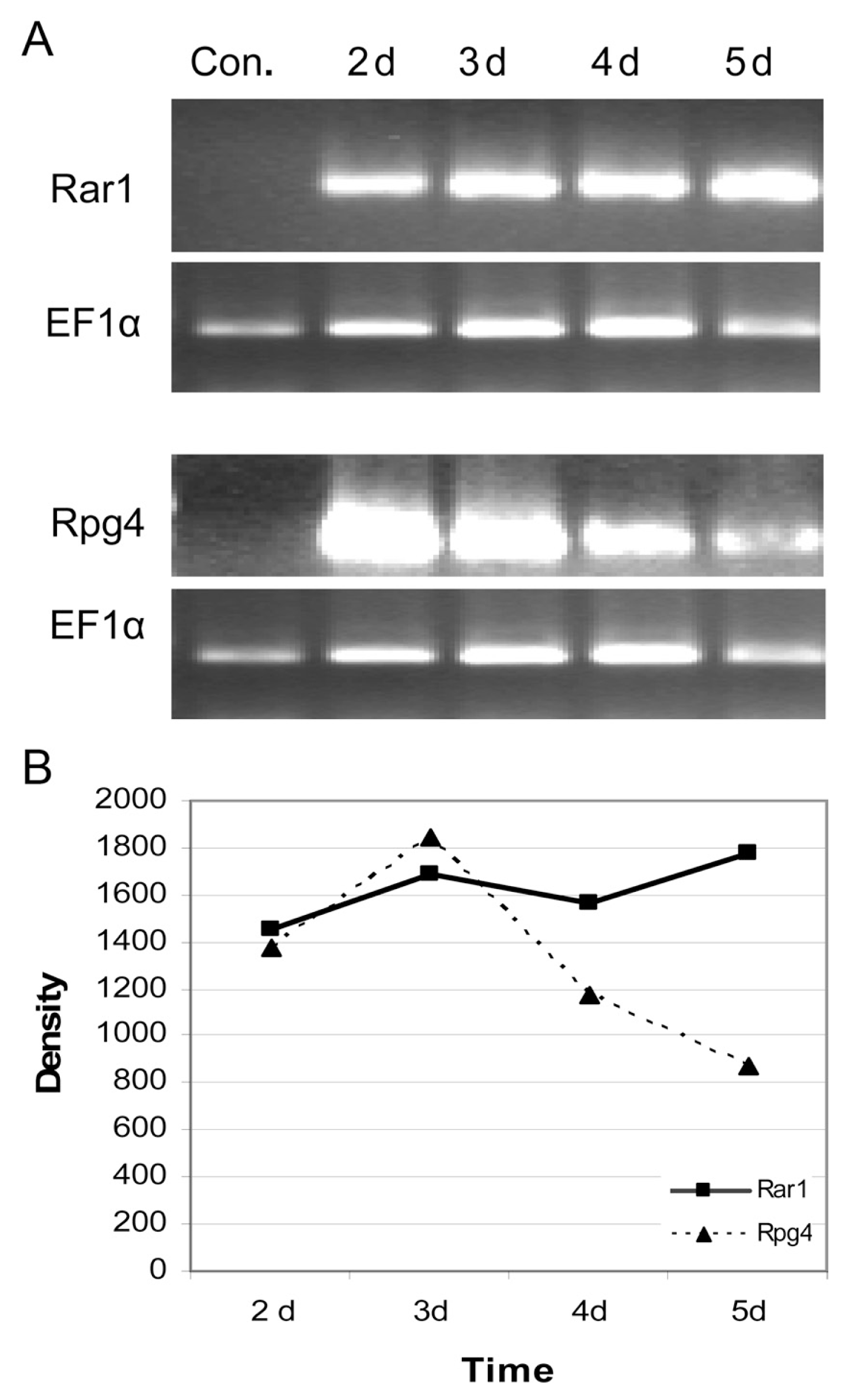
To validate the expression patterns of some R genes detected by the cDNA-AFLP, RT-PCR on candidate genes Rar1 and Rpg4 with significantly changed expression pattern before and after the infection was performed. The oligonucleotides designed from the sequence information used for RT-PCR in inoculated and non-inoculated samples could reveal consistently reproducible and differential amplification profiles. RT-PCR revealed a dramatic increase of Rar1 gene 2 days following the R. secalis inoculation, reaching its highest level of expression at day five of the infection (Fig. 2). Rar1 encodes an intracellular Zn+2 binding protein (Shirasu et al., 1999), and subsequent analyses have shown that Rar1 is required for several R gene-mediated resistance responses in monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous plant species against different pathogen classes (Shirasu and Schulze-Lefert, 2003). Barley Rar1 interacts with Sgt1 (for suppressor of G-two allele of skp1) in the yeast two-hybrid assay and in planta. Sgt1 is another intracellular protein engaged by a subset of NB-LRR R proteins (Azevedo et al., 2002). Genetically, some R genes require Rar1 or Sgt1, whereas others require both or none (reviewed in Shirasu and Schulze-Lefert, 2003). In our study, Rar1 did not require Sgt1 during R. secalis interaction (Table 2).
Rpg4 gene was down-regulated in inoculated barley plants as compared to its expression in healthy plants, suggesting its role in the first stages of defense against R. secalis attack (Fig. 2). This is concordant with the information available from barley stem rust resistance wherein, Rpg4 have been shown to respond rapidly to signals after pathogen attack (Druka et al., 2000). However, it is well known that the rpg4 gene by itself is not sufficient to confer resistance, perhaps due to failure to detect the fungus (Brueggeman et al., 2009).
The transcriptome analysis allowed the discovery of 19 ESTs having no previously described function or sequence identity in barley-R. secalis interaction, as a significant proportion of TDFs are not currently represented in barley EST databases. Database searches with the randomly isolated sequences identified a number of classical pathogenesis-related (PR) or genes that play a role in the signal transduction pathway. However, these results provide a vast amount of information that can guide hypothesis-driven research to elucidate the molecular mechanisms involved in transcriptional regulation and disease signaling networks in barley.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Director General of AECS and the Head of Biotechnology Department for their help throughout the period of this research.
Fig.┬Ā1
A portion of a silver stained AFLP gel using EcoRI+ACG/MseI+CAT primer combination. I: Controls, plants sprayed with water. II: Treatments, plants infected with R. secalis. 2d, 3d, 4d, and 5d are sampling time points in days (d). M: 20bp DNA ladder.
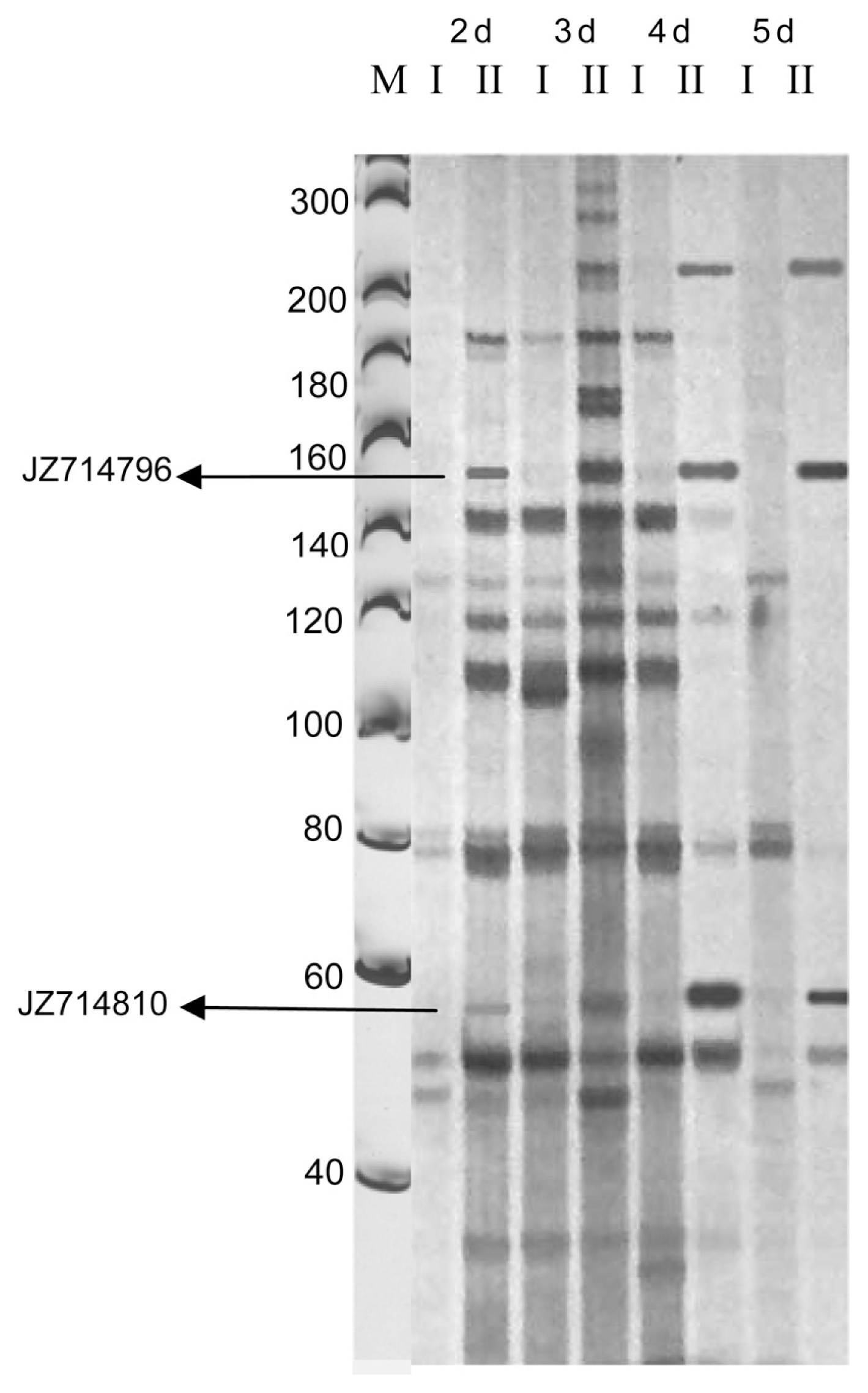
Fig.┬Ā2
(A) Expression profile of Rar1 and Rpg4 genes at the different time points in days (d) following R. secalis infection in the resistant barley cv. Banteng determined by semi-quantitative RT-PCR. EF1╬▒ was used as the control gene. (B) Changes of band genes intensity via time points in days (d).
Table┬Ā1
Sampling time-points according to the developmental stages of R. secalis
Table┬Ā2
Homologies of sequenced AFLP fragements (accession numbers in NCBI databases) to sequences in the databases at 2, 3, 4 and 5 days after inoculation of barley cv. Banteng by the R. secalis Rs46
References
Al-Daoude, A and Jawhar, M 2009. Transcriptional changes in barley-Cochliobolus sativus interaction. Austral Plant Pathol. 38:1-5.
Altschul, SF, Madden, TL, Schaffer, AA, Zhang, J, Zhang, Z, Miller, W and Lipman, DJ 1997. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucl Acids Res. 25:3389-3402.



Arabi, MIE, Al-Shehadah, E and Jawhar, M 2010. Pathogenic groups identified among isolates of Rhynchosporium secalis. Plant Pathol J. 26:260-263.

Azevedo, C, Sadanandom, A, Kitagawa, K, Freialdenhoven, A, Shirasu, K and Schulze-Lefert, P 2002. The RAR1 interactor SGT1, an essential component of R gene-triggered disease resistance. Science. 295:2073-2076.


Bachem, CWB, van der Hoeven, RS, de Bruijn, SM, Vreugdenhil, D, Zabeau, M and Visser, RGF 1996. Visualization of differential gene expression using a novel method of RNA fingerprinting based on AFLP: analysis of gene expression during potato tuber development. Plant J. 9:745-753.


Baldwin, D, Crane, V and Rice, D 1999. A Comparison of gel - based, nylon filter and microarray techniques to detect differential RNA expression in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2:96-103.


Bj├Ėrnstad, A, Patil, V, Tekauz, A, Mar├Ė├Ėy, AG, Skinnes, H, Jensen, A, Magnus, H and MacKey, J 2002. Resistance to scald (Rhynchosporium secalis) in barley (Hordeum vulgare) studied by near-isogenic lines: I. Markers and differential isolates. Phytopathology. 92:710-720.


Breyne, P, Dreesen, R and Vandepoele, K 2002. Transcriptome analysis during cell division in plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 99:14825-14830.



Brueggeman, R, Steffenson, BJ and Kleinhofs, A 2009. The rpg4/Rpg5 stem rust resistance locus in barley; resistance genes and cytoskeleton dynamics. Cell Cycle. 8:977-981.


Datta, K, Velazhahan, R, Oliva, N, Ona, I, Mew, T, Khush, GS, Muthukrishna, S and Datta, SK 1999. Over-expression of the cloned rice thaumatin-like protein (PR-5) gene in transgenic rice plants enhances environmental friendly resistance to Rhizoctonia solani causing sheath blight disease. Theor Appl Genet. 98:1138-1145.


Druka, A, Kudrna, D, Han, F, Kilian, A, Steffenson, B, Frisch, D, Tomkins, J, Wing, R and Kleinhofs, A 2000. Physical mapping of barley stem rust resistance gene rpg4. Mol Gen Genet. 264:283-290.



Kanyuka, K, Druka, A, Caldwell, DG, Tymon, A, McCallum, , Waugh, R and Adams, MJ 2005. Evidence that the recessive bymovirus resistance locus Rym4 in barley corresponding to the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E gene. Mol Plant Pathol. 6:449-458.


Lehnackers, H and Knogge, W 1990. Cytological studies on the infection of barley cultivars with known resistance genotypes by Rhynchosporium secalis. Can J Bot. 68:1953-1961.

Linsell, KJ, Keiper, FJ, Forgan, A and Oldach, KH 2011. New insights into the infection process of Rhynchosporium secalis in barley using GFP. Fungal Genet Biol. 48:124-131.


Looseley, ME 2012. Genetic basis of control Rhynchosporium secalis infection ans symptom expression in barley. Euphytica. 184:47-56.


Shirasu, K, Lahaye, T, Tan, MW, Zhou, FS, Azevedo, C and Schulze-Lefert, P 1999. A novel class of eukaryotic zinc-binding proteins is required for disease resistance signaling in barley and development in Caenorhabditis elegans. Cell. 99:355-366.


Shirasu, K and Schulze-Lefert, P 2003. Complex formation, promiscuity and multi-functionality: Protein interactions in disease-resistance pathways. Trends Plant Sci. 8:252-258.


Steiner-Lange, S, Fischer, A, Boettcher, A, Rouhara, I, Liedgens, H, Schmelzer, E and Knogge, W 2003. Differential defense reactions in leaf tissues of barley in response to infection by Rhynchosporium secalis and to treatment with a fungal avirulence gene product. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact. 16:893-902.


Vuylsteke, M, Peleman, JD and van Eijk, MJ 2007. AFLP-based transcript profiling (cDNA-AFLP) for genome-wide expression analysis. Nat Prot. 2:1399-1413.


Wagner, C 2008. Quantitative resistance of barley against scald: a candidate gene approach. eds. by JL Molina-Cano, P Christou, A Graner, K Hammer, N Jouve, B Keller, JM Lasa, W Powell, C Royo, P Shewry and AM Stanca, In: Cereal science and technology for feeding ten billion people: genomics era and beyond, Zaragoza. CIHEAM / IRTA, 175-177 (Options M├®diterran├®ennes: S├®rie A. S├®min aires M├®diterran├®ens; n. 81).
Wang, X, Richards, J and Gross, T 2013. The Rpg4 -mediated resistance to wheat stem rust (Puccinia graminis) in barley (Hordeum vulgare) requires Rpg5, a second NBS-LRR gene, and an actin depolymerization factor. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact. 26:407-418.


Walters, DR, Avrova, A and Bingham, IJ 2012. Control of foliar diseases in barley: towards an integrated approach. Eur J Plant Pathol. 133:33-37.


Wendy, ED, Rowland, O, Piedras, P, Kim, EH and Jonathan, DGJ 2000. cDNA-AFLP reveals a striking overlap in race-specific resistance and wound response gene expression profiles. Plant Cell. 12:963-977.



- TOOLS
-
METRICS

-
- 1 Web of Science
- 0 Crossref
- 0 Scopus
- 1,768 View
- 11 Download
- Related articles



 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Full text via PMC
Full text via PMC Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print